一、IO:
1、java.io.File类的使用
2、IO原理及流的分类
3、文件流:
FileInputStream/FileOutputStream/FileReader/FileWriter
4、缓冲流:
BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream/
BufferedReader/BufferedWriter
5、转换流:
InputStreamReader/OutputStreamWriter
6、标准输入/输出流
7、打印流:
PrintReader/PrintWriter
8、数据流:
DataInputStream/DataOutputStream
9、对象流——涉及序列化、反序列化
ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream
10、随机存取文件流:
RandomAccessFile
二、File类:File能新建、删除、重命名文件和目录,但File不能访问文件内容本身。
如果需要访问文件内容本身,则需要使用输入/输出流。
1、访问文件名:
File file=new File("D:\Test\tt.txt"); //file就是tt.txt文件 //注:java中\或者/表示文件的分隔符 File f2=new File("D:"+File.separator+"Test"+"\tt.txt"); //也可以用该法表示 System.out.println(file.getName()); //获取文件名 System.out.println(file.getPath()); //获取当前文件或文件夹路径 File f3=new File("src/test2/TestIO.java"); //使用相对路径创建file对象 System.out.println(f3.getPath()); //获取文件或文件夹的相对路径,就是new File时写的路径 System.out.println(f3.getAbsolutePath()); //获取文件夹或文件的绝对路径 System.out.println(f3); System.out.println(f3.getAbsoluteFile()); //返回一个用当前文件的绝对路径构建的file对象 System.out.println(f3.getParent()); //返回当前文件或文件夹的父级路径 file.renameTo(new File("D:\Test\t.txt")); //给文件或文件夹重命名
2、文件检测:
File f4=new File("D:\Test\t.txt"); System.out.println(f4.exists()); //判断文件或者文件夹是否存在 System.out.println(f4.canRead()); //判断文件是否可读写 System.out.println(f4.canWrite()); System.out.println(f4.isFile()); //判断当前的file对象是不是文件 System.out.println(f4.isDirectory()); //判断当前的file对象是不是文件夹或者目录 System.out.println(f4.lastModified()); //获取文件的最后修改时间,返回的是一个毫秒数 System.out.println(f4.length()); //返回文件长度,单位是字节数
3、文件操作相关:
File f5=new File("D:\Test\t1.txt"); System.out.println(f5.exists()); if(!f5.exists()){ //判断文件是否存在 try{ f5.createNewFile(); //创建新的文件 System.out.println("新文件创建成功"); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } f5.delete(); //删除已有文件
4、目录操作相关:
//File f6=new File("D:\Test\tt"); File f6=new File("D:\Test\tt\a\b"); //f6.mkdir(); //创建单层目录 f6.mkdirs(); //创建多层目录
三、IO流体系
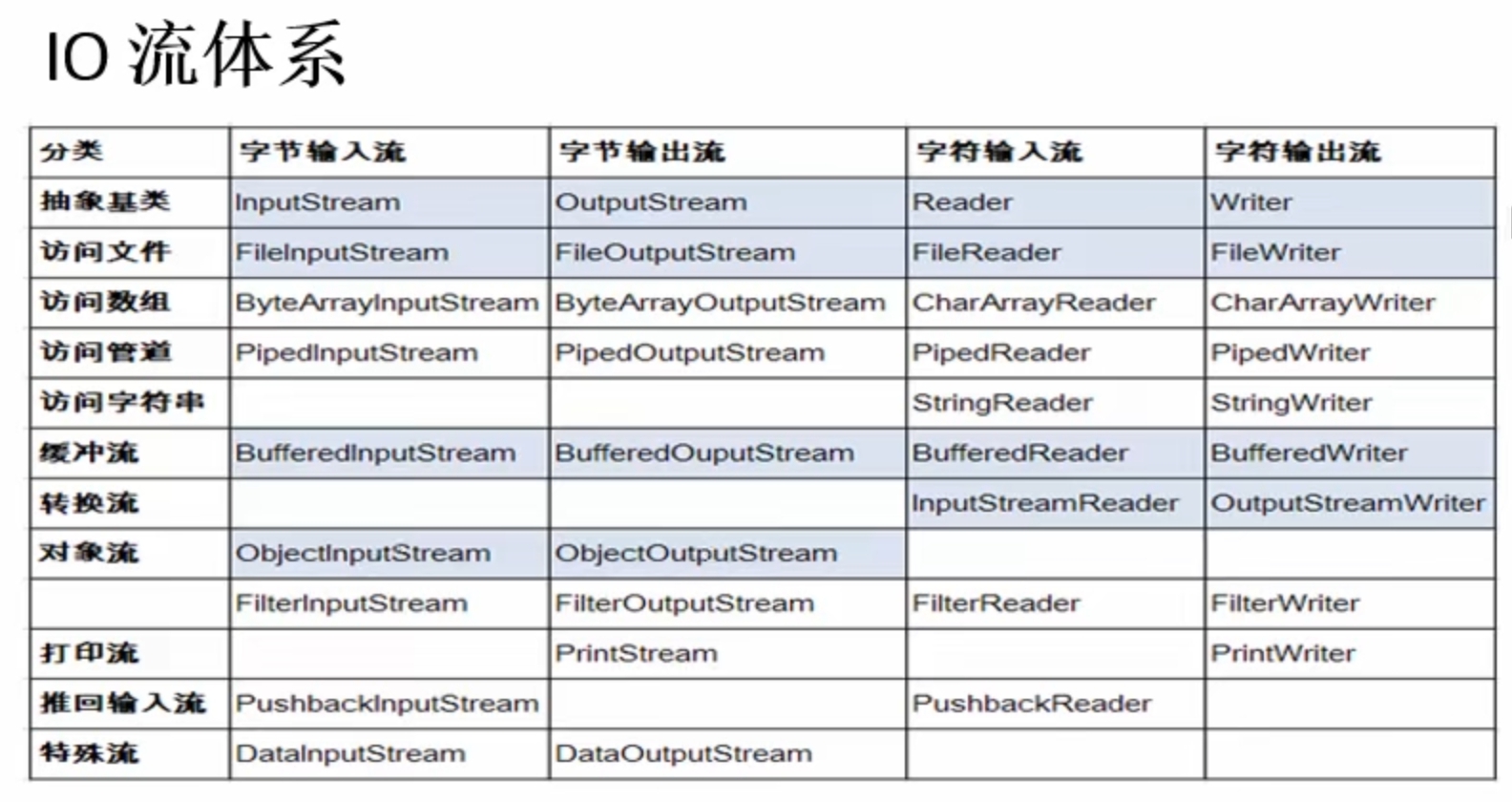
四、文件字节流
1、字节流输入:
/** * 文件字节输入流 */ public static void testFileInputStream(){ try{ FileInputStream fileIn=new FileInputStream("D:\Test\t1.txt"); byte []b=new byte[100]; //设置一个byte数组接收读取的文件内容 //该方法有一个返回值,返回值是读取的数据长度,如果读取到最后一个数据,还会向后再读一个 //也就意味着当in.read()的返回值是-1时,整个文件读取完毕 int len=0; //读取数据的长度 while((len=fileIn.read(b))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(b,0,len)); //参数1是缓冲数据的数组 //参数2是从数组的哪个位置开始转化字符串 //参数3是总共转化的长度 } fileIn.close(); //注意:流在使用完毕后要关闭 } catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }
2、字节流输出:
/** * 文件字节输出流 */ public static void testFileOutputStream(){ try{ FileOutputStream fileOut=new FileOutputStream("D:\Test\t2.txt"); //指定向该文件输出数据 String str="这是输出流测试"; fileOut.write(str.getBytes()); //将数据写入内存 fileOut.flush(); //将内存中的数据写到硬盘 fileOut.close(); //关闭流 System.out.println("输出完毕"); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }
3、文件字节流练习:将一个文件复制到另一个指定文件夹下
public static void copyFile(String inFile,String outFile){ try{ //FileInputStream fileIn=new FileInputStream("D:\Test\t1.txt"); //读取的源文件 FileInputStream fileIn=new FileInputStream(inFile); //读取的源文件 //FileOutputStream fileOut=new FileOutputStream("D:\Test\t3.txt"); //复制到指定文件 FileOutputStream fileOut=new FileOutputStream(outFile); //复制到指定文件 byte []b=new byte[100]; int len=0; while((len=fileIn.read(b))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(b,0,len)); fileOut.write(b, 0, len); //缓冲数组 开始写入位置 数组总长度 } fileOut.flush(); //写入内存的数据刷到硬盘 fileOut.close(); fileIn.close(); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }
五、文件字符流
1、字符流输入:
//先建立一个流对象,将已存在的一个文件加载进流 FIleReader fr=new FileReader("test.txt"); //再创建一个临时存放数据的数组(字节流是byte类型) char[]ch=new char[1024]; //然后调用流对象的读取方法将流中的数据读入到数组中 fr.read(ch);
2、字符流输出:
操作与上面类似
六、缓冲流:

1、缓冲字节输入流:
/** * 缓冲字节输入流 * BufferedInputStream * @throws Exception */ public static void testBufferedInputStream() throws Exception{ //文件字节输入流对象 FileInputStream f=new FileInputStream("D:\Test\t4.txt"); //把文件字节输入流放到缓冲字节输入流对象 BufferedInputStream buf=new BufferedInputStream(f); byte[]b=new byte[100]; int len=0; while((len=buf.read(b))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(b,0,len)); } //关闭流的时候,本着先开后关的原则 buf.close(); f.close(); }
2、缓冲字节输出流
/** * 缓冲字节输出流 * BufferedOutputStream * @throws Exception */ public static void testBufferedOutputStream() throws Exception{ //创建字节输出流对象 FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("D:\Test\t4.txt"); //将字节输出流对象放到缓冲字节输出流 BufferedOutputStream buf=new BufferedOutputStream(f); String str="这是一个测试"; //写到内存中 buf.write(str.getBytes()); //刷入硬盘上 buf.flush(); buf.close(); f.close(); }
七、转换流:
1、转换输入流:
/** * 转换输入流 * 注意:再转换字符流的时候,设置的字符集编码要与读取的文件数据的编码一致 * InputStreamReader * @throws Exception */ public static void testInputStreamReader() throws Exception{ FileInputStream fs=new FileInputStream("D:\Test\t6.txt"); //把字节流转换为字符流 InputStreamReader in=new InputStreamReader(fs,"GBK"); //参数1是字节流 参数2是编码
// InputStreamReader in=new InputStreamReader(fs,"utf-16"); //参数1是字节流 参数2是编码 char []c=new char[100]; int len=0; while((len=in.read(c))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(c,0,len)); } in.close(); fs.close(); }
2、转换输出流:
/** * 转换字节输出为字符输出流 * OutputStreamWriter * @throws Exception */ public static void testOutputStreamWriter() throws Exception{ FileOutputStream fs=new FileOutputStream("D:\Test\t6.txt"); OutputStreamWriter out=new OutputStreamWriter(fs,"GBK"); String str="Hellow Java"; out.write(str); out.flush(); out.close(); fs.close(); System.out.println("执行完成"); }
八、输入输出流:
1、输入流:
/** * 标准的输入流 * @throws Exception */ public static void testSystemIn() throws Exception{ //创建一个接收键盘输入数据的输入流 InputStreamReader ir=new InputStreamReader(System.in); //把输入流放到缓冲流 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(ir); //临时接收数据的字符串 String str=""; while((str=br.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(str); } br.close(); ir.close(); }
九、对象流:

1、首先创建一个待序列化的对象:
/** * 可以序列化和反序列化的对象 * @author 小虞哥哥 * */ public class Person implements Serializable{ /** * 一个表示序列化版本标识符的静态变量 * 用来表明类的不同版本间的兼容性 */ private static final long serialVersionUID=1L; String name; int age; }
2、然后将对象进行序列化:
/** * 对象的序列化 * @throws Exception */ public static void testSerialize() throws Exception{ //创建对象的输出流,把对象序列化之后的流放到指定文件夹 ObjectOutputStream out=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:/Test/t7.txt")); Person p=new Person(); p.name="张三"; p.age=18; out.writeObject(p); out.flush(); out.close(); }
3、再将对象进行反序列化:
/** * 对象的反序列化 * @throws Exception */ public static void testDeserialize()throws Exception{ //创建对象的输入流,从指定文件中把序列化后的流读取出来 ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:/Test/t7.txt")); Object obj=in.readObject(); Person p=(Person)obj; System.out.println(p.name); System.out.println(p.age); }
十、RandomAccessFile类:

1、随机读取文件:
/** * 随机读文件 * @throws Exception */ public static void testRandomAccessFile() throws Exception{ //RandomAccessFile的高早期有两个参数 //参数1是读写的文件路径 参数2是指定RandomAccessFile的访问模式 //r:以只读方式打开 //rw:打开以便读取和写入 //rwd:打开以便读取和写入,同步文件内容的更新 //rws:打开以便读取和写入,同步文内容和元元数据的更新 //最常用的是r和rw RandomAccessFile ra=new RandomAccessFile("D:/Test/t8.txt","r"); //ra.seek(0); //设置读取文件内容的起始点 ra.seek(4); //设置读取文件内容的起始点 byte[]b=new byte[1024]; int len=0; while((len=ra.read(b))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(b,0,len)); } }
2、随机写入文件:
/** * 随机写文件 * @throws Exception */ public static void testRandomAccessFileWrite() throws Exception{ RandomAccessFile ra=new RandomAccessFile("D:/Test/t8.txt","rw"); ra.seek(0); //设置写的起始点 0代表开头 //ra.seek(ra.length()); //设置写的起始点 length()代表从文件的最后结尾写,也就是文件的追加 //注意:如果是在文件开头或中间写入,会覆盖等长的内容 ra.write("你好".getBytes()); ra.close(); }
十一、IO流小节:
