在学习Android应用生命周期章节中,书本上写的有点笼统,较难理解。为了理解的更深,写了个程序测试一下。
1、在layout文件夹中建一个dialog_layout.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="This is a dialog Activity."
/>
</LinearLayout>
2、在layout文件夹中再建一个normal_layout.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="This is a normal Activity."
/>
</LinearLayout>
3、修改layout文件夹中的activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/start_normal_activity"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Start NormalActivity"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/start_dialog_activity"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Start DialogActivity"
/>
</LinearLayout>
4、编写java文件,建立一个DialogActivity.java
package com.example.acitivitylife;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class DialogActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.dialog_layout);
}
}
5、编写java文件,建立一个NormalActivity.java
package com.example.acitivitylife;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class NormalActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.normal_layout);
}
}
6、修改MainActivity.java
package com.example.acitivitylife;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
public static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate");
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button startNormalActivity = (Button)findViewById(R.id.start_normal_activity);
Button startDialogActivity = (Button)findViewById(R.id.start_dialog_activity);
startNormalActivity.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, NormalActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
startDialogActivity.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, DialogActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
Log.d(TAG, "OnStart");
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
Log.d(TAG, "onResume");
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
Log.d(TAG, "OnPause");
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
Log.d(TAG, "onStop");
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy");
}
@Override
protected void onRestart() {
super.onRestart();
Log.d(TAG, "onRestart");
}
}
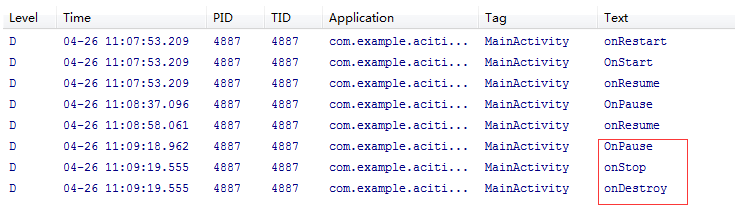
以上步骤完成后,安装到手机,观察LogCat打印出来的消息,对生命周期将一目了然。
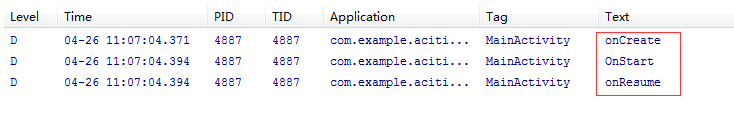
自动安装到手机后,LogCat打印出:
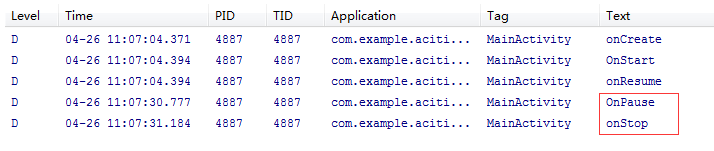
点击Start NormalgActivitya按钮后,LogCat打印出:
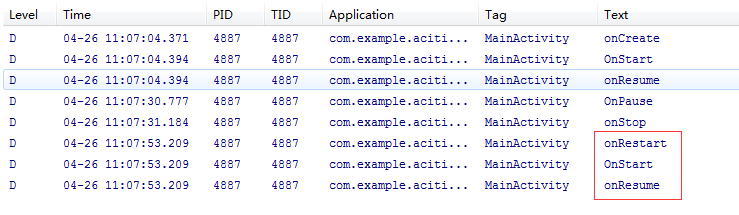
按下返回键后,LogCat打印出:
点击Start DialogActivitya按钮后,LogCat打印出:

按下返回键后,LogCat打印出:

退出程序后,LogCat打印出: