static关键字
1,声明static属性
static是一个关键字,这个关键字主要可以用来定义属性和方法,下面将针对于此关键字的使用进行分析。
·使用static定义属性
在一个类之中,所有的属性一旦定义了实际上内容都交由各自的堆内存空间所保存。
·范例:定义一个程序类
1 class Person{//创建所有同一个国家的类 2 private String name; 3 private int age; 4 String country="中华民国";//暂时先不封装 5 public Person(String name, int age) { 6 this.name = name; 7 this.age = age; 8 } 9 public String getInfo(){ 10 return "【姓名】"+this.name+"【年龄】"+this.age+"【国家】"+this.country; 11 } 12 } 13 public class Main { 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 Person perA=new Person("张三",18); 16 Person perB=new Person("李四",28); 17 Person perC=new Person("王五",38); 18 System.out.println(perA.getInfo()); 19 System.out.println(perB.getInfo()); 20 System.out.println(perC.getInfo()); 21 } 22 }
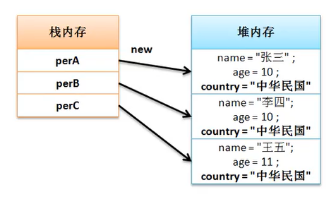
但是当我们需要更改的国家名称的时候,要将所有的Person类的实例化对象的country属性更改内容。
·范例:static定义公共属性
1 class Person{//创建所有同一个国家的类 2 private String name; 3 private int age; 4 static String country="中华民国";//暂时先不封装 5 public Person(String name, int age) { 6 this.name = name; 7 this.age = age; 8 } 9 public String getInfo(){ 10 return "【姓名】"+this.name+"【年龄】"+this.age+"【国家】"+this.country; 11 } 12 } 13 14 public class Main { 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 Person perA=new Person("张三",18); 17 Person perB=new Person("李四",28); 18 Person perC=new Person("王五",38); 19 perA.country="中华人民共和国"; 20 System.out.println(perA.getInfo()); 21 System.out.println(perB.getInfo()); 22 System.out.println(perC.getInfo()); 23 } 24 }
更改任意实例化对象的country内容,其他所有Person类实例化对象的country内容也跟着变化。
但是对于static属性的访问需要注意一点:由于其本身的公共的属性,虽然可以通过对象进行访问,但是最好的做法应该是通过所有对象的最高代表(类)来进行访问,static属性可以由类名称直接调用。
Person.country="中华人民共和国";
static属性虽然定义在类之中,但是其可以在没有实例化对象的时候调用,本质原因:static属性的堆内存在全局数据区,不需要通过new来开辟堆内存空间。
·范例:在没有实例化对象的时候进行static属性调用
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 System.out.println(Person.country); 4 Person.country="中华人民共和国"; 5 System.out.println(Person.country); 6 } 7 }
在以后进行类设计的时候首选的一定是非static属性(95%),而考虑到公共信息存储的时候才会使用到static属性(5%)。
2,声明static方法
static关键字也可以进行方法的定义,static方法的主要特点在于,其可以直接由类名称在没有实例化对象的情况下进行调用。
·范例:定义static方法
1 private static String country="中华民国";//已经封装,不能进行直接访问 2 3 public static void setCountry(String c){ 4 country=c; 5 }
·static方法只允许调用static属性或static方法;这个时候对于程序而言方法就有两种:static方法、非static方法,这两个方法之间在调用上就有了限制:
·非static方法允许调用static属性与static方法;
所有的static属性与方法都可以在没有实例化的前提下使用,但是所有非static定义的属性与方法都必须在实例化之后使用。
this表示当前对象,this.country这个在static方法中就会出现错误!本质原因:有可能没有当前对象!!!
如果说可以理解这个限制,那么对于之前的方法定义就可以得出新的结论:在最早讲解方法定义的时候强调过:“当前定义的方法都是在主类中定义的,并且有主方法调用的”。
·范例:主类中的static方法调用
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 print();//直接调用static方法 4 } 5 static void print(){ 6 System.out.println("在主类中的方法实现的static方法"); 7 } 8 }
一般情况下主类不会写太多代码。
·范例:主类中实现的非static方法调用
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 new Main().print();//实例化匿名对象,之后才调用非static方法 4 } 5 //public void print(){//由于都在主类中所以权限都可以使用 6 7 //private void print(){ 8 9 void print(){//默认权限 10 11 12 System.out.println("在主类中的方法实现的非static方法"); 13 } 14 }
3,static应用案例
略,一个简单的使用static属性进行数量统计的实现