结论
绝对定位的top等的依据元素需满足3个条件:
- 已定位(position:relative/fixed/absolute)
- 最近的
- 祖辈元素(一定是祖辈元素不是同辈元素)
说明
- 一般会为body设置position:relative此属性,方便定位。
- 绝对定位的position的top/left等一定不是根据同辈元素来的。
Demo
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <!-- 规定字符集的编码为utf-8 --> <meta charset="utf-8"> <style type="text/css"> body { position: relative; padding: 0px; height: 500px; } #Outer{ position: fixed; border: 1px solid black; width: 300px; height: 300px; top: 50px; } #Red { width: 200px; height: 80px; border: 1px solid red; position: relative; /*margin-top: 10px;*/ top: 20px; } #Green { position: absolute; width: 200px; height: 80px; border: 1px solid yellowgreen; top: 30px; } #Outer2{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background: yellowgreen; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="Outer"> <div id="Red">Red</div> <div id="Green">Green</div> </div> <div id="Outer2"> </div> </body> </html>
结果如图:
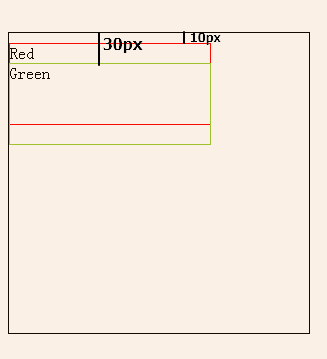
可以看出
- position:absolute 绿色div是根据 父级元素黑色的div 进行定位的。
- position:relative 红色的div是根据原有位置进行定位的。
PS
- 定位的时候,对于未脱离文档流的元素,是根据原有位置进行定位的。
- 定位的时候,对于已脱离文档流的元素,是根据最近的已定位的祖辈元素进行定位的。