红黑树
相关概念
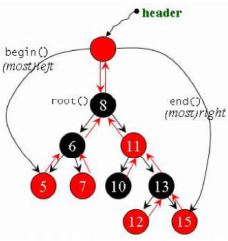
1 rb_tree 是一种高度平衡的搜索二叉树,其元素排列的规则有利于 search 和 insert,并同时保持适度的平衡。
2 rb_tree 提供遍历操作以及 iterator。元素放入后有一定的排列规则,按正常规则(++ iter)迭代器遍历时为输出为排序状态(sorted)。
3 不应使用 rb_tree 的 iterator 改变元素值(影响原有排序)。语法层面是不禁止这种操作的。如此设计的原因是,由 rb_tree 实现的 map 其 key 值(排序以 key 值为依据) 是不能改动的,而通过 iterator 改变 map 的 data 值是允许的。
4 rb_tree 提供两种 insertion 操作:insert_unique() 和 insert_equal()。 前者表示节点的 key 一定在整个 tree 中独一无二,否则安插失败(但不返回error,不做任何操作);后者表示节点的 key 可重复。
实现
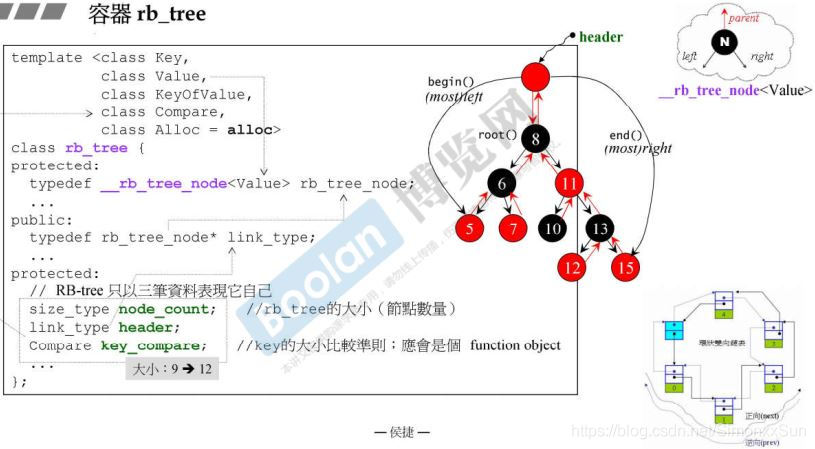
Key 为 key 值的类型,Value 为放入的整个元素节点的数据类型、
KeyOfValue 为从 Value 中 取得 key 值的方法,此处应为一个函数对象、(例:identity
Compare 为比较两个元素大小的函数对象。
测试代码
#include <iostream>
//添加set头文件或者map头文件,否则_Rb_tree找不到定义
#include <set>
using namespace std;
void Test1()
{
/*
在Linux环境下可以正常调用
_Rb_tree<int, int, _Identity<int>, less<int>> itree;
cout << itree.empty() << endl; //1
cout << itree.size() << endl; //0
itree._M_insert_unique(3);
itree._M_insert_unique(8);
itree._M_insert_unique(5);
itree._M_insert_unique(9);
itree._M_insert_unique(13);
itree._M_insert_unique(5); //no effect, since using insert_unique().
cout << itree.empty() << endl; //0
cout << itree.size() << endl; //5
cout << itree.count(5) << endl; //1
itree._M_insert_equal(5);
itree._M_insert_equal(5);
cout << itree.size() << endl; //7, since using insert_equal().
cout << itree.count(5) << endl; //3
*/
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Test1();
return 0;
}
map/multimap-rbtree
相关概念
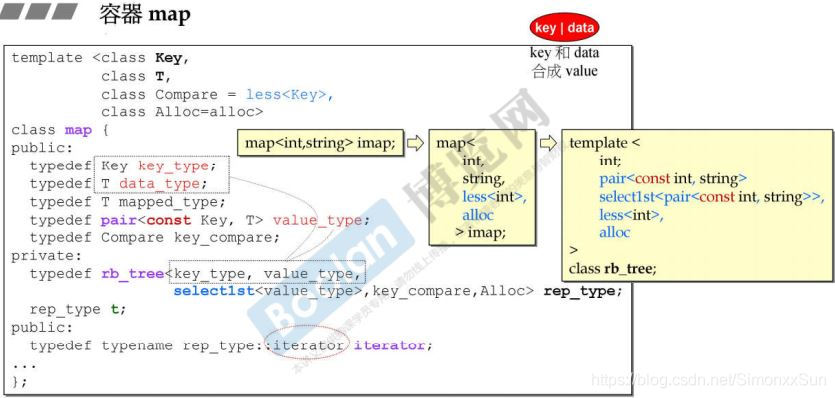
- map/multimap 以 rb_tree 为底层结构,因此有元素自动排序特性。排序的依据是 key。
- key 不能修改,data 可以修改。map/multimap 内部自动将 user 指定的 key type 设为 const,如此便能禁止 user 对 key 的赋值。
实现
-
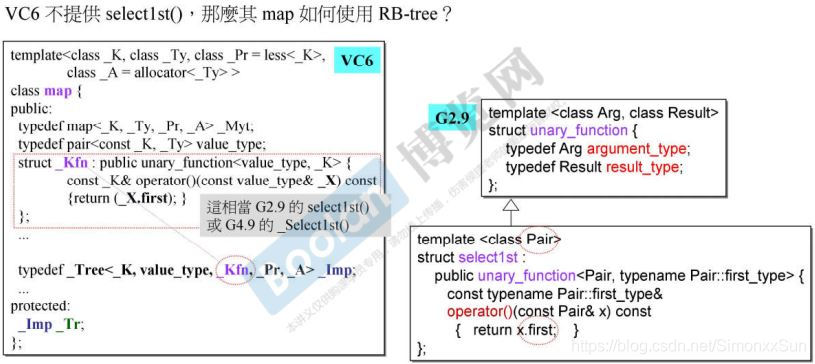
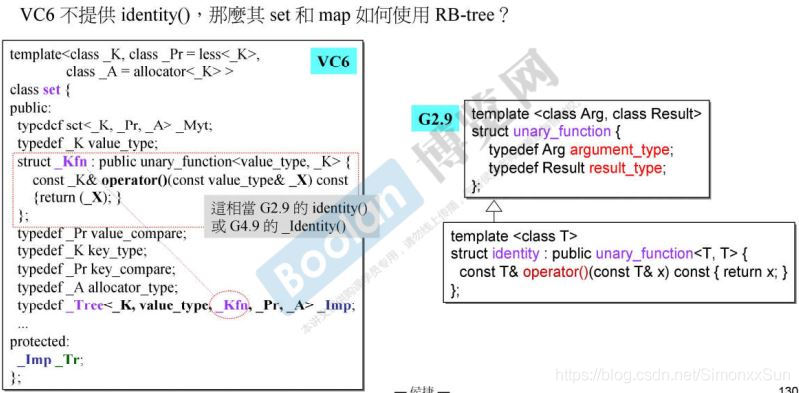
select1st<pair<const int, string>> 从 Value 中 取得 key 值的方法,即取 pair 中的第一个类型 int 作为 key。
-
map 的 iterator 就是 rb_tree 的迭代器。其中 pair 的第一个模板参数为 const int。
map 独有的 operator [ ]
Allows for easy lookup with the subscript (@c[ ]) operator. Returns data asscoiated with the key specified subscript. If the key does not exist, a pair with that key is created using default values, which is then returned.
如果 key 值不存在,则生成一个带有默认 data 值的 value安插进去。
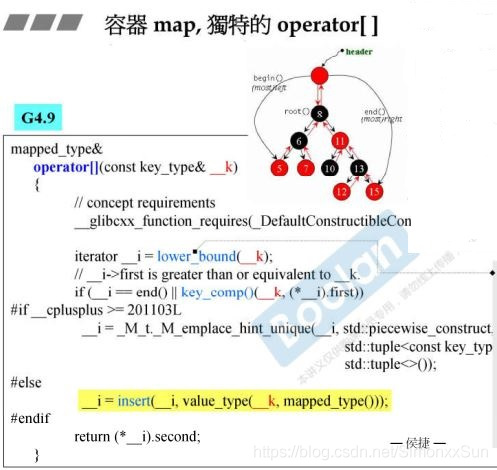
lower_bound() 是二分查找的一种,试图在排序过的元素中寻找 value 。若查找范围内拥有与 value 相等的元素(s),便返回一个 iterator 指向其中第一个元素。如果没有这样的元素存在,便返回“假设该元素存在是应该出现的位置”。也就是说它会返回 iterator 指向第一个不小于 value 的元素。如果 value 大于查找范围内的任何元素,将返回 last 。换句话说,lower_bound 返回的是“不破坏排序得以安插 value 的第一个适当位置”。
而 operator [ ] 最终返回的是这个位置的 .second引用,可以利用这个引用直接赋值,相当于 insert() 操作 。
set/multiset-rbtree
相关概念
1 set/multiset 以 rb_tree 为底层结构,因此有元素自动排序特性。排序的依據是 key,set/multiset 的 value 就是 key。
2 set/multiset 提供遍历操作以及 iterator。元素放入后有一定的排列规则,按正常规则(++ iter)迭代器遍历时为输出为排序状态(sorted)。
3 无法使用 set/multiset 的 iterator 改变元素值(因为 key 就是 value)。其 iterator 底层实现是 RBtree 的 const iterator,禁止对元素赋值。
4 set 的元素不允许重复,所以 insert() 调用 insert_unique()。multiset 的元素可以重复,所以 insert() 调用 insert_equal()。
实现
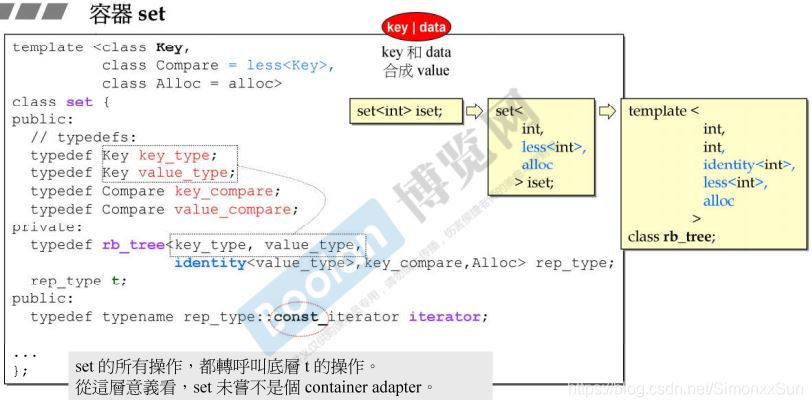
1 rep_type (定义了一个成员变量)说明了其底层实现为一个红黑树。其红黑树的5个模板参数都可由 set 的三个模板参数得来。
2 无法使用 set/multiset 的 iterator 改变元素值(key 就是 value),因为 set 的 iterator 是 const 不允许通过它改变元素。
3 set 的所有操作都转调用底层 t 的类方法。
注意事项
map和set的迭代器类型以及相关操作的时间复杂度
双向迭代器
随机访问每个元素 O(logn)
末尾插入删除元素 O(logn)
中间或开头删插元素 O(logn)
为何map和set的插入删除效率比用其他序列容器高?
map和set中所有元素都是以节点的形式来存储,插入删除操作只涉及到指针的转换,无需像vetor和deque一样考虑内存重新申请与拷贝