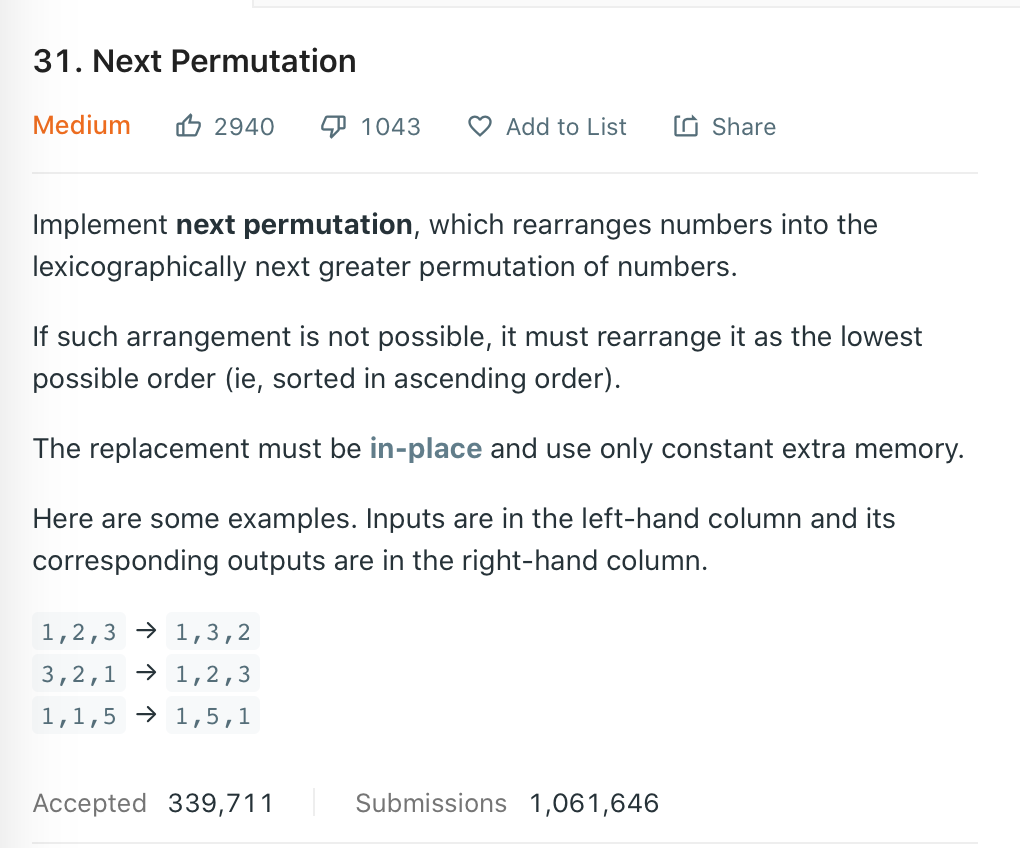
给出一个列表,把这个列表排序成一个相对更大的数。例如[1,2,3]经过改变后,变成[1,3,2],注意必须是所有更大的排列情况中最小的那个数,即这个例子中的答案只能是[1,3,2]而不能是[2,1,3]。返回重新排序的列表。
我的思路是从列表倒数第二个数开始向左寻找,找这个数的右侧是否有比它大的数,比如在i这发现了右侧有比它更大的一些数,从中挑一个最小的,将它们的位置交换,然后对i位置右侧的数进行从小到大排序。这样得到的数组,即可满足题目要求。代码:
class Solution(object): def nextPermutation(self, nums): """ :type nums: List[int] :rtype: None Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead. """ if len(nums) < 2: return nums totalLength = len(nums) p = None q = None for i in xrange(2, totalLength + 1): currMin = None for j in xrange(1, i): if nums[-j] > nums[-i]: if not currMin or nums[-j] < currMin: currMin = nums[-j] p = i q = j if p: break if p: temp = nums[-p] nums[-p] = nums[-q] nums[-q] = temp nums[-p+1:] = sorted(nums[-p+1:]) else: nums.reverse()

给出一串由'('和')'组成的字符串,从中找出一段最长的合法括号段,返回它的长度。思路是用栈来存储各个位置的最长字符串,遇到左括号时存入当前最长合法长度,并将其清零;遇到右括号时,若栈不为空,则对栈进行pop操作,取出相邻的最长合法字符串,加二后记为当前最长合法字符串,并与历史最长合法字符串进行比较;若栈为空,则只进行当前最长合法字符串的清零操作。代码:
class Solution(object): def longestValidParentheses(self, s): """ :type s: str :rtype: int """ if not s: return 0 maxLength = 0 currLength = 0 stack = [] for _s in s: if _s == '(': stack.append(currLength) currLength = 0 elif _s == ')': if stack: preLength = stack.pop() currLength += (preLength + 2) maxLength = max(currLength, maxLength) else: currLength = 0 return maxLength
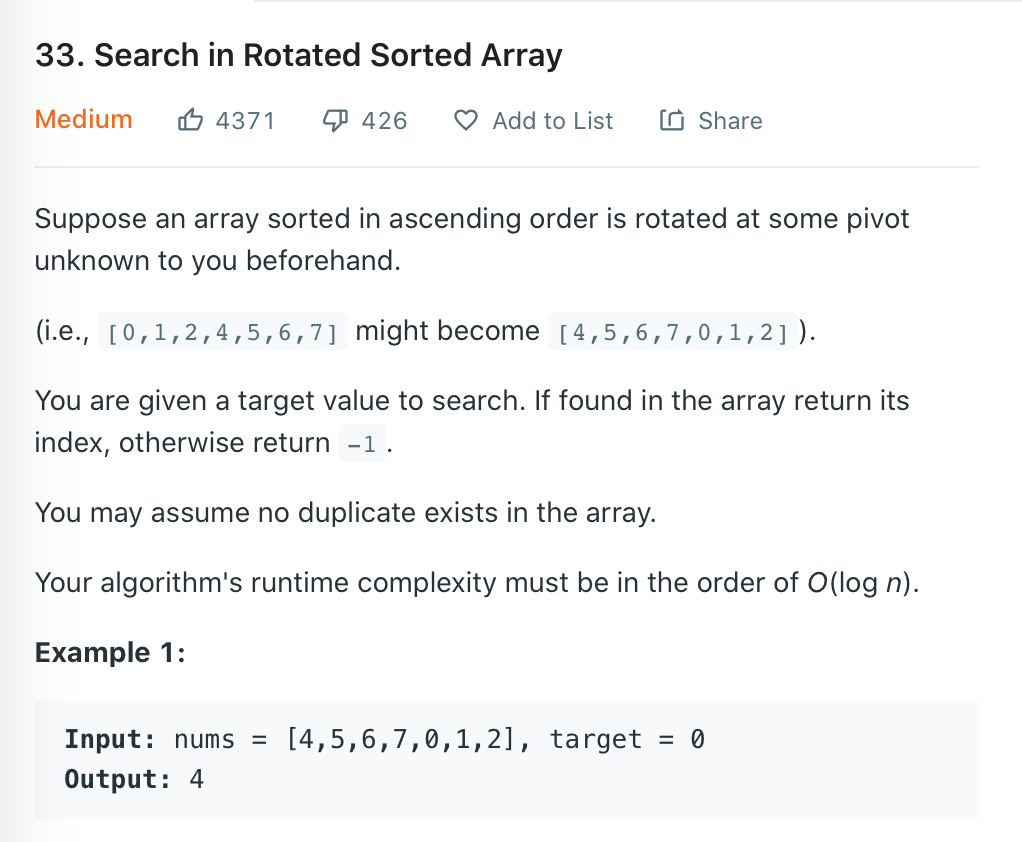
给出一个由几个升序短数组拼接成的长数组,从中寻找target的位置,没有则返回-1,数组里的数不重复。这里直接用了Python内置的index方法对target进行检索:
class Solution(object): def search(self, nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: int """ try: return nums.index(target) except: return -1
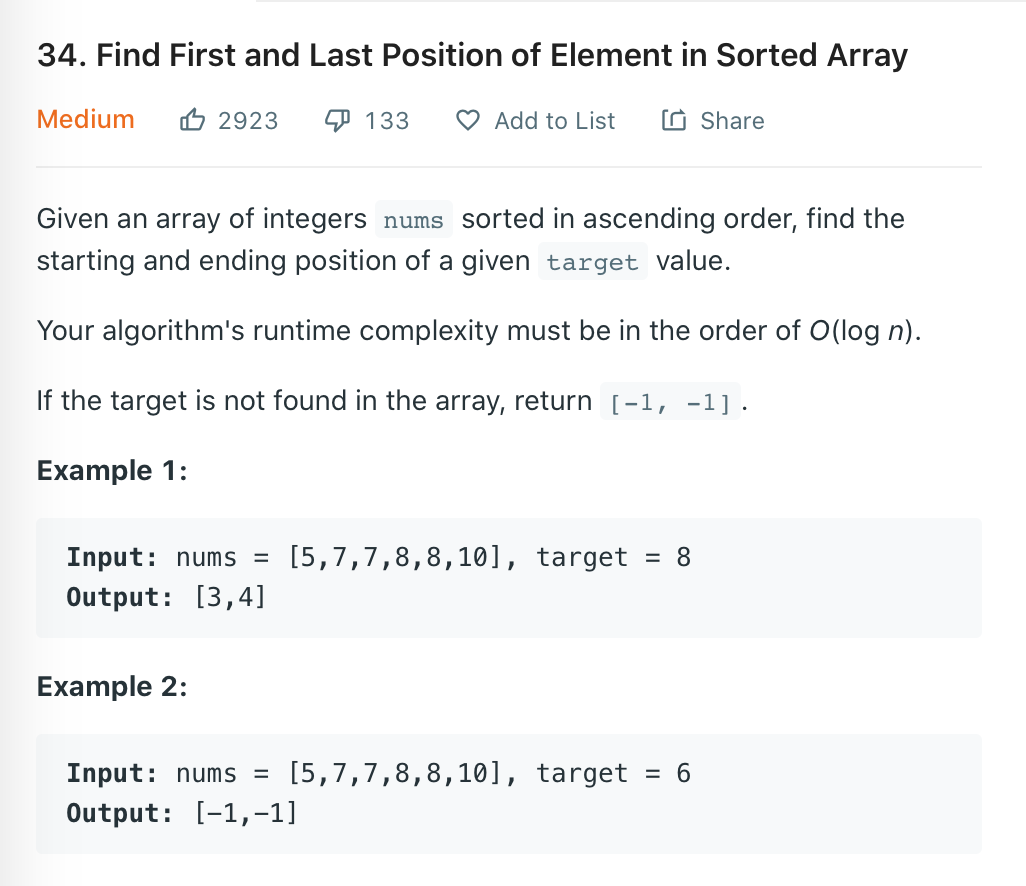
给出一个升序数组(里面的数可以重复)和一个目标数target,找出target在数组中的起始位置和终止位置。同样是利用Python内置的index方法先找到target的起始位置,然后从起始位置开始向右进行遍历,遇到target则更新终止位置,遇到的数不是target则退出。代码:
class Solution(object): def searchRange(self, nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: List[int] """ try: start = nums.index(target) end = start for i, num in enumerate(nums[start:]): if num == target: end = i + start else: break return start, end except: return -1, -1

寻找插入的位置,给出一个升序数组和目标数target,如果target在数组里,则返回它的位置,如果不在,则返回它应该插入的位置(保持数组的升序)。我的思路是用二分法进行查找,中途找到了target直接返回,如果直到最后也没能找到则返回插入位置。代码:
class Solution(object): def searchInsert(self, nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: int """ if not nums: return p = len(nums) / 2 start = 0 end = len(nums) - 1 while(1): if nums[p] == target: return p else: if p == start: if target > nums[end]: return end + 1 if target < nums[start]: return start return end if nums[p] > target: end = p else: start = p p = (start + end) / 2