1、博文相关接口:
功能分析:(改:先查后改,删:查)
| 功能 | 函数名 | Request方法 | 路径 |
| 发布(增) | pub | POST | /pub |
| 看文章(查) | get | GET | /(d+) |
| 列表(分页) | getall | GET | / |
2、创建博文应用:
$ python manage.py startapp post
注意:一定要把应用post 注册到settings.py 找那个,否则不能迁移
字段类型去这里看:https://www.cnblogs.com/JerryZao/p/10002165.html
模型:(如果中途删了数据库,再迁移,必须把数据库中的django_migrations 里的记录也删除了,才能个创建成功)
1 from user.models import User 2 # 两个class上下关系不能调换 3 class Post(models.Model): 4 class Meta: 5 db_table = 'post' 6 id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True)# 可以自动生成 7 title = models.CharField(max_length=256, null=False) 8 postdate = models.DateTimeField(null=False) 9 # 从post 查作者,从post 查内容 10 author = models.ForeignKey(User) # 指定外键, migrate会生成author_id 字段(外键都会变成_id) 11 #### 不同于sqlalchemy 使用relationship 12 # self.content 可以访问Content实例,其内筒是self.content.content 13 14 def __str__(self): 15 return 'post {} {} {} {}'.format(self.id, self.title, self.author_id, self.content) 16 17 class Content(models.Model): 18 class Meta: 19 db_table = 'content' 20 21 # id 不需要手动写,会自动生成一个id 22 post = models.OneToOneField(Post) # 一对一,这边会有一个外键post_id,引用post.id 23 # post = models.ForeignKey(Post) 上面的也是外键,只不过一对一,要有一起有,没有就没有 24 content = models.TextField(null=False) 25 26 def __str__(self): 27 return 'Content {}{}{}'.format(self.post.id,self.post 错误的, self.content[:20])
注意:因为外键因素,导致字段名改变,所以,代码中调用的时候,只能使用改变后的字段名,否则报错
路由:
注册post应用
全局 blog/urls.py

post/urls.py
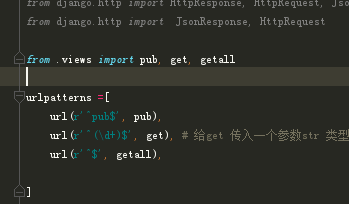
3、pub接口实现
用户从浏览器端提交Json数据,包含title, content。
提交博文需要认证用户,从请求的header中验证jwt
request:POST --> @authenticate pub ---> return post_id
1 from user.views import auth 2 import simplejson 3 import datetime 4 from .models import Post, Content 5 6 @auth #利用user的auth认证 7 def put(request:HttpRequest): 8 post = Post() 9 content = Content() 10 try: 11 payload = simplejson.loads(request.body) 12 13 # post 14 post.title = payload['title'] 15 # post.author = User(id=request.user.id) 16 # author = models.ForeignKey(User) #author是一个实例,只需要将实例传给就行, id 内部自己会处理,这里不能使用 request.user.id 17 post.author = request.user # 因为auth中已将将user这个属性注入到request实例中 18 post.postdate = datetime.datetime.now(datetime.timezone(datetime.timedelta(hours=8)))# 加时区 19 post.save() 20 21 # content 22 content.content = payload['content'] 23 print(content.content,'====== = = = = ') 24 content.post = post # 跟上面的author是一样的,实例对实例 25 content.save() 26 print(content,'========== content =======') 27 28 return JsonResponse({'post_id':post.id}) 29 except Exception as e: 30 print(e) 31 return HttpResponseBadRequest({"a":111111})
4、get接口的实现
根据post_id 查询博文并返回。
不需要认证
如果博文只能作者自己的看,需要认证,我们这里的宫颈癌所有人看,所以不需要认证
request :GET --》 get post by id --> return post + content
1 # Django的做法,通过返回直接提供 *args 2 def get(requset:HttpRequest, id): # post/1 因为不在GET(查询字符串)也不在POST(body中)中 3 print(id, type(id),'-----------------------') # 1 <class 'str'> 4 try: 5 id = int(id) 6 post = Post.objects.get(pk=id) 7 print( post,'--- --- --- --- --') 8 if post: 9 return JsonResponse({ 10 'post':{ 11 "post_id":post.id, 12 "title":post.title, 13 "author":post.author.name, 14 "author_id":post.author_id, 15 "author_id--2":post.author.id, 16 "postdate":post.postdate.timestamp(), 17 "content":post.content.content 一一对应关系,内部会解决 18 } 19 }) 20 except Exception as e: 21 print(e) 22 return JsonResponse({})
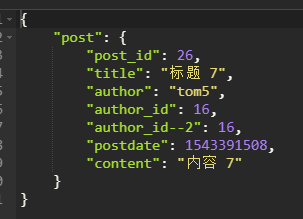
5、getall接口的实现
发起get请求,例如:通过查询字符串 http://url/post/>page=2 查询第二页数据
1 # 参数处理 2 def validate(d:dict, name:str, type_func, default, validat_func): 3 try: 4 result = type_func(d.get(name, default)) 5 result = validat_func(result, default) 6 except: 7 result = default 8 return result 9 10 11 def getall(request:HttpRequest): # post/?page=1&size=2..... 12 # 比较NB 的写法: 13 # 页码: 14 page = validate(request.GET,'page', int, 1, lambda x,y:x if x>0 else 1) 15 # 每页的多少条 16 size = validate(request.GET, 'size', int, 20, lambda x,y:x if x > 0 and x < 101 else y) 17 #注意:这个数据不要轻易让浏览器端改变,如果允许改变,一定要控制范围 18 19 # # 比较low 的写法,如果多个选项,那得多少冗余的代码 20 # try: 21 # size = int(request.GET.get('size',20)) 22 # size = size if size > 0 and size < 101 else 20 23 # except: 24 # size = 20 25 try:# 切片实现分页 26 # 按照id 倒排,一般显示最新的,而且id是主键,顺序IO 27 start = (page - 1) * size # 起点,第一页 从0开始,第二页从 1 开始 28 posts = Post.objects.order_by('-id')# - 表示倒序 29 print(posts.query)# 查看查询语句 30 count = posts.count() 31 32 posts = posts[start:start +size] 33 print(posts.query) 34 35 return JsonResponse({ 36 'posts':[ 37 { 38 'post_id':post.id, 39 'title':post.title 40 } for post in posts 41 ], 42 'pagination':{ 43 'page':page, 44 'size':size, 45 'count':count, 46 'pages':math.ceil(count / size) # 多少页 47 } 48 }) 49 50 except Exception as e: 51 print(e) 52 return HttpResponseBadRequest({})
Django不能设 GET等方法到url的映射,所以只能通过不同的路径来区分