学会Func
前言
首先你要会最基本的委托的使用,如果不会,看起来可能会有难度..
不过第一个例子将帮你复习一下委托delegate
接下来通过几个例子就会学会怎么灵活使用Func了
委托回顾(delegate)
新建控制台
代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace AaronYangFuncDemo
{
delegate string ConvertMethod(string inString); //①
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
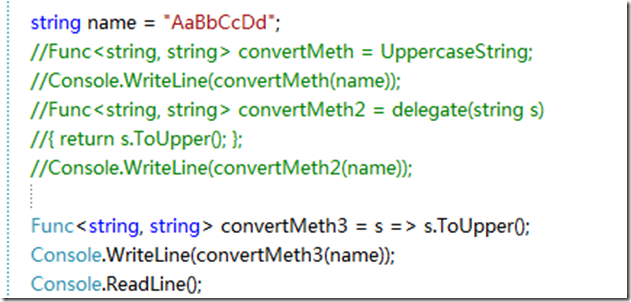
ConvertMethod convertMeth = UppercaseString; //③
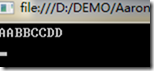
string name = "AaBbCcDd";
Console.WriteLine(convertMeth(name));
Console.ReadLine();
}
private static string UppercaseString(string inputString) //②
{
return inputString.ToUpper();
}
}
}
这是一个将传入的字符串转换成大写的委托
这里我们声明了一个
delegate string ConvertMethod(string inString);
委托可以理解为就是方法(委托定义的签名要和 方法的签名一致(什么返回类型,什么参数列表))的集合,然后可以使用+=绑定同方法签名的方法
然后调用委托名字,传入对应的参数,就可以通过委托间接调用了方法。(纯属个人白话文理解)
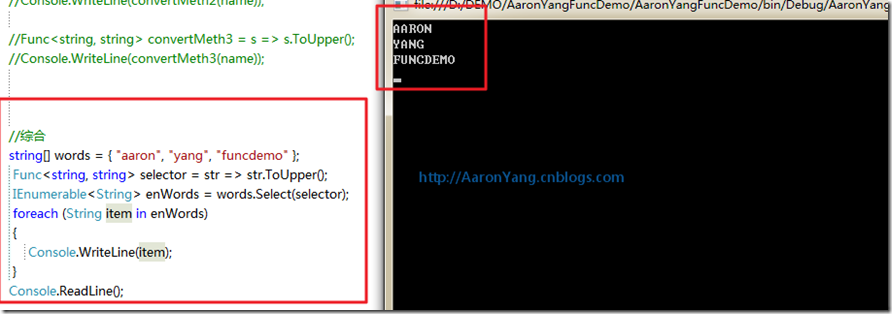
效果:
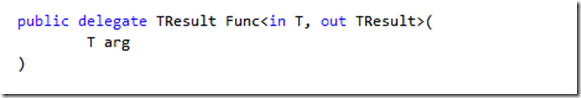
接下来看看 Func
可见Func也是一个泛型委托,第一个参数,是传入参数,等同于
后面一个TResult等同于
所以我们修改一下代码,简化一下代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace AaronYangFuncDemo
{
// delegate string ConvertMethod(string inString); //①
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// ConvertMethod convertMeth = UppercaseString; //③
Func<string, string> convertMeth = UppercaseString;
string name = "AaBbCcDd";
Console.WriteLine(convertMeth(name));
Console.ReadLine();
}
private static string UppercaseString(string inputString) //②
{
return inputString.ToUpper();
}
}
}
方法签名的参数是 string类型的,输出也是string类型的,这里的T(该类型参数是逆变的)和TResult(该类型参数是协变的)
关于泛型中的逆变和协变,这里不讲
Func<T,TResult>委托 和 匿名方法结合
看代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace AaronYangFuncDemo
{
// delegate string ConvertMethod(string inString); //①
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// ConvertMethod convertMeth = UppercaseString; //③
string name = "AaBbCcDd";
//Func<string, string> convertMeth = UppercaseString;
//Console.WriteLine(convertMeth(name));
Func<string, string> convertMeth2 = delegate(string s)
{ return s.ToUpper(); };
Console.WriteLine(convertMeth2(name));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
delegate会用的都是知道的, delegate(方法的参数){ 方法体 }
既然匿名方法可以使用,那么lambda表达式也可以用,我们再简化一下代码
s通过传入参数是string的,所以vs可以推断出来,这个s是string类型的,所以你可以使用string的方法操作参数,最终返回TResult的是string类型就行了。
这样子,我们已经很简化代码了
Func<T,TResult>委托 和 LINQ一些方法结合
过程:
声明一个数组
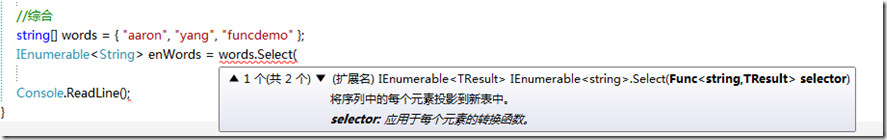
string[] words = { "aaron", "yang", "funcdemo" };
通过LINQ将这个数组中变成大写的
我们使用数组的select方法,发现,这样的一个参数
所以我们在操作之前,先声明个Func<string,TResult> TResult由最终保存的IEnumerable<TResult>的TResult决定,这里也是string
所以声明一个Func<string,string> 的选择器
整体代码:
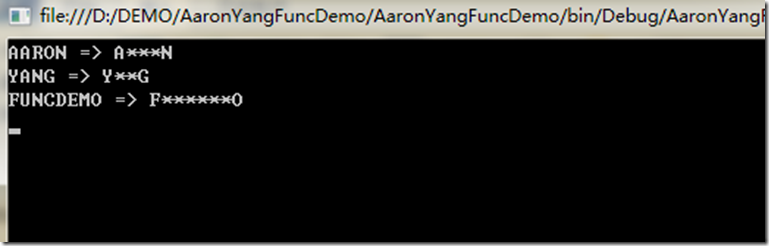
为了更进一步了解Func,我们要求输出这样的结果
AARON => A***N
YANG => Y**G
等等
代码如下:
//综合
string[] words = { "aaron", "yang", "funcdemo" };
Func<string, char[]> selector = str => str.ToUpper().ToCharArray();
IEnumerable<char[]> enWords = words.Select(selector);
foreach (char[] item in enWords)
{
int itemlength = item.Length;
IEnumerable<string> endStr = Enumerable.Repeat("*", item.Length - 2);
Console.WriteLine(
new string(item)+" => "+
item[0].ToString()+String.Join("", endStr)+ item[itemlength - 1].ToString());
}
Console.ReadLine();
效果图
同理传入参数是对象,一个实例,然后操作属性等等
同理
作为Func的传入参数当然不止一个,可以有多个,等同于一个方法含有多个参数,这里做多16个传入参数,每一种必然有一个返回类型参数了。如果没有返回参数,那么你可以使用 Action<T>委托尝试,这里不做讲解