官方题解:
If you choose any n - 1 roads then price of reducing overall dissatisfaction is equal to min(c1, c2, ..cn - 1) where сi is price of reducing by 1 dissatisfaction of i-th edge. So the best solution is to choose one edge and reduce dissatisfaction of it until running out of budget.
Let's construct minimal spanning tree using Prim or Kruskal algorithm using edges of weights equal to dissatisfaction and calculate minimal price of reducing dissatisfaction. Time complexity —  .
.
Now we can iterate over edges implying that current is the one to be reduced to minimum. For example, for every edge we can build new MST and recalculate answer. It's 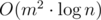 . Therefore we should use this fact: it's poinless to reduce dissatisfaction of edges which weren't selected to be main.
. Therefore we should use this fact: it's poinless to reduce dissatisfaction of edges which weren't selected to be main.
Then we can transform original MST instead of constructing m new ones. Add next edge to MST, now it contains a cycle from which edge with maximal dissatisfaction is about to be deleted. This can be achieved in such a way: find LCA of vertices of new edge in 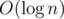 and using binary lifting with precalc in
and using binary lifting with precalc in 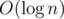 find the edge to delete.
find the edge to delete.
Time complexity — 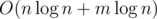 .
.
大意是:
经分析所有的预算用在一条干道上最合算(这条干道的修路花费是所挑选的n-1条干道中最小的),首先建立一棵最小生成树MST,然后枚举M条边,假设当前枚举到的边编号是i,将所有预算用到边 i 上然后添加到MST中形成一个环,找到环中权值最大的边删除。设边i的两端点为 a, b, 找到结点u = LCA(MST,a, b),那么这个环就是由 a~u,b~u 以及边 i 围成。
如何找到权值最大的边呢?可以通过倍增法,具体做法如下:
设mw[a][j]表示结点 a 到它的第 2^j 倍祖先的路径上权值最大的边编号,类似LCA倍增法的做法预处理出所有结点的mw[a][j]值
for(int j = 1; (1<<j) < n; j++) //倍增 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if(pa[i][j-1] != -1){ pa[i][j] = pa[pa[i][j-1]][j-1]; //计算节点i的第2^j倍祖先 int e1 = mw[i][j-1]; int e2 = mw[pa[i][j-1]][j-1]; mw[i][j] = weight[e1] < weight[e2] ? e2 : e1; }
然后计算更换边之后新树的权值,找到使总干道权值最低的更新方法,最后跑一边最小生成树算法即可。
代码如下:
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <vector> 6 #include <queue> 7 8 using namespace std; 9 const int maxn = 2e5 + 10; 10 11 #define rep(i, x, n) for(int i = x; i <= n; i++) 12 struct edge{ 13 int u, v; 14 int w, c; 15 edge(int uu, int vv, int ww, int cc): u(uu), v(vv), w(ww), c(cc){} 16 bool operator<(const edge& b) const { 17 return w < b.w; 18 } 19 }; 20 21 typedef long long LL; 22 vector<edge> E; 23 int r[maxn]; 24 vector<int> G[maxn]; 25 26 void add_edge(int a, int b, int w, int c) { 27 E.push_back(edge(a, b, w, c)); 28 int id = E.size() - 1; 29 G[a].push_back(id); 30 G[b].push_back(id); 31 } 32 33 int n, m, S; 34 int w[maxn]; 35 int c[maxn]; 36 int fa[maxn]; 37 LL w_mst; 38 int findfa(int x) {return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = findfa(fa[x]);} //并查集 39 vector<int> G2[maxn]; 40 bool cmp(int a, int b) { 41 return E[a] < E[b]; 42 } 43 vector<int> A; 44 LL kurskal() { //计算MST 45 LL ans = 0; 46 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) fa[i] = i; 47 for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) r[i] = i; 48 sort(r, r+m, cmp); 49 for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) { 50 edge e = E[r[i]]; 51 int x = findfa(e.u); 52 int y = findfa(e.v); 53 if(x != y) { 54 fa[x] = y; 55 ans += e.w; 56 A.push_back(r[i]); //将添加的边同时保存在A中 57 G2[e.u].push_back(r[i]); 58 G2[e.v].push_back(r[i]); 59 } 60 } 61 return ans; 62 } 63 int dep[maxn]; 64 int pa[maxn][50]; //表示结点a的第 2^j 倍祖先 65 int mw[maxn][50]; //表示结点 a 到它的第 2^j 倍祖先的路径上权值最大的边编号 66 void dfs(int u, int f, int d) { //dfs计算MST中所有结点的深度,初始化pa数组和mw数组 67 dep[u] = d; 68 pa[u][0] = f; 69 for(int i = 0; i < G2[u].size(); i++) { 70 edge& e = E[G2[u][i]]; 71 int v = e.u == u ? e.v : e.u; 72 if(v != f) { 73 mw[v][0] = G2[u][i]; 74 dfs(v, u, d+1); 75 } 76 } 77 } 78 void pre() { //预处理出所有结点的mw,pa 79 for(int j = 1; (1<<j) < n; j++) 80 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if(pa[i][j-1] != -1){ 81 pa[i][j] = pa[pa[i][j-1]][j-1]; 82 int e1 = mw[i][j-1]; 83 int e2 = mw[pa[i][j-1]][j-1]; 84 mw[i][j] = E[e1] < E[e2] ? e2 : e1; 85 } 86 } 87 88 int lca(int a, int b, int &me) { //计算最近公共祖先的同时算出a,b路径中权值最大的边保存到me中 89 me = -1; 90 if(dep[a] < dep[b]) swap(a, b); 91 int i, j; 92 for(i = 0; (1<<i) <= dep[a]; i++); 93 i--; 94 for(j = i; j >= 0; j--) 95 if(dep[a] - (1<<j) >= dep[b]) { 96 int e_id = mw[a][j]; 97 a = pa[a][j]; 98 if(me == -1) me = e_id; 99 me = E[me] < E[e_id] ? e_id : me; 100 } 101 if(a == b) return a; 102 for(j = i; j >= 0; j--) 103 if(pa[a][j] != -1 && pa[a][j] != pa[b][j]) { 104 int e1 = mw[a][j]; 105 int e2 = mw[b][j]; 106 a = pa[a][j]; 107 b = pa[b][j]; 108 if(me == -1) me = e1; 109 me = E[me] < E[e1] ? e1 : me; 110 me = E[me] < E[e2] ? e2 : me; 111 } 112 int e1 = mw[a][0]; 113 int e2 = mw[b][0]; 114 if(me == -1) me = e1; 115 me = E[me] < E[e1] ? e1 : me; 116 me = E[me] < E[e2] ? e2 : me; 117 return pa[a][0]; 118 } 119 int main() { 120 scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); 121 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) scanf("%d", &w[i]); 122 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) scanf("%d", &c[i]); 123 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { 124 int a, b; 125 scanf("%d%d", &a, &b); 126 add_edge(a, b, w[i], c[i]); 127 } 128 scanf("%d", &S); 129 w_mst = kurskal(); 130 memset(pa, -1, sizeof pa); 131 memset(mw, 0, sizeof mw); 132 dfs(1, -1, 0); 133 pre(); 134 LL ans_w = w_mst; 135 int ans_e = -1; 136 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { 137 int e = i-1; 138 int me; 139 lca(E[e].u, E[e].v, me); 140 LL temp = w_mst - E[me].w + E[e].w - S/c[i]; 141 //cout << i <<" : me : "<< me <<endl; 142 if(temp < ans_w) { 143 ans_w = temp; 144 ans_e = e; 145 //cout << "ans_w : " << ans_w<< "ans_e : " << ans_e+1 <<endl; 146 } 147 } 148 if(ans_e != -1) E[ans_e].w -= S/c[ans_e+1]; 149 A.clear(); 150 w_mst = kurskal(); 151 cout << ans_w << endl; 152 for(int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++) 153 cout << A[i] + 1<< " " << E[A[i]].w << endl; 154 return 0; 155 }