JSTL JSP Standard Tag Library 标准标签库
JSTL允许开人员可以像使用HTML标签 那样在JSP中开发Java功能。
JSTL库有core, i18n, fmt, sql 等等。
i18n和sql用的很少,core和fmt在工作中会用到,本章节主要讲解core和fmt
步骤1:导入jar包
步骤2:set out remove
步骤3:if else
步骤4:choose
步骤5:forEach
步骤6:forTokens
步骤7:fmt:formatNumber 格式化数字
步骤8:fmt:formatDate 格式化日期
步骤9:fn:
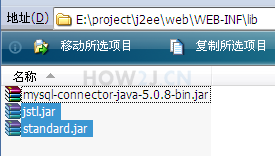
步骤 1 : 导入jar包
为了能够在JSP 中使用JSTL,首先需要两个jar包,分别是jstl.jar 和standard.jar
可以在右侧下载
把这两个jar包放在web/WEB-INF/lib 下
步骤 2 : set out remove
在页面中使用JSTL需要在jsp中 通过指令进行设置
prefix="c" 表示后续的标签使用都会以<c: 开头
|
<c:set var="name" value="${'gareen'}" scope="request" />
|
在作用域request中设置name,相当于
<%request.setAttribute("name","gareen")%>
|
<c:out value="${name}" />
|
相当于 <%=request.getAttribute("name")%>
|
<c:remove var="name" scope="request" />
|
在作用域request中删掉name,相当于
<%request.removeAttribute("name")%>
作用域可以是pageContext, request, session, application, 参考 作用域
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<c:set var="name" value="${'gareen'}" scope="request" />
通过标签获取name: <c:out value="${name}" /> <br>
<c:remove var="name" scope="request" /> <br>
通过标签获取name: <c:out value="${name}" /> <br>
|
步骤 3 : if else
JSTL通过<c:if test=""> 进行条件判断
但是JSTL没有<c:else,所以常用的办法是在<c:if的条件里取反
配合if使用的还有通过empty进行为空判断
empty可以判断对象是否为null,字符串长度是否为0,集合长度是否为0
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8" import="java.util.*"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<c:set var="hp" value="${10}" scope="request" />
<c:if test="${hp<5}">
<p>这个英雄要挂了</p>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${!(hp<5)}">
<p>这个英雄觉得自己还可以再抢救抢救</p>
</c:if>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("weapon", null);
pageContext.setAttribute("lastwords", "");
pageContext.setAttribute("items", new ArrayList());
%>
<c:if test="${empty weapon}">
<p>没有装备武器</p>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${empty lastwords}">
<p>挂了也没有遗言</p>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${empty items}">
<p>物品栏为空</p>
</c:if>
|
步骤 4 : choose
虽然JSTL没有提供else标签,但是提供了一个else功能的标签
|
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${hp<5}">
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
|
我个人觉得看上去繁琐,还是习惯用<c:if test="!" 来表示else
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8" import="java.util.*"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<c:set var="hp" value="${3}" scope="request" />
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${hp<5}">
<p>这个英雄要挂了</p>
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
<p>这个英雄觉得自己还可以再抢救抢救</p>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
|
步骤 5 : forEach
可以在JSP中使用for循环,但是其可读性很差。 借助JSTL的c:forEach标签,可以改善可读性
在本例中,分别使用for循环和<c:forEach标签来演示遍历一个List的区别
|
<c:forEach items="${heros}" var="hero" varStatus="st" >
|
items="${heros}" 表示遍历的集合
var="hero" 表示把每一个集合中的元素放在hero上
varStatus="st" 表示遍历的状态
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8" import="java.util.*"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<%
List<String> heros = new ArrayList<String>();
heros.add("塔姆");
heros.add("艾克");
heros.add("巴德");
heros.add("雷克赛");
heros.add("卡莉丝塔");
request.setAttribute("heros",heros);
%>
<!-- 使用jsp中的for循环来遍历List -->
<table width="200px" align="center" border="1" cellspacing="0">
<tr>
<td>编号</td>
<td>英雄</td>
</tr>
<%
int i =0;
for (String hero : heros) {
i++;
%>
<tr>
<td><%=i%></td>
<td><%=hero%></td>
</tr>
<%}%>
</table>
<br>
<!-- 使用JSTL中的c:forEach 循环来遍历List -->
<table width="200px" align="center" border="1" cellspacing="0">
<tr>
<td>编号</td>
<td>英雄</td>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${heros}" var="hero" varStatus="st" >
<tr>
<td><c:out value="${st.count}" /></td>
<td><c:out value="${hero}" /></td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
|
步骤 6 : forTokens
<c:forTokens专门用于字符串拆分,并且可以指定多个分隔符
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8" import="java.util.*"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<c:set var="heros" value="塔姆,艾克;巴德|雷克赛!卡莉丝塔" />
<c:forTokens items="${heros}" delims=":;|!" var="hero">
<c:out value="${hero}" /> <br />
</c:forTokens>
|
步骤 7 : fmt:formatNumber 格式化数字
fmt 标签常用来进行格式化,其中fmt:formatNumber用于格式化数字
使用之前要加上
|
<fmt:formatNumber type="number" value="${money}" minFractionDigits="2"/>
|
<fmt:formatNumber 表示格式化数字
minFractionDigits 小数点至少要有的位数
maxFractionDigits 小数点最多能有的位数
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8" import="java.util.*"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix='fmt' %>
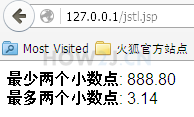
<c:set var="money" value="888.8" />
<c:set var="pi" value="3.1415926" />
最少两个小数点:
<fmt:formatNumber type="number" value="${money}" minFractionDigits="2"/>
<br>
最多两个小数点:
<fmt:formatNumber type="number" value="${pi}" maxFractionDigits="2" />
|
步骤 8 : fmt:formatDate 格式化日期
fmt 标签常用来进行格式化,其中fmt:formatDate 用于格式化日期
和fmt:formatNumber 格式化数字一样,使用之前要加上
|
<fmt:formatDate value="${now}" pattern="G yyyy年MM月dd日 E"/>
<fmt:formatDate value="${now}" pattern="a HH:mm:ss.S z"/>
<fmt:formatDate value="${now}" pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"/>
|
<fmt:formatDate 表示格式化日期
yyyy 表示年份
MM 表示月份
dd 表示日期
E 表示星期几
a 表示是上午还是下午
HH 表示小时
mm 表示分钟
ss 表示秒
S 表示毫秒
z 表示时区

|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8" import="java.util.*"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix='fmt' %>
<%
Date now = new Date();
pageContext.setAttribute("now",now);
%>
完整日期: <fmt:formatDate value="${now}" pattern="G yyyy年MM月dd日 E"/><br>
完整时间: <fmt:formatDate value="${now}" pattern="a HH:mm:ss.S z"/><br>
常见格式: <fmt:formatDate value="${now}" pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"/>
|
步骤 9 : fn:
更多内容,点击了解: https://how2j.cn/k/jsp/jsp-jstl/578.html