来源http://blog.csdn.net/wuzhekai1985
问题1 :输入一个字符串,打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。例如输入字符串abc,则输出由字符a、b、c所能排列出来的所有字符串abc、acb、bac、bca、cab和cba。
思路:这是个递归求解的问题。递归算法有四个特性:(1)必须有可达到的终止条件,否则程序将陷入死循环;(2)子问题在规模上比原问题小;(3)子问题可通过再次递归调用求解;(4)子问题的解应能组合成整个问题的解。
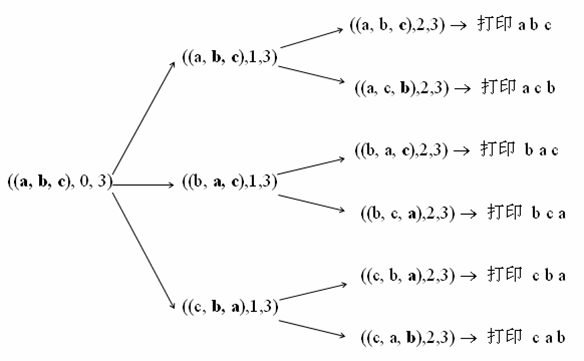
对于字符串的排列问题。如果能生成n - 1个元素的全排列,就能生成n个元素的全排列。对于只有1个元素的集合,可以直接生成全排列。全排列的递归终止条件很明确,只有1个元素时。下面这个图很清楚的给出了递归的过程。
参考代码:解法1通过Permutation_Solution1(str, 0, n); 解法2通过调用Permutation_Solution2(str, str)来求解问题。
1 //函数功能 : 求一个字符串某个区间内字符的全排列 2 //函数参数 : pStr为字符串,begin和end表示区间 3 //返回值 : 无 4 void Permutation_Solution1(char *pStr, int begin, int end) 5 { 6 if(begin == end - 1) //只剩一个元素 7 { 8 for(int i = 0; i < end; i++) //打印 9 cout<<pStr[i]; 10 cout<<endl; 11 } 12 else 13 { 14 for(int k = begin; k < end; k++) 15 { 16 swap(pStr[k], pStr[begin]); //交换两个字符 17 Permutation_Solution1(pStr, begin + 1, end); 18 swap(pStr[k],pStr[begin]); //恢复 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 23 //函数功能 : 求一个字符串某个区间内字符的全排列 24 //函数参数 : pStr为字符串,pBegin为开始位置 25 //返回值 : 无 26 void Permutation_Solution2(char *pStr, char *pBegin) 27 { 28 if(*pBegin == '\0') 29 { 30 cout<<pStr<<endl; 31 } 32 else 33 { 34 char *pCh = pBegin; 35 while(*pCh != '\0') 36 { 37 swap(*pBegin, *pCh); 38 Permutation_Solution2(pStr, pBegin + 1); 39 swap(*pBegin, *pCh); 40 pCh++; 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 //提供的公共接口 45 void Permutation(char *pStr) 46 { 47 Permutation_Solution1(pStr, 0, strlen(pStr)); 48 //Permutation_Solution2(pStr,pStr); 49 }
问题2:输入一个字符串,输出该字符串中字符的所有组合。举个例子,如果输入abc,它的组合有a、b、c、ab、ac、bc、abc。
思路:同样是用递归求解。可以考虑求长度为n的字符串中m个字符的组合,设为C(n,m)。原问题的解即为C(n, 1), C(n, 2),...C(n, n)的总和。对于求C(n, m),从第一个字符开始扫描,每个字符有两种情况,要么被选中,要么不被选中,如果被选中,递归求解C(n-1, m-1)。如果未被选中,递归求解C(n-1, m)。不管哪种方式,n的值都会减少,递归的终止条件n=0或m=0。
1 //函数功能 : 从一个字符串中选m个元素 2 //函数参数 : pStr为字符串, m为选的元素个数, result为选中的 3 //返回值 : 无 4 void Combination_m(char *pStr, int m, vector<char> &result) 5 { 6 if(pStr == NULL || (*pStr == '\0'&& m != 0)) 7 return; 8 if(m == 0) //递归终止条件 9 { 10 for(unsigned i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) 11 cout<<result[i]; 12 cout<<endl; 13 return; 14 } 15 //选择这个元素 16 result.push_back(*pStr); 17 Combination_m(pStr + 1, m - 1, result); 18 result.pop_back(); 19 //不选择这个元素 20 Combination_m(pStr + 1, m, result); 21 } 22 //函数功能 : 求一个字符串的组合 23 //函数参数 : pStr为字符串 24 //返回值 : 无 25 void Combination(char *pStr) 26 { 27 if(pStr == NULL || *pStr == '\0') 28 return; 29 int number = strlen(pStr); 30 for(int i = 1; i <= number; i++) 31 { 32 vector<char> result; 33 Combination_m(pStr, i, result); 34 } 35 }
问题3:打靶问题。一个射击运动员打靶,靶一共有10环,连开10 枪打中90环的可能性有多少?
思路:这道题的思路与字符串的组合很像,用递归解决。一次射击有11种可能,命中1环至10环,或脱靶。
参考代码:
1 //函数功能 : 求解number次打中sum环的种数 2 //函数参数 : number为打靶次数,sum为需要命中的环数,result用来保存中间结果,total记录种数 3 //返回值 : 无 4 void ShootProblem_Solution1(int number, int sum, vector<int> &result, int *total) 5 { 6 if(sum < 0 || number * 10 < sum) //加number * 10 < sum非常重要,它可以减少大量的递归,类似剪枝操作 7 return; 8 if(number == 1) //最后一枪 9 { 10 if(sum <= 10) //如果剩余环数小于10,只要最后一枪打sum环就可以了 11 { 12 for(unsigned i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) 13 cout<<result[i]<<' '; 14 cout<<sum<<endl; 15 (*total)++; 16 return; 17 } 18 else 19 return; 20 } 21 for(unsigned i = 0; i <= 10; i++) //命中0-10环 22 { 23 result.push_back(i); 24 ShootProblem_Solution1(number-1, sum-i, result, total); //针对剩余环数递归求解 25 result.pop_back(); 26 } 27 } 28 //提供的公共接口 29 void ShootProblem(int number, int sum) 30 { 31 int total = 0; 32 vector<int> result; 33 ShootProblem_Solution1(number, sum, result, &total); 34 cout<<"total nums = "<<total<<endl; 35 }