原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water-ii/?tab=Description
题目:
Given an m x n matrix of positive integers representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note:
Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example:
Given the following 3x6 height map: [ [1,4,3,1,3,2], [3,2,1,3,2,4], [2,3,3,2,3,1] ]
Return 4.
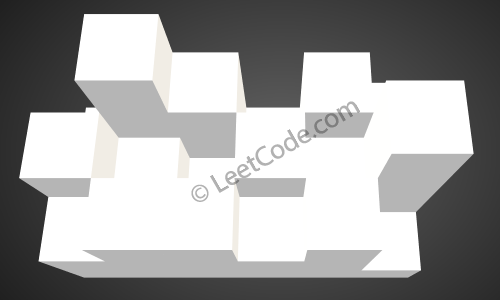
The above image represents the elevation map [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] before the rain.
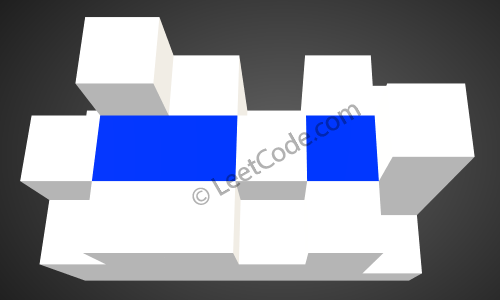
After the rain, water are trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
题解:
是Trapping Rain Water进阶题目.
从四周开始每次找边界中最小的值,这里利用minHeap, minHeap里需要保存坐标和高度组合的点, 然后向内扩展。
若最小边界高度大于当前高度,则求高度差为蓄水量,并把当前坐标配上原高度放回minHeap中.
若最小边界高度小于当前高度,则改点不存水,把当前坐标配上当前高度放回minHeap中.
Time Complexity: O(mn * log(m+n)).
m = heightMap.length, n = heightMap[0].length. 四周边界加进minHeap用时O((m+n) * log(m+n)). 中间部分用时O(m*n*log(m+n)), 每个点都有一次入minHeap和一次出minHeap.
Space: O(m*n). boolean array size.
AC Java:
1 public class Solution { 2 public int trapRainWater(int[][] heightMap) { 3 if(heightMap == null || heightMap.length < 3 || heightMap[0].length < 3){ 4 return 0; 5 } 6 int m = heightMap.length; 7 int n = heightMap[0].length; 8 boolean [][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; 9 PriorityQueue<Cell> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<Cell>(1, new Comparator<Cell>(){ 10 public int compare(Cell c1, Cell c2){ 11 return c1.height - c2.height; 12 } 13 }); 14 15 for(int i = 0; i<m; i++){ 16 visited[i][0] = true; 17 visited[i][n-1] = true; 18 minHeap.offer(new Cell(i, 0, heightMap[i][0])); 19 minHeap.offer(new Cell(i, n-1, heightMap[i][n-1])); 20 } 21 22 for(int j = 0; j<n; j++){ 23 visited[0][j] = true; 24 visited[m-1][j] = true; 25 minHeap.offer(new Cell(0, j, heightMap[0][j])); 26 minHeap.offer(new Cell(m-1, j, heightMap[m-1][j])); 27 } 28 29 int res = 0; 30 int [][] dirs = new int [][]{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}; 31 while(!minHeap.isEmpty()){ 32 Cell c = minHeap.poll(); 33 for(int [] dir : dirs){ 34 int x = c.i+dir[0]; 35 int y = c.j+dir[1]; 36 if(x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n && !visited[x][y]){ 37 visited[x][y] = true; 38 res += Math.max(c.height, heightMap[x][y]) - heightMap[x][y]; 39 minHeap.offer(new Cell(x, y, Math.max(c.height, heightMap[x][y]))); 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 return res; 44 } 45 } 46 47 class Cell{ 48 int i, j, height; 49 public Cell(int i, int j, int height){ 50 this.i = i; 51 this.j = j; 52 this.height = height; 53 } 54 }