

Linux是如何来处理中断嵌套的:
所谓的中断嵌套就是,当一种中断正在执行的时候,又产生了另外中断。可以是同类型的,也可以是不同类型的。
首先先来分析第一种类型:慢速中断:是指在进行中断处理的时候,中断的总开关是不关闭的。允许其他类型中断产生。
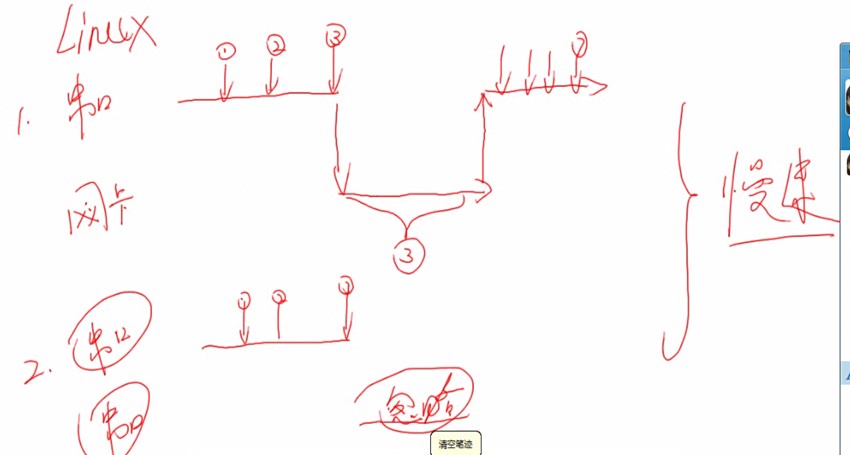
快速中断:当中断产生的时候,控制位的IF为被置1,别的中断被禁止发生。这样就会产生我们不想看到的情况:中断丢失。
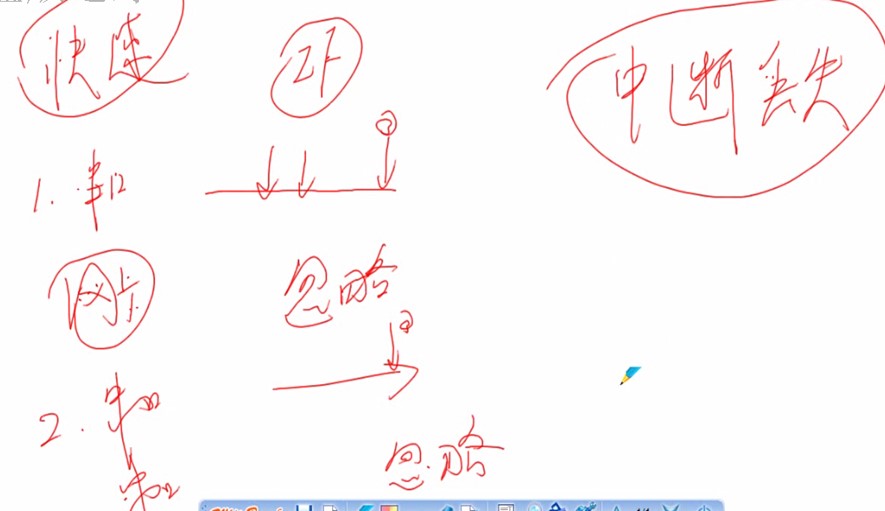
这就是中断分层技术解决的问题:

所谓的中断分层就是,把一个中断分为了上部分和下部分。上部分是硬件相关的,必须要执行的。下部分是检查,处理工作的。可以先不做。这样就缩短了中断工作的时间。尽量避免了中断丢失的问题。


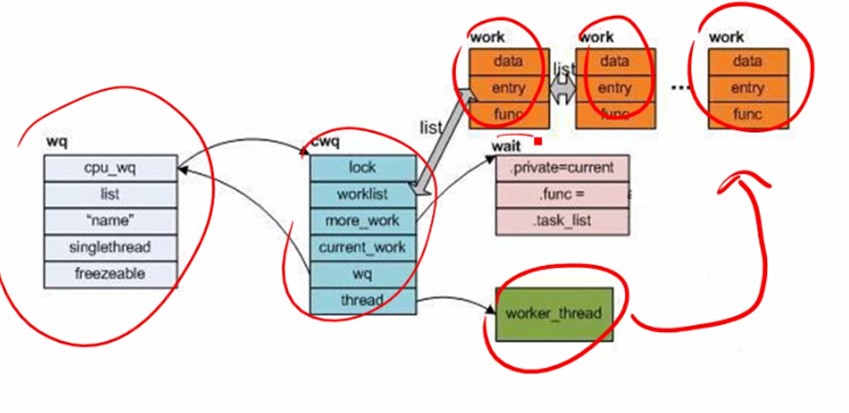
Work在工作队列里有多个,并不是所有的work都会得到工作,得有daemon线程来调度。


最重要的是func,一项工作就是一个函数的执行。就是func的执行。


Queue.c:
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
struct workqueue_struct *my_wq;
struct work_struct *work1;
struct work_struct *work2;
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
void work1_func(struct work_struct *work)
{
printk("this is work1-> ");
}
void work2_func(struct work_struct *work)
{
printk("this is work2-> ");
}
int init_que(void)
{
//1. 创建工作队列
my_wq = create_workqueue("my_que");
//2. 创建工作
work1 = kmalloc(sizeof(struct work_struct),GFP_KERNEL);
INIT_WORK(work1, work1_func);
//3. 挂载(提交)工作
queue_work(my_wq,work1);
//2. 创建工作
work2 = kmalloc(sizeof(struct work_struct),GFP_KERNEL);
INIT_WORK(work2, work2_func);
//3. 挂载(提交)工作
queue_work(my_wq,work2);
return 0;
}
void clean_que()
{
}
module_init(init_que);
module_exit(clean_que);
这是视频的代码,在编译的时候会报错误:
error: implicit declaration of function 'kmalloc'
解决的方法就是加个头文件:<linux/slab.h>就可以了。编译通过:
生成queue.ko驱动文件。
make -C /home/samba/linux-ok6410 M=/home/module/queue modules ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
make[1]: Entering directory `/home/samba/linux-ok6410'
CC [M] /home/module/queue/queue.o
/home/module/queue/queue.c:44: warning: function declaration isn't a prototype
Building modules, stage 2.
MODPOST 1 modules
CC /home/module/queue/queue.mod.o
LD [M] /home/module/queue/queue.ko
make[1]: Leaving directory `/home/samba/linux-ok6410'
接下来是拷贝到开发板运行,看结果:
Insmod queue.ko输出:
This is work1->
This is work2->
但是在很多情况下,驱动并不需要自己建立工作队列,只需定义工作,然后提交工作到内核已经定义好的工作队列keventd_wq中。
1.提交工作到默认队列:schedule_work中。
就是修改init_que函数的代码为:
int init_que(void)
{
//2. 创建工作
work1 = kmalloc(sizeof(struct work_struct),GFP_KERNEL);
INIT_WORK(work1, work1_func);
//3. 挂载(提交)工作
schedule_work(work1);
//2. 创建工作
work2 = kmalloc(sizeof(struct work_struct),GFP_KERNEL);
INIT_WORK(work2, work2_func);
//3. 挂载(提交)工作
schedule_work(work2);
return 0;
}
修改完后执行make,生成.ko文件,拷贝到开发板。输出同样的效果:
[root@FORLINX6410]# insmod queue1.ko
this is work1->
this is work2->
接下来是今天最重要的事情,就是把工作队列用到按键的驱动程序里面去,用到按键中断处理程序当中去。接下来就是对前面的驱动程序进行改造。把他改成分成的中断处理的方式:
Nnnkey.c:
#include <linux/module.h> /* For module specific items */
#include <linux/fs.h> /* For file operations */
#include <linux/ioport.h> /* For io-port access */
#include <linux/io.h> /* For inb/outb/... */
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#define GPNCON 0x7f008830
struct work_struct *work1;
void work1_func(struct work_struct *work)
{
printk("<0>key down! ");
}
irqreturn_t key_int(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
//1.检测是否发生了按键中断
//2.清除已经发生的按键中断
//前面的都是硬件相关的工作,必须在中断里面执行
//下面是硬件无关的工作,我们把它提到中断以外的work1_func函数去处理。
//3.打印按键值
schedule_work(work1);
return 0;
}
void key_hw_init()
{
unsigned int *gpio_config;
unsigned short data;
gpio_config = ioremap(GPNCON,4);
data = readw(gpio_config);
data &= ~0b11;
data |= 0b10;
writew(data,gpio_config);
}
int key_open(struct inode *node, struct file *filp)
{
return 0;
}
struct file_operations key_fops =
{
.open = key_open,
};
struct miscdevice key_miscdevice =
{
.minor = 200,
.name = "OK6410key",
.fops = &key_fops,
};
static int key_init()
{
misc_register(&key_miscdevice);
//硬件初始化
key_hw_init();
//注册中断处理程序
request_irq(IRQ_EINT(0),key_int, IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING,"OK6410key",0);
//2. 创建工作
work1 = kmalloc(sizeof(struct work_struct),GFP_KERNEL);
INIT_WORK(work1, work1_func);
return 0;
}
static void key_exit()
{
misc_deregister(&key_miscdevice);
}
module_init(key_init);
module_exit(key_exit);
Makefile:
obj-m := nnnkey.o
KDIR := /home/samba/linux-ok6410
all :
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
clean :
rm *.order *.symvers *.ko *.o *.mod.c
编译的结果是:
[root@FORFISH queue]# make
make -C /home/samba/linux-ok6410 M=/home/module/queue modules ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-
make[1]: Entering directory `/home/samba/linux-ok6410'
CC [M] /home/module/queue/nnnkey.o
/home/module/queue/nnnkey.c:28: warning: function declaration isn't a prototype
/home/module/queue/nnnkey.c:53: warning: function declaration isn't a prototype
/home/module/queue/nnnkey.c:67: warning: function declaration isn't a prototype
Building modules, stage 2.
MODPOST 1 modules
CC /home/module/queue/nnnkey.mod.o
LD [M] /home/module/queue/nnnkey.ko
make[1]: Leaving directory `/home/samba/linux-ok6410'