调和级数

#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <stack> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; #define R register /*【hdu6315】naive operations 有两个长度为n的整数序列a和b。b是一个静态排列。 操作序列a:1.区间+1;2.区间求和[ai/bi]。 */ //树状数组(或另外一棵线段树)维护每个位置的答案,即[ai/bi]。 //线段树维护区间内ai%bi-bi的max,可以通过维护区间max查询全局max, //当(ai%bi-bi)max=0时,[ai/bi]要加1,这时才需要修改树状数组元素。 //如果有一个位置是0,把那个位置改成-bi。在树状数组上对点值++。 void reads(int &x){ //读入优化(正负整数) int f=1;x=0;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} x*=f; //正负号 } const int N=100019; int n,m,x,y,b[N]; char s[15]; int sum[N<<2],min_last[N<<2],lazy[N<<2]; void build(int rt,int l,int r){ lazy[rt]=sum[rt]=0; //因为有多组数据,所以要清零 if(l==r){ min_last[rt]=b[l]; return; } //叶子节点 int mid=(l+r)>>1; //↓↓递归左右子树 build(rt*2,l,mid),build(rt*2+1,mid+1,r); min_last[rt]=min(min_last[rt*2],min_last[rt*2+1]); } //第一棵线段树维护区间ai%bi-bi的max void PushDown(int rt,int l,int r){ if(lazy[rt]==0) return; lazy[rt*2]+=lazy[rt],lazy[rt*2+1]+=lazy[rt]; min_last[rt*2]+=lazy[rt],min_last[rt*2+1]+=lazy[rt],lazy[rt]=0; } void add(int rt,int l,int r,int aiml,int aimr){ if(l>aimr||r<aiml) return; //区间不相交 if(l>=aiml&&r<=aimr){ lazy[rt]--,min_last[rt]--; return; } PushDown(rt,l,r); int mid=(l+r)>>1; add(rt*2,l,mid,aiml,aimr),add(rt*2+1,mid+1,r,aiml,aimr); min_last[rt]=min(min_last[rt*2],min_last[rt*2+1]); } void addsum(int rt,int l,int r,int aim){ if(l>aim||r<aim) return; //第二棵的线段树值变化 if(l==r&&r==aim){ sum[rt]++; return; } int mid=(l+r)>>1; addsum(rt*2,l,mid,aim); addsum(rt*2+1,mid+1,r,aim); sum[rt]=sum[rt*2]+sum[rt*2+1]; } void update(int rt,int l,int r){ if(min_last[rt]>0) return; //不是为0的那一处 if(l==r){ min_last[rt]=b[l],addsum(1,1,n,l); return; } //↑↑找到了第二棵线段树需要修改的位置,addsum修改sum值 PushDown(rt,l,r); int mid=(l+r)>>1; update(rt*2,l,mid),update(rt*2+1,mid+1,r); min_last[rt]=min(min_last[rt*2],min_last[rt*2+1]); } int query(int rt,int l,int r,int aiml,int aimr){ if(l>aimr||r<aiml) return 0; if(l>=aiml&&r<=aimr) return sum[rt]; int mid=(l+r)>>1; return query(rt*2,l,mid,aiml,aimr)+query(rt*2+1,mid+1,r,aiml,aimr); } int main(){ while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF){ for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) reads(b[i]); build(1,1,n); //建树 for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ scanf("%s%d%d",s,&x,&y); if(s[0]=='a'){ add(1,1,n,x,y); if(min_last[1]==0) update(1,1,n); } //↑↑从b[i]开始每次减1,到为0时,需要修改值 else printf("%d ",query(1,1,n,x,y)); } } }
启发式合并
操作过程:每次把小的集合合并进大的集合里。
每个点所在集合大小每次至少会翻倍,每点最多被插入O( logn )次。
(1)洛谷p3224 永无乡
#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <stack> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; #define R register /*【p3224】永无乡 n个点,每个点有权值:1.用一条无向边连接两个点; 2.查询一个点所在联通块里面点第kth权值。 */ //如何查询连通块第k大?平衡树。 /*【平衡树启发式合并】 对于每个联通块,用一个平衡树来维护这个联通块里面所有点的权值。 每次连接两个联通块的时候,把小的联通块的平衡树插入到大的联通块的平衡树里。 使用splay或者带finger search的数据结构的总复杂度是O( nlogn )。*/ void reads(int &x){ //读入优化(正负整数) int f=1;x=0;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} x*=f; //正负号 }
(2)洛谷p3302 森林
- 1.link 两个点;2.查询一条链上的kth。保证随时是一棵树,强制在线。
【分析】先考虑静态链kth怎么做。
从根DFS,建立可持久化Trie(主席树);每次查询链,把链差分为四个前缀的差。
如图所示(用四个前缀表示链):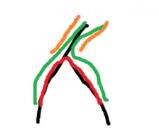
然后在这四个可持久化Trie(主席树)上面一起二分即可。然后考虑启发式合并。
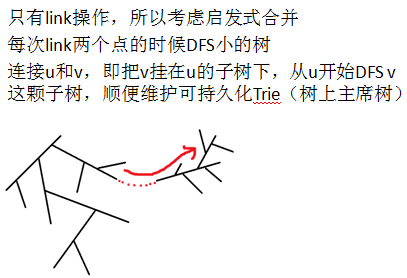
#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <stack> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; #define R register /*【p3302】森林 1.link 两个点;2.查询一条链上的kth。 保证随时是一棵树,强制在线。 */ /*【分析】先考虑静态链kth怎么做。 从根DFS,建立可持久化Trie(主席树); 每次查询链,把链差分为四个前缀的差。 然后在这四个可持久化Trie(主席树)上面一起二分即可。然后考虑启发式合并。*/ void reads(int &x){ //读入优化(正负整数) int f=1;x=0;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} x*=f; //正负号 }
finger search
 --->
---> 
即:从上一次到达的位置开始,经过lca走到所需节点。
序列染色段数均摊
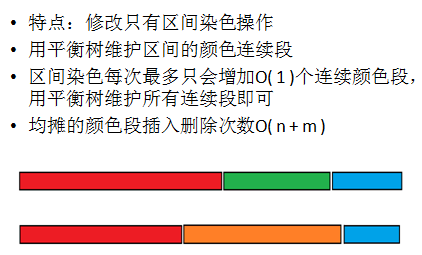
相关问题: 1.区间染色,维护区间的复杂信息;
2.区间排序; 3.ODT类问题。
树染色段数均摊
类似序列颜色段数均摊,不过是均摊O( (n+m)logn )次修改。
复杂度证明:和lct的access类似。
“重量”平衡树
平衡树旋转/重构的节点的size的和是O( nlogn ),
这样可以在旋转的时候暴力重构一些信息。
(1)洛谷p4690 镜中的昆虫
(2)洛谷p2824 排序
(3)洛谷p3703 树点涂色
(4)洛谷p3987 我永远喜欢珂朵莉
#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <stack> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; #define R register /*【p3987】珂朵莉 1 l r x : 把区间[l,r]中所有x的倍数/x, 2 l r : 查询区间[l,r]的和。 */ /*【分析】考虑一个数最多被除logxT次,问题变成了如何快速找出x的倍数。 把每个下标插入到其约数的所有平衡树里, 每次x的倍数/x,就在x对应的平衡树里面暴力查询一段区间的每个数是否是x倍数。 平衡树复杂度O(logn+s)(s是区间点数),总复杂度O(nd(n)+nlog^2n+mlogn)。*/ void reads(int &x){ //读入优化(正负整数) int f=1;x=0;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} x*=f; //正负号 }
特殊的“暴力”数据结构题目
(1)CF250D
#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <stack> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; #define R register /*【CF250D】 单点修改,区间modp,区间和。*/ //If(x>=p) --> x modp <= x–p --> x modp <= x/2 //每次减半,最多log次就会变成0。线段树维护区间max即可。 void reads(int &x){ //读入优化(正负整数) int f=1;x=0;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} x*=f; //正负号 }
(2)洛谷p3332 K大数查询
(3)洛谷p3747 相逢是问候
老司机树(ODT)
【例题】洛谷p4117 五彩斑斓的世界
莫队和分块
分块的分类
静态分块:每块为整体,零散用暴力。
【经典例子】区间众数,区间逆序对数。
动态分块:每块里面维护一个数据结构,可动态修改。
【经典例子】区间加区间rank,区间加区间kth。
相关题目可见:https://blog.csdn.net/flora715/article/details/83213029
根号平衡
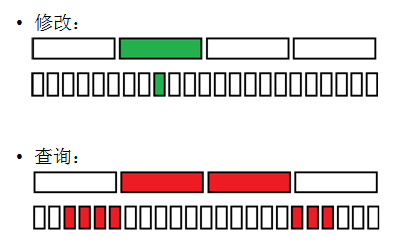
(1)维护一个序列,支持:O(1)单点修改,O(sqrt(n))区间求和。
--> 分块维护块内和,修改时更新块内和、和对应数组上的值。
(2)维护一个序列,支持:O(sqrt(n))单点修改,O(1)区间求和。
--> 分块维护块内前缀和、块外前缀和。
即:维护每个块块内位置前x数的和、以及前x的块的和。
更新的时候分别更新,查询的时候把这两个前缀和拼起来。

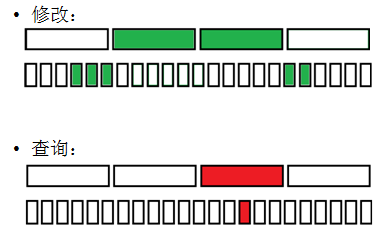
(3)维护一个序列,支持:O(sqrt(n))区间加,O(1)单点求值。
--> 直接分块即可。按整块、零散块修改,单点求值。
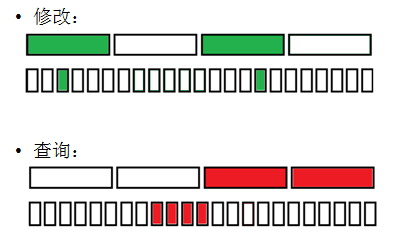
(4)维护一个序列,支持:O(1)区间加,O(sqrt(n))单点求值。
--> 每次对区间[l,r]加x的时候,差分为前缀[1,l-1]减x,前缀[1,r]加x。
同时在数组上和块上打标记,使得区间[l,r]加x。
查询的时候就扫过块外的标记和块内的标记即可。
(5)维护一个集合,支持:O(1)插入一个数,O(sqrt(n))查询第k小。
--> 离散化后对值域进行分块,维护第i个块里面有多少个数。
查询时从第一块开始往右,最多走过sqrt(n)个整块和sqrt(n)个零散数。

(6)维护一个集合,支持:O(sqrt(n))插入一个数,O(1)查询第k小。
--> 值域分块。对于每个数维护一下其在哪个块里面。
对于每个块维护一个OV(有序表)表示这个块内的所有数存在的数,从小到大。
这样我们修改的时候只会改变sqrt( n )个数所从属的块。
查询的时候定位到其所属于的块,然后找到其在该块中对应的值。
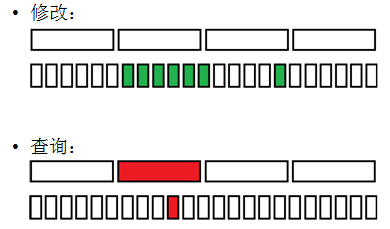
【相关应用】图中每次把一个点一圈加,查一个点的值;
第四分块,即每次给两个颜色,查询这两个颜色的最近路。BZOJ3351
普通莫队
(1)洛谷p3245 大数
#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <stack> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; #define R register /*【p3245】大数 求 数字串S 的一个子串中有多少子串是 P 的倍数。 */ /*【分析】记suf[i]为i -> n构成的后缀串。 如果对于l,r有suf[l] % p == suf[r+1] % p。 即(suf[l] – suf[r+1]) % p == 0。 那么问题转化为统计多少个二元组lr满足suf[]%p相等。 则s[l...r] * 10 ^ ( n - r - 1 )为p的倍数。 注意:对p=2、5时特判。数据离散化,得到类似小z的袜子。 */ void reads(int &x){ //读入优化(正负整数) int f=1;x=0;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} x*=f; //正负号 }
(2)洛谷p4396 作业
(3)洛谷p4462 异或序列
树上莫队
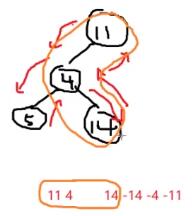
括号序的概念


 --->
---> 
带修改莫队


不删除莫队

二维莫队


莫队二次离线
【例题】洛谷p5047 Yuno
- 给你一个长为n的序列a,m次询问,每次查询一个区间的逆序对数。




二次离线有很多种实现方法,可以将询问再次差分。


虚树
动态树 Link Cut Tree


动态树的辅助树


树分治:点分治,边分治,链分治,Top Tree。
——时间划过风的轨迹,那个少年,还在等你。

