A binary tree is a finite set of vertices that is either empty or consists of a root r and two disjoint binary trees called the left and right subtrees. There are three most important ways in which the vertices of a binary tree can be systematically traversed or ordered. They are preorder, inorder and postorder. Let T be a binary tree with root r and subtrees T1,T2.
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.
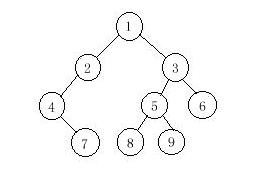
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.

InputThe input contains several test cases. The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1<=n<=1000), the number of vertices of the binary tree. Followed by two lines, respectively indicating the preorder sequence and inorder sequence. You can assume they are always correspond to a exclusive binary tree.
OutputFor each test case print a single line specifying the corresponding postorder sequence.
Sample Input
9 1 2 4 7 3 5 8 9 6 4 7 2 1 8 5 9 3 6Sample Output
7 4 2 8 9 5 6 3 1
两种方法
1.建树
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int pre[1020],mid[1020],ans[1020],k;
struct node
{
int value;
node *l,*r;
node(int value=0,node *l=NULL,node *r=NULL):value(value),l(l),r(r){}
};
void build(int l,int r,int &t,node *&root)
{
int flag=-1;
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++)
{
if(mid[i]==pre[t])
{
flag=i;
break;
}
}
if(flag==-1)
{
return;
}
root=new node(mid[flag]);
t++;
if(flag>l)
{
build(l,flag-1,t,root->l);
}
if(flag<r)
{
build(flag+1,r,t,root->r);
}
}
void slove(node *root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
slove(root->l);
slove(root->r);
ans[k++]=root->value;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin>>n)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>pre[i];
};
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>mid[i];
};
node *root;
k=0;
int t=1;
build(1,n,t,root);
slove(root);
for(int i=0;i<k-1;i++)
{
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
}
printf("%d
",ans[k-1]);
}
return 0;
}
2.深度搜索
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <list>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int pre[1020],mid[1020];
void dfs(int a,int b,int n,int flag)
{
if(n==1)
{
printf("%d ",pre[a]);
return;
}
if(n==0)
{
return;
}
int i;
for(i=0;pre[a]!=mid[b+i];i++);
dfs(a+1,b,i,0);
dfs(a+i+1,b+i+1,n-i-1,0);
if(flag==0)
{
printf("%d ",pre[a]);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin>>n)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>pre[i];
};
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>mid[i];
};
dfs(1,1,n,1);
printf("%d
",pre[1]);
}
return 0;
}
灰灰考研教的,方便理解可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40724865/article/details/79356445
https://www.cnblogs.com/jiangjing/archive/2013/01/14/2860163.html