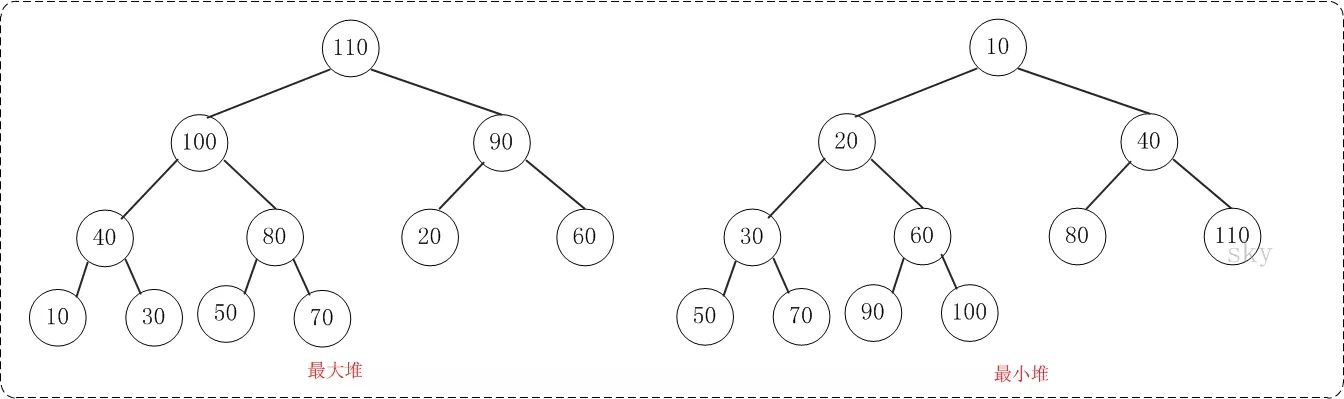
最大堆:父结点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值;如下图左
最小堆:父结点的键值总是小于或等于任何一个子节点的键值。如下图右

1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String []args){ 3 MaxHeap mh = new MaxHeap(20); 4 mh.insert(90); 5 mh.insert(80); 6 mh.insert(89); 7 mh.insert(60); 8 mh.insert(40); 9 mh.insert(88); 10 mh.insert(87); 11 mh.insert(10); 12 mh.insert(50); 13 mh.insert(30); 14 mh.insert(20); 15 mh.insert(86); 16 mh.printHeap(); 17 System.out.println("==================="); 18 System.out.println(mh.remove(60)); 19 mh.printHeap(); 20 } 21 } 22 23 class MaxHeap{ 24 public MaxHeap(int capacity){ 25 this.capacity = capacity; //数组实际大小 26 this.size = 0; //数组中现有元素个数 27 this.items = new int[capacity]; 28 } 29 30 31 //获取指定元素所在下标 32 public int getIndex(int item){ 33 //如果数据量为0或者所找的数比最大堆的堆顶大,则返回-1,即数组中不存在所查元素 34 if(size == 0 || item > items[0]){ 35 return -1; 36 } 37 38 //遍历查找 39 for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){ 40 if(item == items[i]){ 41 return i; 42 } 43 } 44 return -1; 45 } 46 47 public boolean insert(int item){ 48 if(size == capacity){ 49 return false; 50 } 51 items[size++] = item; 52 //每次插入时堆已经有序,只需将最新插入的元素向上移动 53 upAdjust(size - 1); 54 return true; 55 } 56 57 public boolean remove(int item){ 58 int index = getIndex(item); 59 if(index != -1){ 60 items[index] = items[--size]; 61 /* 62 *删除某个元素是向上调整和向下调整是必须都要执行的 63 *从数组[90, 80, 89, 60, 40, 88, 87, 10, 50, 30, 20, 86]可以看出 64 * 如果删除60,只进行向下调整会破坏最大堆的性质 65 * 加upAdujst时的结果: [90, 86, 89, 80, 40, 88, 87, 10, 50, 30, 20] 66 * 不加upAdujst时的结果:[90, 80, 89, 86, 40, 88, 87, 10, 50, 30, 20] 67 */ 68 downAdjust(index); 69 upAdjust(index); 70 return true; 71 } 72 return false; 73 } 74 75 public void printHeap(){ 76 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 77 sb.append('['); 78 for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){ 79 sb.append(items[i] + ", "); 80 } 81 sb.replace(sb.length() - 2, sb.length(), "]"); 82 System.out.println(sb.toString()); 83 } 84 85 private void upAdjust(int index){ 86 int childIndex = index; 87 int parentIndex = (childIndex - 1) / 2; 88 int temp = items[childIndex]; 89 90 while(childIndex > 0 && temp > items[parentIndex]){ 91 items[childIndex] = items[parentIndex]; 92 childIndex = parentIndex; 93 parentIndex = (parentIndex - 1) / 2; 94 } 95 items[childIndex] = temp; 96 } 97 98 private void downAdjust(int index){ 99 int parentIndex = index; 100 int childIndex = parentIndex * 2 + 1; 101 int temp = items[index]; 102 103 while(childIndex < size && temp < items[childIndex]){ 104 if(childIndex + 1 < size && items[childIndex] < items[childIndex + 1]){ 105 childIndex++; 106 } 107 items[parentIndex] = items[childIndex]; 108 parentIndex = childIndex; 109 childIndex = (parentIndex - 1) / 2; 110 } 111 items[parentIndex] = temp; 112 } 113 114 private int[] items; 115 private int capacity; 116 private int size; 117 }
