背景
有很多Sparse PCA 算法运用了收缩算法,但是呢,往往只考虑如何解决,每一次迭代的稀疏化问题,而忽略了收缩算法的选择。
总括
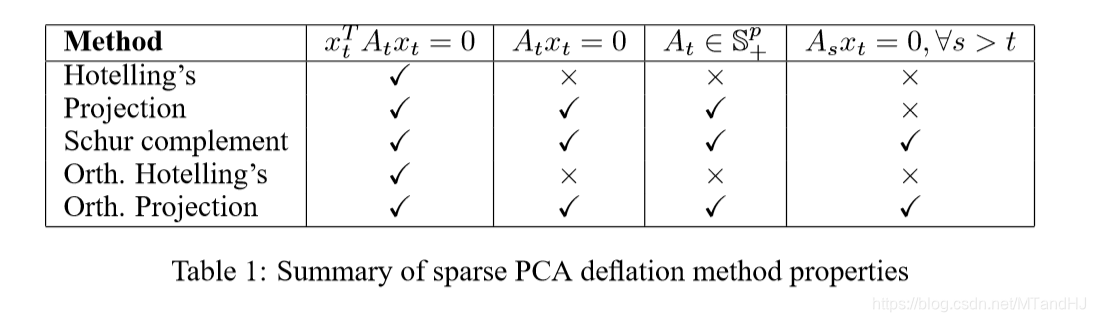
Hotelling's deflation
公式
(A_t = A_{t-1}-x_tx_t^{mathrm{T}}A_{t-1}x_tx_t^{mathrm{T}})
特点
如果(x_t)是(A_{t-1})的特征向量
那么
(A_tx_t = (A_{t-1}-x_tx_t^{mathrm{T}}A_{t-1}x_tx_t^{mathrm{T}})x_t
=0)
所以,(x_t)依然是A_t的特征值为0所对应的特征向量。
但是,如果(x_t)不是特征向量,(A_tx_t=0)这个性质就不存在了,而且,(A_t)不一定是半正定矩阵。

Projection deflation
公式
(A_t = (I-x_tx_t^{mathrm{T}})A_{t-1}(I-x_tx_t^{mathrm{T}}))
特点
半正定
假设(A_{t-1})是半正定的。那么,对于任意的(x)
(x^{mathrm{T}}A_tx = [x^{mathrm{T}}(I-x_tx_t^{mathrm{T}})]A_{t-1}[(I-x_tx_t^{mathrm{T}})x]geq0)
另外(A_tx_t=0)
(A_tx_t=(I-x_tx_t^{mathrm{T}})A_{t-1}(I-x_tx_t^{mathrm{T}})x_t=0)
不过,(A_sx_t quad s>t)的值往往不是0
Schur complement deflation

Orthogonalized projection deflation
公式
(A_t = (I-mathcal{P}^{(t)})A(I-mathcal{P}^{(t)}))
(mathcal{P}^{(t)})是投影矩阵,满足:
(mathcal{P}^{(t)mathrm{T}}mathcal{P}^{(t)}=mathcal{P}^{(t)})
(mathcal{P}^{(t)}mathcal{P}^{(t)}=mathcal{P}^{(t)})
若
(X=[x_1,x_2,ldots,x_t]=QR)
则:
(mathcal{P}^{(t)}=Q_{1...t}Q_{1...t}^{mathrm{T}})(假设X的秩为t)
其中(Q_{1...t})为(Q)的前t列。
Orthogonalized Hotelling's deflation
公式
(A_t = A_{t-1} - q_tq_t^{mathrm{T}}A_{t-1}q_tq_t^{mathrm{T}})
(q_t=frac{(I-mathcal{P}^{(t-1)})x_t}{|(I-mathcal{P}^{(t-1)})x_t|})
特点
XXX