numpy
数组的运算 多维的数组对象, 简称ndarray
- 实际数据
- 元数据 描述信息
1 # ndarray 2 # 规范,推荐,复用 3 import numpy as np 4 5 ar = np.array([1,2,3,4,5]) 6 print(ar) 7 print([1,2,3,4,5]) 8 print(ar.ndim) 9 print(ar.shape) 10 print(ar.size) 11 print(ar.dtype) 12 print(ar.itemsize)
[1 2 3 4 5] [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] 1 (5,) 5 int32 4
# 创建数组: array()函数,列表,元组,数组,生成器,序列 arr1 = np.array(range(10)) arr2 = np.array([1,2,3,4,5.5]) arr3 = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8]]) print(arr3) print(arr3.ndim) print(arr3.shape)
[[1 2 3 4] [5 6 7 8]] 2 (2, 4)
# arange() ,类似于python range() np.arange(10) np.arange(10.) np.arange(1,10,0.1) np.arange(10000)
array([ 0, 1, 2, ..., 9997, 9998, 9999])
# linspace(): 返回在间隔[开始,停止]上 num个均匀间隔的样本 np.linspace(2.0,3.0, num=5) np.linspace(2.0, 3.0, num=5, endpoint=False) np.linspace(2.0,3.0, num=5, retstep=True)
(array([2. , 2.25, 2.5 , 2.75, 3. ]), 0.25)
# zeros()/zeros_like()/ones()/ones_like() # numpy.zeros(shape, dtype=float, order='C'):返回给定形状和类型的新数组,用零填充。 np.zeros(5) np.zeros((2,3,2), dtype=np.int) arr1 = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) np.zeros_like(arr1) np.ones(6)
array([1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
# eye() # 正方形的N*N的单位矩阵,对角线为1,其余为0 np.eye(5)
array([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 1., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 1., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 1., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]]) numpy 通用函数基本操作
numpy 通用函数基本操作# 数组形状 .T/.reshape()/.resize() # 转置 (2, 5) -> (5, 2) arr1 = np.arange(10) arr2 = np.ones((5,2)) arr3 = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) print(arr1,arr1.T) print('_______') print(arr2) print(arr2.T) print('______') print(arr3) print(arr3.T)
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] _______ [[1. 1.] [1. 1.] [1. 1.] [1. 1.] [1. 1.]] [[1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]] ______ [[1 2 3] [4 5 6]] [[1 4] [2 5] [3 6]]
1 arr2.reshape((10,)) 2 # reshape只提供形状的改变,元素数量保持一致 3 arr4 = np.resize(arr2, (3,5)) 4 print(np.arange(1,13).reshape(3,4)) 5 np.resize(np.arange(1,13).reshape(3,4), (3,5)) 6 7 # np.resize 改变形状,如果元素不够,重复填充
File "<ipython-input-33-dd63d7909c36>", line 7 np.resize 改变形状,如果元素不够,重复填充 ^ SyntaxError: invalid character in identifier1 # 数组的复制 2 arr1 = np.arange(10) 3 arr2 = arr1 4 arr1 is arr2 5 arr3 = arr1.copy() 6 arr1 is arr3 7 # copy 复制一个副本 8 # .T, reshape,resize 返回一个新的数组
False
1 # 数组类型转换 .astype() 默认返回一个新的数组 2 ar1 = np.arange(10, dtype=np.float) 3 ar1.astype(np.int32)
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
# 数组的堆叠 a1 = np.arange(5) a2 = np.arange(4) # print(a1.shape, a2.shape) # 水平堆叠 np.hstack((a1, a2)) # 水平堆叠时,行数要一致 ar1 = np.arange(12).reshape((3,4)) ar2 = np.arange(15).reshape((3,5)) np.hstack((ar1, ar2)) # 垂直堆叠 # np.vstack() # 垂直堆叠,列数要一致 # np.stack() 通过指定哪个维度,哪个轴 # help(np.stack) ar1 = np.arange(12).reshape((3,4)) ar2 = np.ones((3,4)) print(ar1) print(ar2) np.stack((ar1,ar2),axis=0).ndim
[[ 0 1 2 3] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 8 9 10 11]] [[1. 1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1. 1.]]
Out[79]:array([[[ 0., 1., 2., 3.], [ 4., 5., 6., 7.], [ 8., 9., 10., 11.]], [[ 1., 1., 1., 1.], [ 1., 1., 1., 1.], [ 1., 1., 1., 1.]]])
1 # 数组的拆分 2 ar = np.arange(16).reshape(4,4) 3 print(ar) 4 # 水平拆分 按列拆 5 ars = np.hsplit(ar,2) 6 #print(ars) 7 #print(ars[0]) 8 #print(ars[1]) 9 # 垂直拆分,按行拆 10 11 ars = np.vsplit(ar,4) 12 print(ars) 13 print(ars[0]) 14 print(ars[1])
[[ 0 1 2 3] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 8 9 10 11] [12 13 14 15]] [array([[0, 1, 2, 3]]), array([[4, 5, 6, 7]]), array([[ 8, 9, 10, 11]]), array([[12, 13, 14, 15]])] [[0 1 2 3]] [[4 5 6 7]]
1 # 简单的运算 2 # 矢量化 3 ar = np.arange(12).reshape(3,4) 4 # 与标量的运算 5 # print(ar) 6 # print(ar+1) 7 # print(ar*2) 8 # print(1/(ar+1)) 9 # print(ar**0.5) 10 # 常用的统计函数 11 print(ar.mean()) # 求平均值 12 print(ar.max()) # 求最大值 13 print(ar.min()) # 求最小值 14 print(ar.std()) # 求标准差 15 print(ar.var()) # 求方差 16 17 # 可以在不同维度上进行操作 18 print(ar) 19 np.sum(ar, axis=0) 20 np.sum(ar, axis=1) 21 np.sort(np.array([4,3,2,1]))
5.5 11 0 3.452052529534663 11.916666666666666 [[ 0 1 2 3] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 8 9 10 11]]
array([1, 2, 3, 4])
numpy 索引和切片1 # 基本索引 2 ar = np.arange(20) 3 # print(ar) 4 # print(ar[4]) 5 # print(ar[:3]) 6 # 一维的 7 ar = np.arange(16).reshape(4,4) 8 print(ar) 9 # print(ar[0]) # 切出一行 切片为下一个维度的一个元素 10 # print(ar[0][-1]) # 二次索引,得到一维中的一个值 11 print(ar[:3]) # 切出多行, 12 print(ar[1,1]) # 类似于二次索引 13 print(ar[:2, 1:]) 14 # 二维的
[[ 0 1 2 3] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 8 9 10 11] [12 13 14 15]] [[ 0 1 2 3] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 8 9 10 11]] 5 [[1 2 3] [5 6 7]]
1 # 布尔型索引 2 ar = np.arange(12).reshape(3,4) 3 i = np.array([True, False, True]) 4 j = np.array([False, True, False, True]) 5 # print(ar) 6 # print(i) 7 # print(j) 8 # print(ar[i]) 9 # print(ar[i,:]) # 选行 10 # print(ar[:, j]) # 选列 11 # 基本的布尔型索引 12 ai = ar > 5 13 print(ar) 14 print(ai) 15 print(ar[ar % 2 != 0]) # 选取所有的奇数 16 print(ar[i,j])
[[ 0 1 2 3] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 8 9 10 11]] [[False False False False] [False False True True] [ True True True True]] [ 1 3 5 7 9 11] [ 1 11]
numpy 随机数
numpy.random1 # 生成 2 samples = np.random.normal(size=(4,4)) # 符合标准正态分布的4*4样本值 3 print(samples)
[[ 0.85235645 0.85512049 -0.29868382 1.03635971] [-1.42338011 -1.20987794 1.74704175 0.08565753] [ 1.11191625 0.5263941 0.21444175 0.08820261] [ 0.60592032 0.93473874 -0.28916297 -1.41480416]]
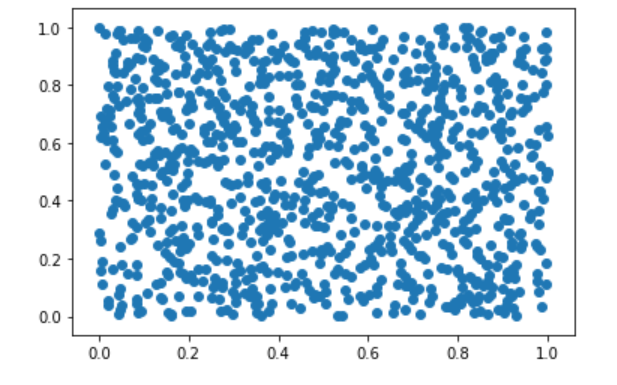
1 # numpy.random.rand() : [0, 1) 之间的随机样本或N维浮点数组 ---均匀分布 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 4 a = np.random.rand() 5 b = np.random.rand(4) 6 c = np.random.rand(3,4) 7 s1 = np.random.rand(1000) 8 s2 = np.random.rand(1000) 9 plt.scatter(s1, s2) 10 plt.show()
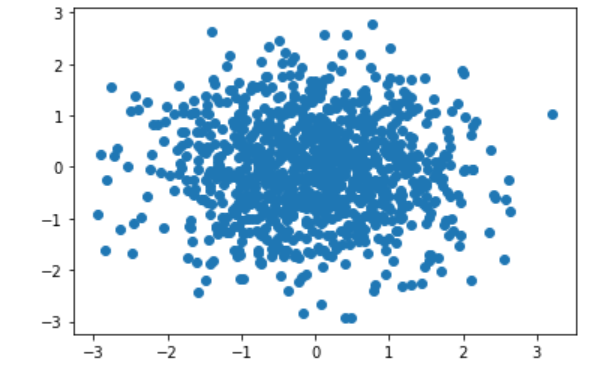
1 # numpy.random.randn() :生成一个浮点数或者N维的浮点数组---正态分布 2 s1 = np.random.randn(1000) 3 s2 = np.random.randn(1000) 4 plt.scatter(s1, s2) 5 plt.show()
1 # numpy.random.randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype='l'): 生成一个整数或者N维的整数数组 2 # 若high不为None时,取[low,high)之间随机整数,否则取值[0,low)之间随机整数,且high必须大于low 3 # dtype参数:只能是int类型 4 np.random.randint(2) 5 np.random.randint(2, 6, size=5) 6 np.random.randint(1,100, size=[3,5])
array([[30, 84, 1, 94, 18], [95, 57, 92, 38, 82], [95, 25, 33, 74, 57]])numpy的输入输出
读写数组数据,文本数据1 # 二进制文件 2 # 存数据 3 import numpy as np 4 ar = np.random.rand(5,5) 5 np.save('test.npy',ar) 6 np.load('test.npy')
array([[0.61427194, 0.69416288, 0.1939631 , 0.60784977, 0.25270645], [0.27015826, 0.21855706, 0.86313053, 0.81490094, 0.72308043], [0.95732625, 0.08912547, 0.58596282, 0.75812357, 0.43485775], [0.41967473, 0.42947078, 0.98010856, 0.26209422, 0.69600965], [0.95892746, 0.48951498, 0.98279041, 0.44956069, 0.41290226]])1 # 文本数据 2 # 存 3 np.savetxt('test.txt', ar, delimiter=',')
1 # 读取 2 np.loadtxt('test.txt', delimiter=',')
array([[0.61427194, 0.69416288, 0.1939631 , 0.60784977, 0.25270645], [0.27015826, 0.21855706, 0.86313053, 0.81490094, 0.72308043], [0.95732625, 0.08912547, 0.58596282, 0.75812357, 0.43485775], [0.41967473, 0.42947078, 0.98010856, 0.26209422, 0.69600965], [0.95892746, 0.48951498, 0.98279041, 0.44956069, 0.41290226]])
总结思维导图:
https://img2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1816772/201910/1816772-20191023000450837-1220857330.png