1. 本周学习总结
1.1 面向对象学习暂告一段落,请使用思维导图,以封装、继承、多态为核心概念画一张思维导图或相关笔记,对面向对象思想进行一个总结。
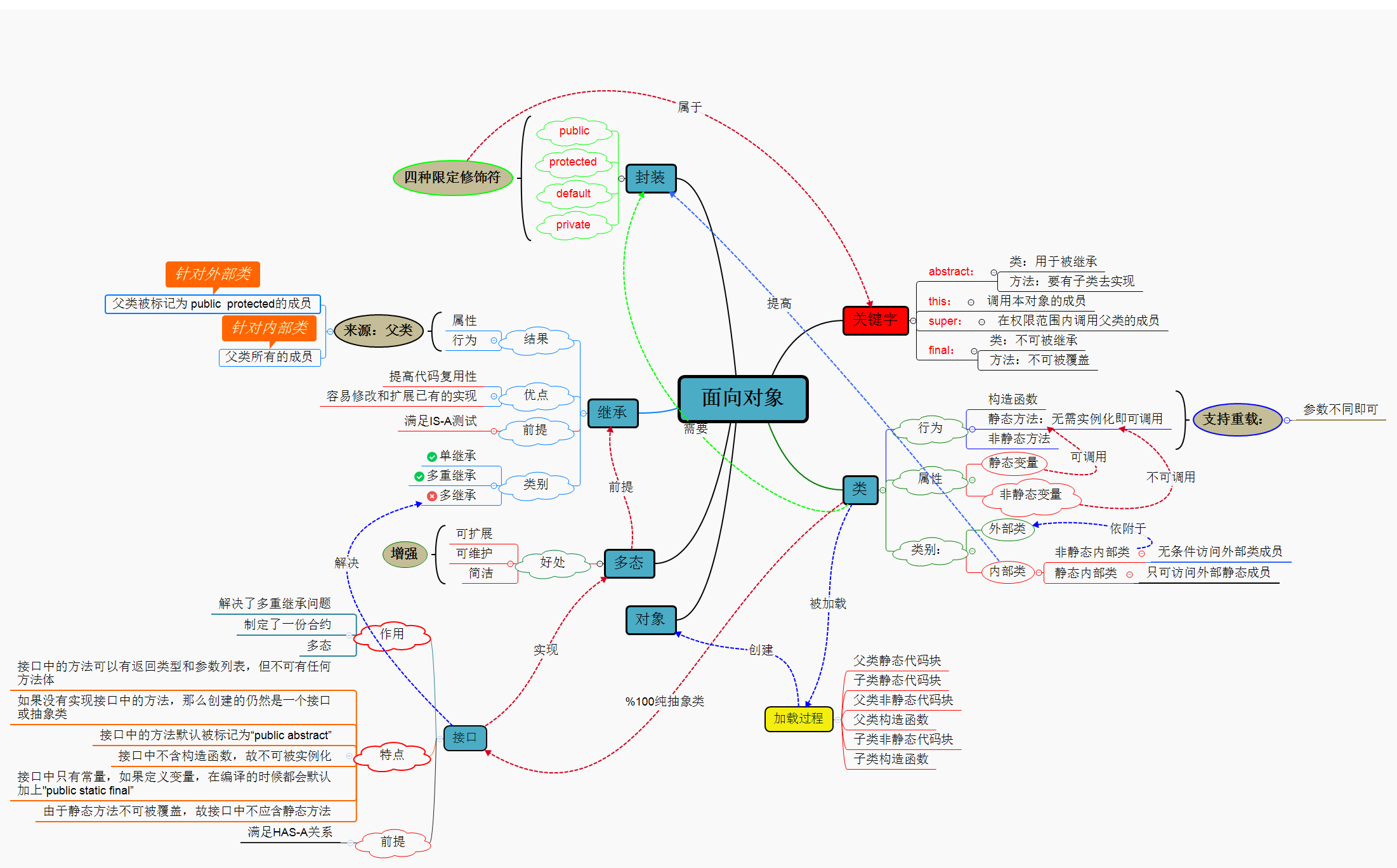
2. 书面作业
1. clone方法
1.1 在test1包中编写Employee类,在test2包中新建一个Test类,并在其main中新建test1包中的Employee的对象,然后使用clone方法克隆一个新对象,能否成功?为什么?
Object类源代码:

分析:不能成功。查看Object类中clone方法源代码可以发现,该方法被修饰为protected,Employee类继承自Object含有Object的clone方法,故只能在test1包中实现对Employee的克隆。
解决:在Employee中覆盖clone方法,并将方法的限定修饰符protected改为public。
补充native关键字:引自jiakw_1981博客
1.2 如果要为自定义的类覆盖clone方法,需注意什么?
-
被克隆的类需实现Cloneable接口。
-
使用
super.clone()调用Object中的的clone方法时,只是实现浅克隆。 -
可根据需要提高方法的访问权限,但不可降低。
-
安全起见,若被克隆的对象含有引用类型的变量时,最好实现深度克隆。
1.3 Object对象中的toString, equals, hashCode方法都使用public修饰,而clone方法却被protected修饰,请尝试解释原因。为什么不声明为public呢?
分析:在Object中clone方法实现的是浅克隆且被标记为protected也就意味着只能在java.lang包中或object的子类中访问该方法,object类本身没有实现Cloneable接口,故我们不能对Object类的对象进行克隆,这是出于安全性的考虑,而Object是终极父类,任何一个类只要实现Cloneable接口通过super.clone()调用Object的clone方法就可进行浅克隆,往往我们会根据实际情况对clone进行覆盖,我们知道子类覆盖父类的方法时不能小于父类方法的访问权限,如果Object中的clone标记为public则其子类只能用public限定该方法的作用域,也就意味着我们可以在外部对一个含有引用类型成员变量的类进行克隆,如果克隆为浅克隆,则就可以在外部对数据进行修改,这是极不安全的。
2. 内部类
2.1 使用匿名类与Lambda表达式改写题集面向对象2-进阶-多态接口内部类的题目7-2。请贴图关键代码与运行结果,请在运行结果中出现你的学号与姓名。
关键代码:
Arrays.sort(personList,(o1,o2)->o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()));
Arrays.sort(personList,(o1,o2)->o1.getAge()-o2.getAge());
运行结果:

2.2. 分析下列代码,回答shapeComparator所指向的对象与Comparator接口有什么关系?
Comparator<Shape> shapeComparator = new Comparator<Shape>() { @Override
public int compare(Shape o1, Shape o2) { //你的代码 } };
分析: shapeComparator所指向的对象实现了Comparator接口,重写了compare方法。
2.3 题集:6-1(匿名内部类)实验总结。你觉得使用匿名内部类有什么好处?
总结: 根据题目要求,对于ActionListener接口中的某一功能,实现一次即可,若为了只需实现一次的功能而再创建一个实现ActionListener的类,就会让我们的代码看起来非常冗余,此时使用内部类不仅可以提高代码的简洁性,也提高了封装性。
3. PTA实验总结
3.1 PTA(自定义接口)。并回答:相比较不写接口,直接写一个类包含IntegerStack相应的方法来说,定义IntegerStack接口,然后定义其实现类这种方式有什么好处?
分析:接口就是制定了一份共有协议,一来方便多态的使用,二来可将某一功能模块抽象出来,方便不同环境下进行使用。正如上篇所讲cat和dog都具有宠物行为这相当于制定了一个规则,即cat,dog都是宠物,但是其宠物行为的具体表现可以不同。
3.2 PTA(静态内部类)。并回答:你觉得什么时候应该使用静态内部类?静态内部类与内部类有什么区别?
分析:回答这个问题之前我们先想想为什么成员内部类可以无限制的访问外部类的成员?我们都知道成员内部类依附于外部类而存在,也就是说要想创建出成员内部类实例得先存在一个外部类实例,那为什么成员内部类可以无限制访问外部类的成员呢?那是因为在创建成员内部类实例的时候,编译器默认给其加了一个外部类的引用。静态内部类是不依附与外部类的,也就是说就算没有外部类的实例我们照样可以创建出静态内部类实例,创建静态内部类的时候编译器可没有办法给我们一个外部类的引用,因为外部类存不存在还不知道,怎么能给出引用呢。说了这么多,大概总结一下,如果内部类需要对外部类非静态成员进行访问的话,就不能将其声明为静态内部类,否则还是将其声明为静态内部类比较好,不然一大堆的对外部类的引用也蛮耗费空间的。
3.3 PTA(继承覆盖综合练习-Person、Student、Employee、Company)。并回答:使用Collections.sort对引用类型数组进行排序需要有一个什么前提条件?
分析:这道题一直是格式错误,很无奈。查看相关源代码可以发现,要想使用该方法进行排序则必须要有一个实现Comparator的对象。
4.大作业-继续完善(尝试使用接口改造你们的系统)
参考Case-StudentDao.zip案例
假设在不同的实现中,购物车里的商品有的是存放在ArrayList,有的是存放在数组中。
4.1 现在希望将系统中购物车的操作抽象到相应的DAO接口。
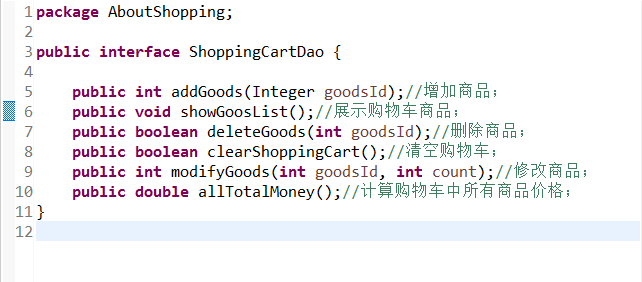
4.2 为该接口定义至少两个实现(如数组、列表、文件)。截图自己负责部分的关键代码,要求出现名字与学号。
Map:
package AboutShopping;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
/**
*
* @author 周文华
*
*/
public class ShoppingCartMap implements ShoppingCartDao{
private Map<Integer, GoodsItem> goodsList = new TreeMap<Integer, GoodsItem>();
// 添加商品到购物车
public int addGoods(Integer goodsId) {
boolean b = Storage.storageGoodsList.containsKey(goodsId);
if (b == true) {
GoodsItem storageGoodsItem = Storage.storageGoodsList.get(goodsId);
if (goodsList.containsKey(goodsId)) {
if (goodsList.get(goodsId).getCount() < storageGoodsItem.getCount()) {
GoodsItem temp = goodsList.get(goodsId);
temp.setCount(temp.getCount() + 1);
return 1;
} else
return 0;
} else {
goodsList.put(goodsId, new GoodsItem(storageGoodsItem.getGood(), 1));
return 1;
}
} else {
return -1;
}
}
// 展示购物车内容
public void showGoosList() {
Collection<GoodsItem> goodsItems = goodsList.values();
Iterator<GoodsItem> iterator = goodsItems.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
GoodsItem goodsItem = iterator.next();
Goods goods = goodsItem.getGood();
int goodsId = goods.getGoodId();
int stock = Storage.storageGoodsList.get(goodsId).getCount();
System.out.println(String.format("GoodsId:%-4dGoodsName:%-10sGoodCategory:%-10sGoodsCount:%d/%-4dTotalMoney:%-5.3f元",
goods.getGoodId(), goods.getGoodName(), goods.getGoodCategory(),goodsItem.getCount(), stock, goodsItem.totalMoney()));
}
}
// 删除购物车中的商品
public boolean deleteGoods(int goodsId) {
if (goodsList.containsKey(goodsId)) {
goodsList.remove(goodsId);
return true;
} else
return false;
}
// 清空购物车
public boolean clearShoppingCart() {
goodsList.clear();
return goodsList.isEmpty();
}
// 对购物车中的商品进行修改
public int modifyGoods(int goodsId, int count) {
if (goodsList.containsKey(goodsId)) {
if (count > 0 && count <= Storage.storageGoodsList.get(goodsId).getCount()) {
GoodsItem goodsItem = goodsList.get(goodsId);
goodsItem.setCount(count);
return 1;
}
if (count == 0) {
deleteGoods(goodsId);
return 1;
}
if (count > Storage.storageGoodsList.get(goodsId).getCount())
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
// 计算购物车中所有商品的总价
public double allTotalMoney() {
double allmoney = 0;
Collection<GoodsItem> goodsItems = goodsList.values();
Iterator<GoodsItem> itrator = goodsItems.iterator();
while (itrator.hasNext()) {
GoodsItem goodsItem = itrator.next();
double money = goodsItem.totalMoney();
allmoney += money;
}
return allmoney;
}
}
List:
package AboutShopping;
import java.util.*;
/**
*
* @author 周文华
*
*/
public class ShoppingCartList implements ShoppingCartDao {
private List<GoodsItem> goodsList = new ArrayList<GoodsItem>();
@Override
public int addGoods(Integer goodsId) {
boolean b = Storage.storageGoodsList.containsKey(goodsId);
if (b) {
int flag = 0;
Goods goods=null;
GoodsItem cartGoodsItem = null;
GoodsItem storageGoodsItem = Storage.storageGoodsList.get(goodsId);
for (int i = 0; i < goodsList.size(); i++) {
cartGoodsItem = goodsList.get(i);
goods = cartGoodsItem.getGood();
if (goods.getGoodId().equals(goodsId)) {
flag = 1;
}
}
if (flag == 0) {
goodsList.add(new GoodsItem(storageGoodsItem.getGood(), 1));
return 1;
} else {
if (cartGoodsItem.getCount() < storageGoodsItem.getCount()) {
cartGoodsItem.setCount(cartGoodsItem.getCount() + 1);
return 1;// 成功添加。
} else
return 0;// 库存不足
}
} else
return -1;// 仓库没有该商品
}
@Override
public void showGoosList() {
Iterator<GoodsItem> iterator = goodsList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
GoodsItem goodsItem = iterator.next();
Goods goods = goodsItem.getGood();
int goodsId = goods.getGoodId();
int stock = Storage.storageGoodsList.get(goodsId).getCount();
System.out.println(
String.format("GoodsId:%-4dGoodsName:%-10sGoodCategory:%-10sGoodsCount:%d/%-4dTotalMoney:%-5.3f元",
goods.getGoodId(), goods.getGoodName(), goods.getGoodCategory(), goodsItem.getCount(),
stock, goodsItem.totalMoney()));
}
}
@Override
public boolean deleteGoods(int goodsId) {
int flag=0;
int index = 0;
GoodsItem goodsItem=null;
Goods goods=null;
for(int i=0;i<goodsList.size();i++) {
goodsItem=goodsList.get(i);
goods=goodsItem.getGood();
if(goods.getGoodId().equals(goodsId)) {
flag=1;
index=i;
}
}
if(flag==0) {
return false;//购物车不含该商品;
}else {
goodsList.remove(index);
return true;
}
}
@Override
public boolean clearShoppingCart() {
goodsList.clear();
return goodsList.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public int modifyGoods(int goodsId, int count) {
int flag=0;
int index = 0;
GoodsItem goodsItem=null;
Goods goods=null;
for(int i=0;i<goodsList.size();i++) {
goodsItem=goodsList.get(i);
goods=goodsItem.getGood();
if(goods.getGoodId().equals(goodsId)) {
flag=1;
index=i;
}
}
if(flag!=0) {
if(count>0&&count<=Storage.storageGoodsList.get(goodsId).getCount()) {
goodsItem=goodsList.get(index);
goodsItem.setCount(count);
return 1;//修改成功
}
if (count == 0) {
deleteGoods(goodsId);
return 1;
}
if (count > Storage.storageGoodsList.get(goodsId).getCount())
return 0;//库存不足
}
return -1;////购物车不含该商品;
}
@Override
public double allTotalMoney() {
double allMoney = 0;
Iterator iterator = goodsList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
GoodsItem goodsItem = (GoodsItem) iterator.next();
double money = goodsItem.totalMoney();
allMoney += money;
}
return allMoney;
}
}
4.3 给出你们的Main程序,说明定义DAO接口的好处。
弄图形界面把代码改的有点乱,这只给出了一个使用List测试。
package AboutShopping;
import java.util.*;
public class ShoppingCartListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShoppingCartList cart = new ShoppingCartList();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Storage.showStorage();
System.out.println("菜单");
System.out.println("1.添加商品");
System.out.println("2.修改商品");
System.out.println("3.删除商品");
System.out.println("4.清空购物车");
System.out.println("5.查看购物车");
System.out.println("0.退出程序");
out: while (true) {
String input = sc.next();
switch (input) {
case "1":
System.out.println("请输入商品Id");
int result1 = cart.addGoods(sc.nextInt());
if (result1 == 1)
System.out.println("成功添加");
else if (result1 == 0)
System.out.println("库存不足");
else
System.out.println("仓库不存在该商品");
break;
case "2":
System.out.println("请输入商品Id及数量");
int result2 = cart.modifyGoods(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt());
if (result2 == 1)
System.out.println("修改成功");
else if (result2 == 0)
System.out.println("库存不足");
else
System.out.println("购物车不存在该商品");
break;
case "3":
System.out.println("请输入商品Id");
boolean result3 = cart.deleteGoods(sc.nextInt());
if (result3)
System.out.println("删除成功");
else
System.out.println("购物车不存在该商品");
break;
case "4":
boolean result4 = cart.clearShoppingCart();
if (result4)
System.out.println("购物车已清空");
else
System.out.println("清空失败");
break;
case "5":
cart.showGoosList();
System.out.println(cart.allTotalMoney());
break;
default:
break out;
}
}
}
}
使用DAO优点: DAO接口就是制定了一份协议,只要遵照这个协议,其内部实现的细节可以不同。
5. 代码阅读:PersonTest.java(abstract、多态、super)
5.1 画出类的继承关系
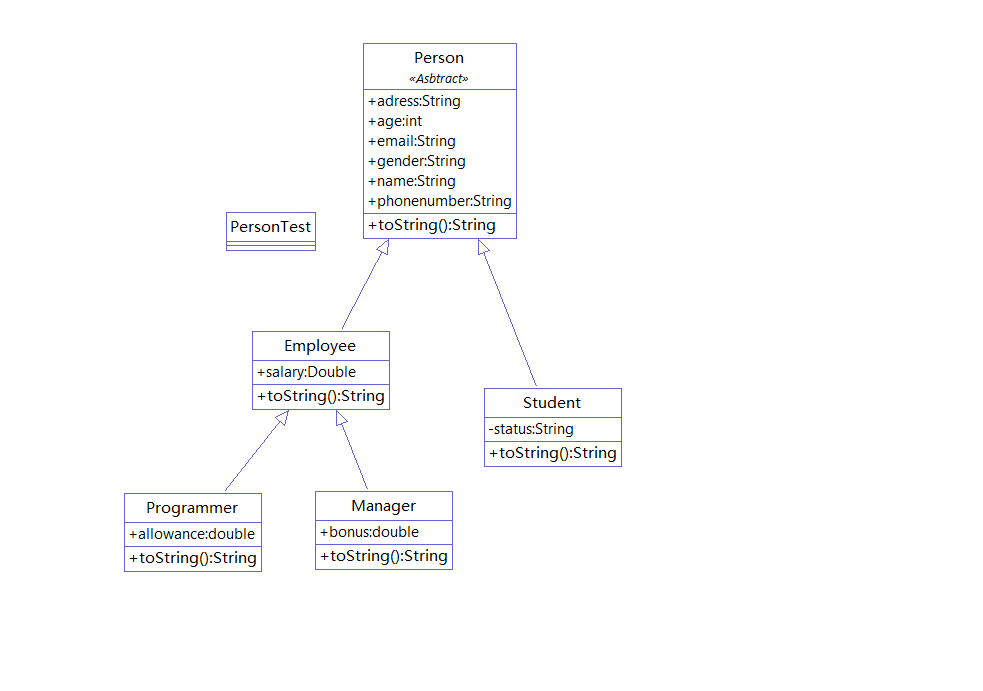
5.2 main函数的代码实现什么功能?
分析:对四个都继承自Person类的对象进行排序。
5.3 如果将子类中的super构造函数去掉行不行?
分析:答案当然是不可以!还是要强调一遍构造函数不可被继承,只是编译器在子类构造函数第一行中默认的加了super()才得以调用父类的构造函数,要注意的是编译器默认加的是无参的构造函数,若父类中没有无参构造函数,则需显式的调用父类的构造函数。
5.4 PersonTest.java中哪里体现了多态?
看代码:
Person[] peoples = new Person[4];
peoples[0] = new Employee("zhang", "136", "1360", "1360@mail.com", 21, "female", 1000.0);
peoples[1] = new Student("wang", "110", "15959", "15959@163.com", 18, "male", "1");
peoples[2] = new Programmer("Gates", "usa", "911", "911@com", 59, "male", 100000.0, 50000.0);
peoples[3] = new Manager("Clark", "GE", "111", "111@mail.com", 10, "mail", 90000.1, 12000.3);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
if (peoples[j].getAge() > peoples[j + 1].getAge()) {
Person temp = peoples[j];
peoples[j] = peoples[j + 1];
peoples[j + 1] = temp;
}
分析:返回5.1查看类图可以知道Person类是继承层次最上层的,当我们使用Person类的数组进行存储其继承层次下方的子类时就是多态的体现。
3.码云及PTA
题集:jmu-Java-04-面向对象2-进阶-多态接口内部类
3.1. 码云代码提交记录
3.2 截图PTA题集完成情况图
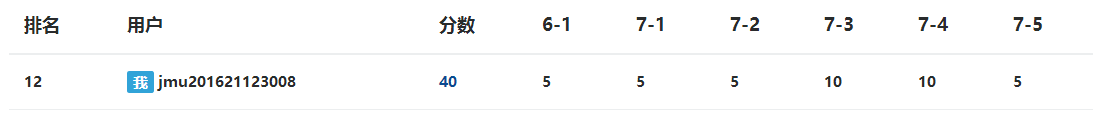


3.3 统计本周完成的代码量
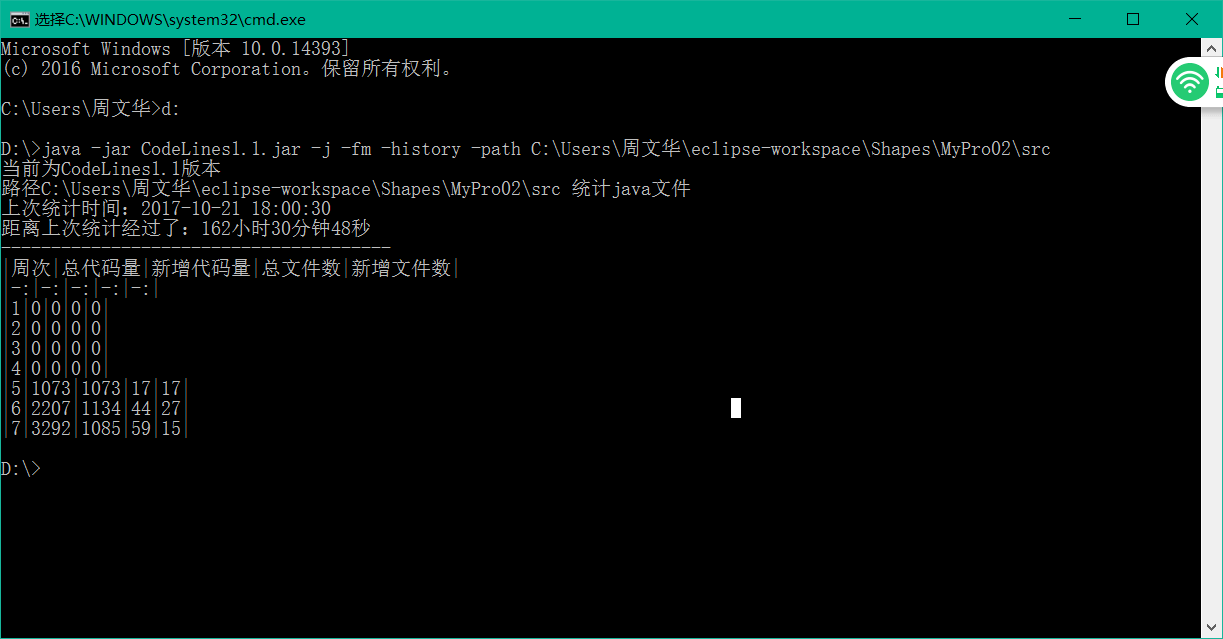
| 周次 | 总代码量 | 新增文件代码量 | 总文件数 | 新增文件数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 665 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| 2 | 1705 | 23 | 23 | 23 |
| 3 | 1834 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| 4 | 1073 | 1073 | 17 | 17 |
| 5 | 1073 | 1073 | 17 | 17 |
| 6 | 2207 | 1134 | 44 | 27 |
| 7 | 3292 | 1085 | 59 | 15 |