本文基于ArcGIS Runtime SDK for .NET(100.9.0),官方有2D的资料Spatial relationships,本文完成三维的立方体是否相交的判定,效果如图
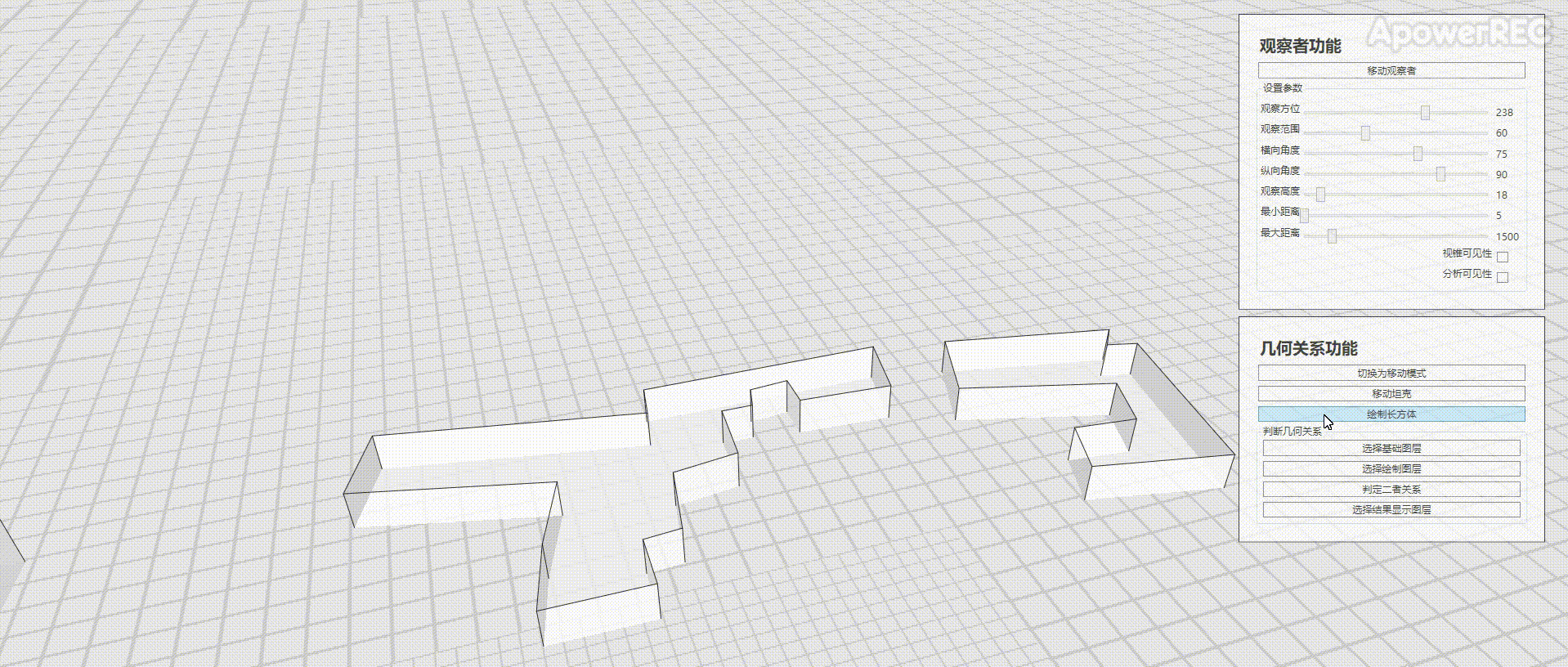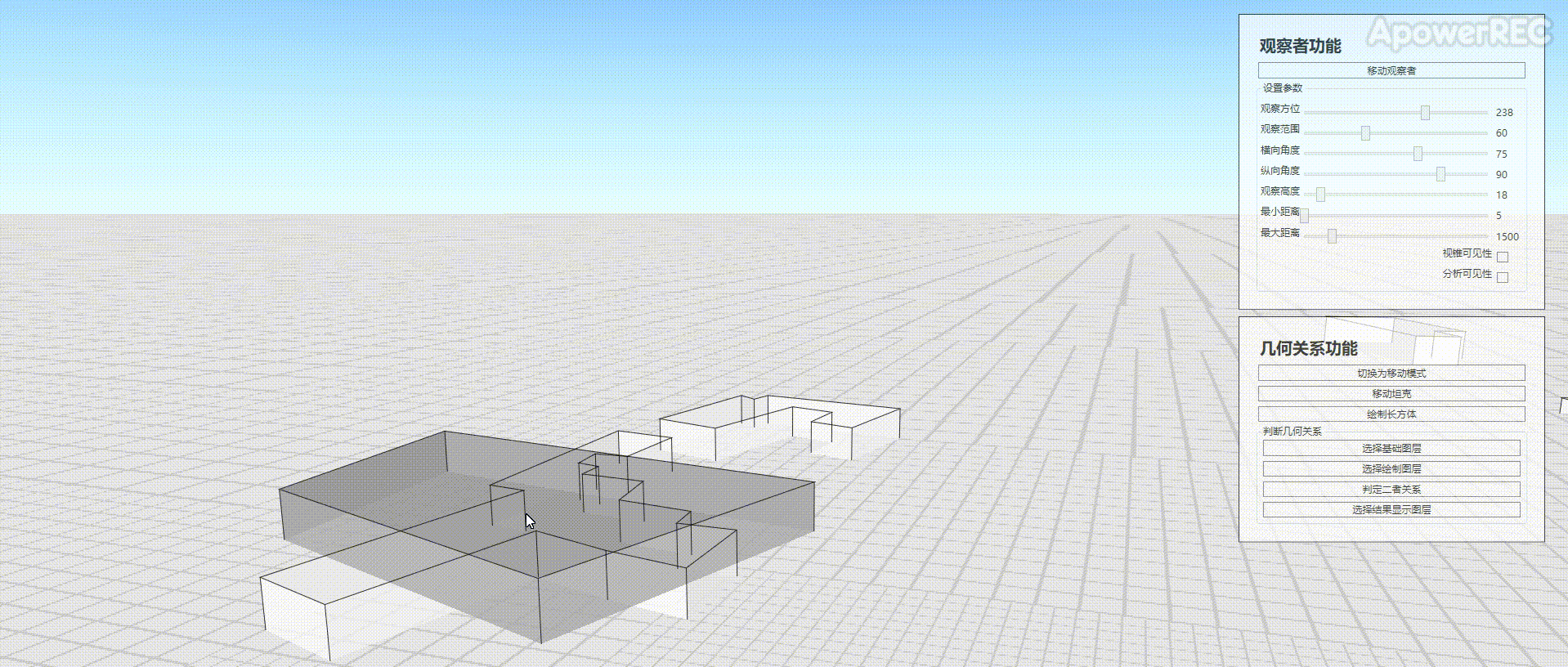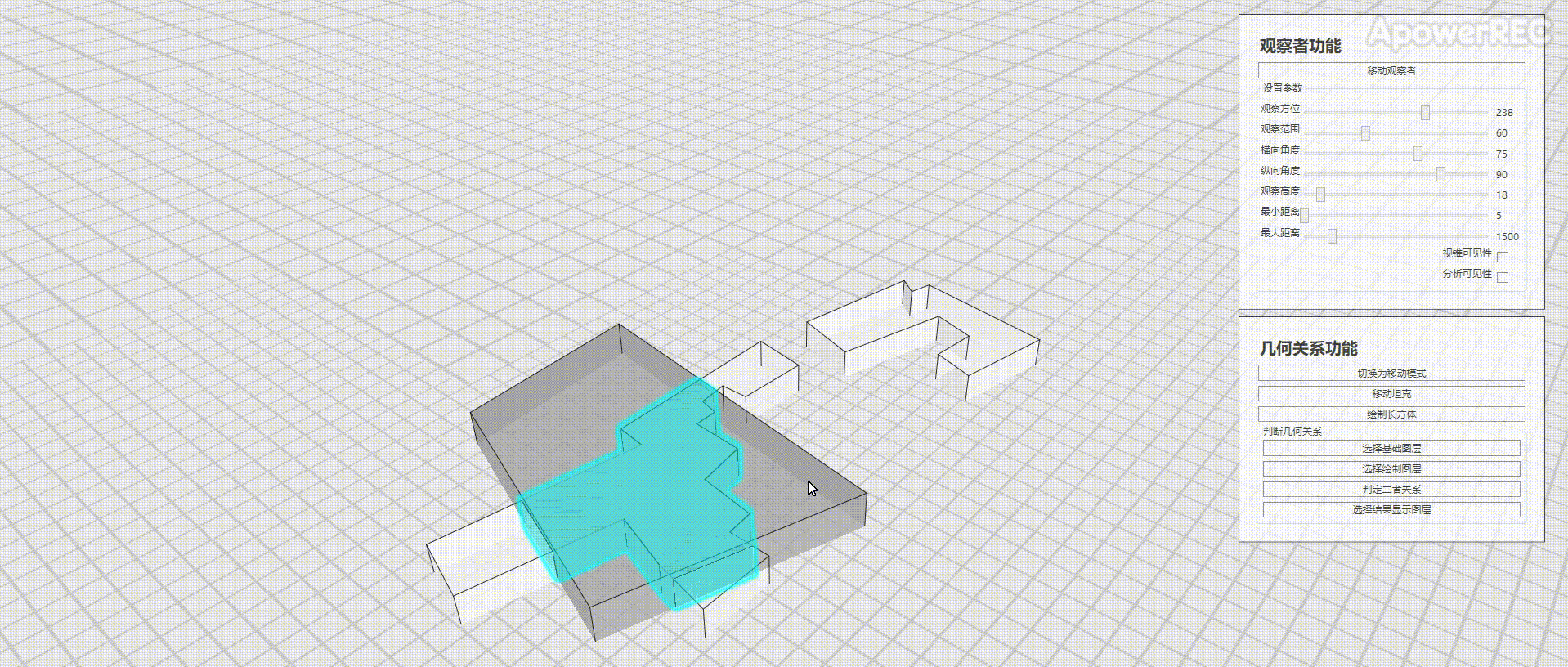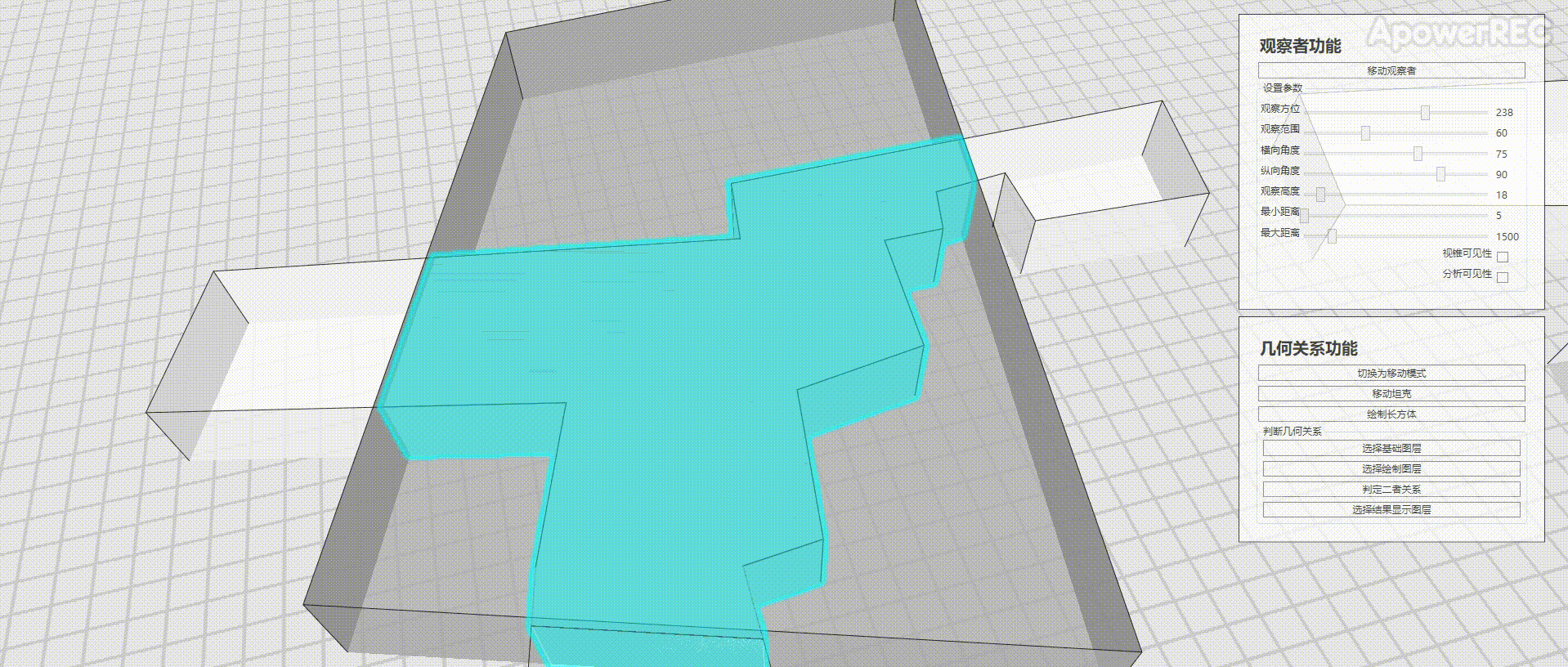
实现思路
地图初始化
使用SceneView初始化地图
创建三个图层,原始建筑数据的基础图层,绘制立方体的绘制图层,和显示相交结果的结果图层(这里均使用了shp文件作为基础创建图层)
设置图层的Renderer属性,将Z属性作为高程显示出来
SimpleLineSymbol mySimpleLineSymbol = new SimpleLineSymbol(SimpleLineSymbolStyle.Solid, System.Drawing.Color.Black, 1);
SimpleFillSymbol mysimpleFillSymbol = new SimpleFillSymbol(SimpleFillSymbolStyle.Cross, System.Drawing.Color.DarkGray, mySimpleLineSymbol);
SimpleRenderer mySimpleRenderer = new SimpleRenderer(mysimpleFillSymbol);
RendererSceneProperties myRendererSceneProperties = mySimpleRenderer.SceneProperties;
myRendererSceneProperties.ExtrusionMode = ExtrusionMode.AbsoluteHeight;
myRendererSceneProperties.ExtrusionExpression = "[Z]";
graphicLayer.Renderer = mySimpleRenderer;
绘制立方体
通过交互获得点坐标
// Get the mouse position.
Point cursorSceenPoint = mouseEventArgs.GetPosition(MySceneView);
// Get the corresponding MapPoint.
MapPoint onMapLocation = MySceneView.ScreenToBaseSurface(cursorSceenPoint);
弹窗设置立方体的高程
注意,这里可以绘制多于六面的立方体,只是示例使用了六面立方体
根据点集合和高程数据,在绘制图层创建立方体
var feature = graphicLayer.FeatureTable.CreateFeature();
feature.Attributes.Remove("Z");
feature.Attributes.Add("Z", setHeight.height);
List<MapPoint> pointsWithZ = new List<MapPoint>();
foreach (var p in points)
{
pointsWithZ.Add(new MapPoint(p.X, p.Y, p.SpatialReference));
}
Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry.Polygon polygon = new Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry.Polygon(pointsWithZ, points[0].SpatialReference);
feature.Geometry = polygon;
await graphicLayer.FeatureTable.AddFeatureAsync(feature);
计算二者关系
根据点击位置,查询在指定范围内目标图层是否有数据,如果有,则选中
private async Task<GeoElement> SetSelectForGraphicLayer(GeoViewInputEventArgs e)
{
var result = await MySceneView.IdentifyLayerAsync(graphicLayer, e.Position, 1, false);
GeoElement geoElement = result.GeoElements.FirstOrDefault();
if (geoElement != null)
{
QueryParameters queryParams = new QueryParameters
{
// Set the geometry to selection envelope for selection by geometry.
Geometry = geoElement.Geometry
};
// Select the features based on query parameters defined above.
await graphicLayer.SelectFeaturesAsync(queryParams, Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Mapping.SelectionMode.New);
}
return geoElement;
}
选择了基础图层和绘制图层的数据后,经过数据处理(创建有正确高程的Polygon对象),调用GeometryEngine中的Intersects和Intersections方法查询二者是否有相交,以及相交的结果
private async void CheckOBBCollision_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (selectGraphic == null || selectFeatureGeoElement == null)
{
MessageBox.Show("请选择一个shp数据和一个绘制数据!");
return;
}
//创建shp几何体
Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry.Polygon selectFeatureGeometryRealCube = GetSelectFeatureGeometryRealCube(selectFeatureGeoElement);
//创建绘画几何体
Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry.Polygon selectGraphicGeometryRealCube = GetSelectFeatureGeometryRealCube(selectGraphic);
var b = GeometryEngine.Intersects(selectGraphicGeometryRealCube, selectFeatureGeometryRealCube);
var g2 = GeometryEngine.Intersections(selectGraphicGeometryRealCube, selectFeatureGeometryRealCube);
if (b)
{
foreach (var g in g2)
{
if(g is Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry.Polygon)
{
var p = g as Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry.Polygon;
foreach(var part in p.Parts)
{
var feature = intersectionLayer.FeatureTable.CreateFeature();
feature.Attributes.Remove("Z");
double z = double.MaxValue;
List<MapPoint> pointsWithZ = new List<MapPoint>();
foreach (var point in part.Points)
{
//只能计算平面体(即同一平面Z相同的数据)
if (point.Z < z)
{
z = point.Z;
}
pointsWithZ.Add(new MapPoint(point.X, point.Y, point.SpatialReference));
}
feature.Attributes.Add("Z", z);
Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry.Polygon polygon = new Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry.Polygon(pointsWithZ, pointsWithZ[0].SpatialReference);
feature.Geometry = polygon;
await intersectionLayer.FeatureTable.AddFeatureAsync(feature);
graphicLayer.ClearSelection();
featureLayer.ClearSelection();
}
}
}
MessageBox.Show("二者相交");
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("二者不相交");
}
}
private Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry.Polygon GetSelectFeatureGeometryRealCube(GeoElement geoElement)
{
Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry.Polygon selectFeatureGeometryRealCube = null;
var feature = geoElement as Feature;
var selectFeatureGeometryPolygon = geoElement.Geometry as Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry.Polygon;
if (selectFeatureGeometryPolygon.Parts.Count > 0)
{
List<MapPoint> points = new List<MapPoint>();
var part = selectFeatureGeometryPolygon.Parts[0];
foreach (var point in part.Points)
{
//从属性中获得z
object z = 0;
feature.Attributes.TryGetValue("Z", out z);
points.Add(new MapPoint(point.X, point.Y, (double)z, selectFeatureGeometryPolygon.SpatialReference));
}
selectFeatureGeometryRealCube = new Esri.ArcGISRuntime.Geometry.Polygon(points, selectFeatureGeometryPolygon.SpatialReference);
}
return selectFeatureGeometryRealCube;
}
示例代码
CubeCollision.xaml
CubeCollision.xaml.cs
注意事项
本文只完成了同一立方体高程相同的情况的讨论