1. 基本特点
1.1 save computation(惰性运行)
x = 2
y = 3
add_op = tf.add(x, y)
mul_op = tf.multiply(x, y)
useless = tf.multiply(x, add_op)
pow_op = tf.pow(add_op, mul_op)
with tf.Session() as sess:
z = sess.run(pow_op)
如上,因为sess.run(pow_op)不需要用到useless,所以useless的运算不会被执行(save computation)
1.2 Distributed Computation
-
大图分解为子图多GPU并行计算, e.g.
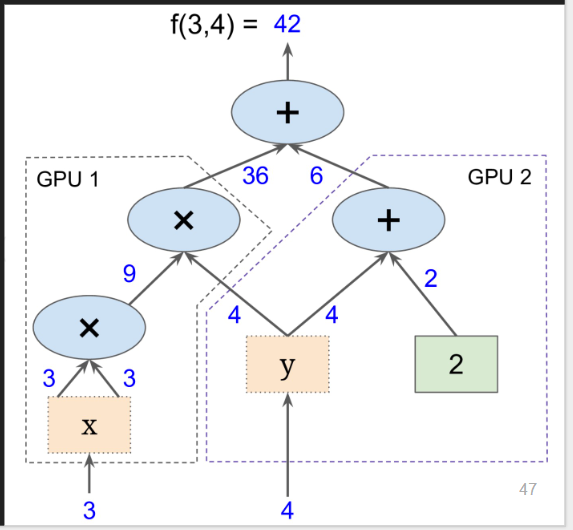
freamework举例
-
Multiple graphs有很多问题,如果非要实现Multiple graphs,可以考虑It’s better to have disconnected subgraphs within one graph
-
创建一个Graph
some codes,待整理
-
Why Graph:
- Save computation. Only run subgraphs that lead to the values you want to fetch.
- Break computation into small, differential pieces to facilitate auto-differentiation
- Facilitate distributed computation, spread the work across multiple CPUs, GPUs, TPUs, or other devices
- Many common machine learning models are taught and visualized as directed graphs