You are given a rooted tree with vertices numerated from 11 to nn. A tree is a connected graph without cycles. A rooted tree has a special vertex named root.
Ancestors of the vertex ii are all vertices on the path from the root to the vertex ii, except the vertex ii itself. The parent of the vertex ii is the nearest to the vertex ii ancestor of ii. Each vertex is a child of its parent. In the given tree the parent of the vertex ii is the vertex pipi. For the root, the value pipi is −1−1.
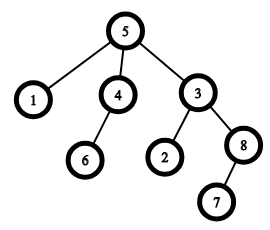 An example of a tree with n=8n=8, the root is vertex 55. The parent of the vertex 22 is vertex 33, the parent of the vertex 11 is vertex 55. The ancestors of the vertex 66 are vertices 44 and 55, the ancestors of the vertex 77 are vertices 88, 33 and 55
An example of a tree with n=8n=8, the root is vertex 55. The parent of the vertex 22 is vertex 33, the parent of the vertex 11 is vertex 55. The ancestors of the vertex 66 are vertices 44 and 55, the ancestors of the vertex 77 are vertices 88, 33 and 55You noticed that some vertices do not respect others. In particular, if ci=1ci=1, then the vertex ii does not respect any of its ancestors, and if ci=0ci=0, it respects all of them.
You decided to delete vertices from the tree one by one. On each step you select such a non-root vertex that it does not respect its parent and none of its children respects it. If there are several such vertices, you select the one with the smallest number. When you delete this vertex vv, all children of vv become connected with the parent of vv.
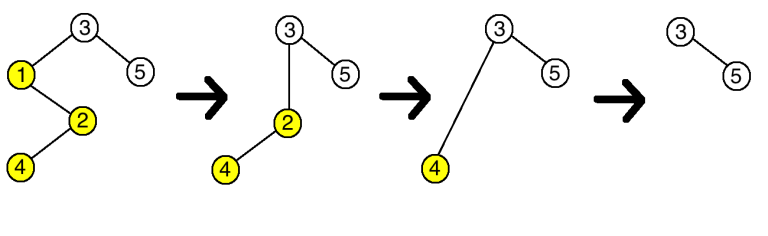
 An example of deletion of the vertex 77.
An example of deletion of the vertex 77.Once there are no vertices matching the criteria for deletion, you stop the process. Print the order in which you will delete the vertices. Note that this order is unique.
The first line contains a single integer nn (1≤n≤1051≤n≤105) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The next nn lines describe the tree: the ii-th line contains two integers pipi and cici (1≤pi≤n1≤pi≤n, 0≤ci≤10≤ci≤1), where pipi is the parent of the vertex ii, and ci=0ci=0, if the vertex ii respects its parents, and ci=1ci=1, if the vertex ii does not respect any of its parents. The root of the tree has −1−1 instead of the parent index, also, ci=0ci=0 for the root. It is guaranteed that the values pipi define a rooted tree with nn vertices.
In case there is at least one vertex to delete, print the only line containing the indices of the vertices you will delete in the order you delete them. Otherwise print a single integer −1−1.
5 3 1 1 1 -1 0 2 1 3 0
1 2 4
5 -1 0 1 1 1 1 2 0 3 0
-1
8 2 1 -1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 4 0 5 1 7 0
5
The deletion process in the first example is as follows (see the picture below, the vertices with ci=1ci=1 are in yellow):
- first you will delete the vertex 11, because it does not respect ancestors and all its children (the vertex 22) do not respect it, and 11 is the smallest index among such vertices;
- the vertex 22 will be connected with the vertex 33 after deletion;
- then you will delete the vertex 22, because it does not respect ancestors and all its children (the only vertex 44) do not respect it;
- the vertex 44 will be connected with the vertex 33;
- then you will delete the vertex 44, because it does not respect ancestors and all its children (there are none) do not respect it (vacuous truth);
- you will just delete the vertex 44;
- there are no more vertices to delete.
In the second example you don't need to delete any vertex:
- vertices 22 and 33 have children that respect them;
- vertices 44 and 55 respect ancestors.

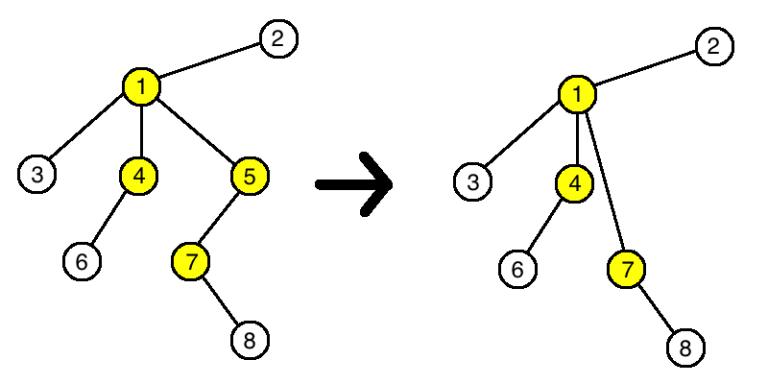
In the third example the tree will change this way:
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 100;
struct node
{
int to, dist;
node(int to=0,int dist=0):to(to),dist(dist){}
};
vector<node>vec[maxn];
int cnt=0,a[maxn];
int dfs(int s,int d)
{
int flag = 1;
int len = vec[s].size();
// if (len == 0 && d) return 1;
// if (len == 0 && !d) return 0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if (dfs(vec[s][i].to, vec[s][i].dist) == 0) flag = 0;
}
if (d)
{
//printf("%d %d %d
",cnt, s, d);
if(flag) a[cnt++] = s;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int root = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int b, x;
cin >> b >> x;
if (b == -1) root = i;
else
{
vec[b].push_back(node(i, x));
}
}
cnt = 0;
int ans=dfs(root,0);
// printf("cnt=%d
", cnt);
sort(a, a+cnt);
if(cnt==0)
{
printf("-1
");
return 0;
}
for(int i=0;i<cnt-1;i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("%d
", a[cnt - 1]);
return 0;
}