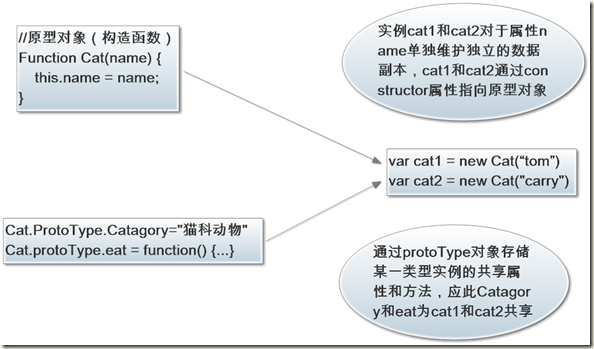
一、JavaScript中原型对象(构造函数)和实例对象以及protoType的关系:
二、JS中通过构造函数实现继承的五种方式:
1、使用apply()或call()方法:
<script type="text/javascript">
function Animal () {
this.species = "动物";
}
Animal.prototype.categroy = "猫科";
function Cat (name, color) {
//Animal.apply(this, arguments);
Animal.call(this, name, color);
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
var cat1 = new Cat("tom", "yellow");
alert(cat1.species);
//不能继承prototype上的属性和方法
alert(cat1.categroy);//undefined
</script>
2、使用prototype对象
<script type="text/javascript">
function Animal () {
this.species = "动物";
}
Animal.prototype.catagory = "猫科";
function Cat (name, color) {
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
Cat.prototype.weight = "30";
Cat.prototype = new Animal();
alert(Cat.prototype.constructor == Animal);//true,此时constructor指向Animal
Cat.prototype.constructor = Cat;//将constructor指回Cat
var cat1 = new Cat("tom", "yellow");
alert(cat1.constructor == Cat);//true,实例的constructor默认调用prototype对象的constructor属性
//能继承构造函数内和prototype上的所有属性和方法
alert(cat1.species);
alert(cat1.catagory);
//Cat.prototype上原有的属性和方法将被清除
alert(Cat.prototype.weight);
</script>
某一对象使用prototype对象实现继承另一对象后,原对象的constructor属性指向被继承的另一对象,此时必须将原对象constructor属性指回原对象,否则会导致继承链的紊乱。设计继承时务必遵守。如下:
o.prototype = {};
o.prototype.constructor = o;
3、直接继承prototype对象
<script type="text/javascript">
function Animal () {
this.species = "动物";
}
Animal.prototype.catagory = "猫科";
function Cat (name, color) {
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
Cat.prototype.weight = "30";
Cat.prototype = Animal.prototype;
/**此时constructor指向Animal**/
alert(Animal.prototype.constructor);
alert(Cat.prototype.constructor);
/****************************************/
Cat.prototype.constructor = Cat;//将constructor指回Cat
var cat1 = new Cat("tom", "yellow");
alert(cat1.constructor == Cat);//true,实例的constructor默认调用prototype对象的constructor属性
alert(cat1.catagory);
/**直接使用prototype对象继承后,Animal.prototype.constructor和Cat.prototype.constructor指向同一对象**/
/**应此对Cat.prototype的修改也会反应到Animal.prototype上**/
alert(Animal.prototype.constructor == Cat);//true
Cat.prototype.catagory = "猫科动物";
alert(Animal.prototype.catagory);//猫科动物
/***********************************/
//不能继承构造函数内的属性和方法
alert(cat1.species);//undefined
</script>
4、间接继承prototype对象
<script type="text/javascript">
function Animal () {
this.category = "猫科";
}
Animal.prototype = {species: "动物"};
function Cat (name, color) {
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
var f = function() {}
f.prototype = Animal.prototype;
Cat.prototype = new f();
Cat.prototype.constructor = Cat;//将constructor指回Cat
var cat1 = new Cat("tom", "yellow");
alert(cat1.constructor == Cat);//true,实例的constructor默认调用prototype对象的constructor属性
alert(cat1.species);
//不能继承构造函数内的属性和方法
alert(cat1.category);//undefined
/**使用空对象间接继承后,对Cat.prototype的修改不会反应到Animal.prototype上**/
alert(Animal.prototype.constructor == Cat);//false
Cat.prototype.species = "哺乳动物";
alert(Animal.prototype.species);//动物
/***********************************/
</script>
对上面间接继承方法的封装如下:
<script type="text/javascript">
function extend(child, parent){
var f = function() {};
f.prototype = parent.prototype;
child.prototype = new f();
child.prototype.constructor = child;
//在子对象上打开一条通道,可以直接调用父对象的方法。这一行放在这里,只是为了实现继承的完备性,纯属备用性质。
child.uber = parent.prototype;
}
function Animal () {
}
Animal.prototype = {species: "动物"};
function Cat (name, color) {
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
extend(Cat, Animal);
var cat1 = new Cat();
alert(cat1.species);
</script>
在使用prototype对象实现继承时,子对象只能继续父对象的prototype对象的属性和方法。
5、使用属性复制实现继承
<script type="text/javascript">
function extend(child, parent){
var p = parent.prototype;
var c = child.prototype;
for(var i in p){
c[i] = p[i];
}
//在子对象上打开一条通道,可以直接调用父对象的方法。这一行放在这里,只是为了实现继承的完备性,纯属备用性质。
c.uber = p;
}
function Animal () {
this.category = "猫科";
}
Animal.prototype = {species: "动物"};
function Cat (name, color) {
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
Cat.prototype.species = "小动物";
Cat.prototype.weight = "30";
extend(Cat, Animal);
var cat1 = new Cat();
alert(cat1.species);
//不能继承构造函数内的属性和方法
alert(cat1.category);//undefined
//子对象的prototype上的不同名的属性和方法不会被清除
alert(Cat.prototype.weight);
//子对象的prototype上的同名的属性和方法会被重写
alert(Cat.prototype.species);
</script>
三、非构造函数(json对象)的继承
1、使用空对象间接继承
<script type="text/javascript">
function object(o){
var F = function(){};
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
var chinese = {nation : "cn"};
var doctor = new object(chinese);
doctor.career = "doctor";
alert(doctor.nation);
</script>
2、通过属性复制实现继承
<script type="text/javascript">
/**浅复制**/
function extendCopy(p){
var c = {};
for(var i in p){
c[i] = p[i];
}
c.uber = p;
return c;
}
var chinese = {nation : "cn"};
var doctor = extendCopy(chinese);
doctor.career = "doctor";
alert(doctor.nation);
/*************/
</script>
若父对象有数组或对象级别的属性,通过上面的属性复制方法实现继承后,对子对象继承的这些属性的修改将会影响到父对象这些属性的值。因为在js中对于对象级别变量的赋值都是传递的对象引用,并非数据副本,对变量的修改都是操作同一对象。
通过以下深复制的方法可以实现对象的复制:
<script type="text/javascript">
/**深复制**/
function deepCopy(p, c){
var c = c || {};
for(var i in p){
if(typeof p[i] === 'object'){
c[i] = (p[i].constructor === Array) ? [] : {};
deepCopy(p[i], c[i]);
}
else{
c[i] = p[i];
}
}
return c;
}
var chinese = {birthPlaces : ['shanghai', 'beijing', 'guangzhou']};
var doctor = deepCopy(chinese);
alert(doctor.birthPlaces.join(','));
doctor.birthPlaces.push('shenz');
alert(chinese.birthPlaces.join(','));
/**************/
</script>