03-树1 树的同构(25 point(s))
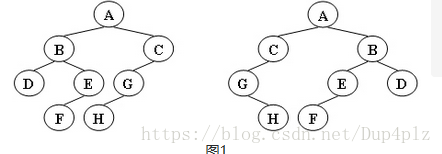
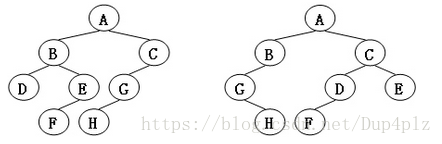
给定两棵树T1和T2。如果T1可以通过若干次左右孩子互换就变成T2,则我们称两棵树是“同构”的。例如图1给出的两棵树就是同构的,因为我们把其中一棵树的结点A、B、G的左右孩子互换后,就得到另外一棵树。而图2就不是同构的。
图1
图2
现给定两棵树,请你判断它们是否是同构的。
输入格式:
输入给出2棵二叉树树的信息。对于每棵树,首先在一行中给出一个非负整数N (≤10),即该树的结点数(此时假设结点从0到N−1编号);随后N行,第i行对应编号第i个结点,给出该结点中存储的1个英文大写字母、其左孩子结点的编号、右孩子结点的编号。如果孩子结点为空,则在相应位置上给出“-”。给出的数据间用一个空格分隔。注意:题目保证每个结点中存储的字母是不同的。
输出格式:
如果两棵树是同构的,输出“Yes”,否则输出“No”。
输入样例1(对应图1):
8
A 1 2
B 3 4
C 5 -
D - -
E 6 -
G 7 -
F - -
H - -
8
G - 4
B 7 6
F - -
A 5 1
H - -
C 0 -
D - -
E 2 -
输出样例1:
Yes
输入样例2(对应图2):
8
B 5 7
F - -
A 0 3
C 6 -
H - -
D - -
G 4 -
E 1 -
8
D 6 -
B 5 -
E - -
H - -
C 0 2
G - 3
F - -
A 1 4
输出样例2:
No
思路
因为 题目有一个限制条件 就是 每个结点存储的字母是不同的
所以 我们可以 以 字母 作为一个标记
意思就是
我们可以层序遍历 把每个结点的 字母 压入 字符串
最后比较 两个字符串 是否相同
就可以了
什么意思呢
就是 字母 是有一个 字典序的 然后 树的 同构的 定义 呢 就是 可以互换 左右儿子
那么 我们对于 每个 根节点 如果 同时存在 左右儿子 就将 字典序 小的 先 压入 队列 和 写入 字符串
这样 我们就 避免了 左右儿子的概念 如果 树 的同构的 那么最后得到的字符串 就是相同的
比如
左边 这棵树
得到的字符串 就是
ABCDEGFH
右边 这棵 树 得到的
ABCDEGFH
左边这棵树
ABCDEGFH
右边
ABCGDEHF
AC代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <climits>
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <numeric>
#include <sstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <limits>
#define CLR(a) memset(a, 0, sizeof(a))
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair <int, int> pii;
typedef pair <ll, ll> pll;
typedef pair<string, int> psi;
typedef pair<string, string> pss;
const double PI = 3.14159265358979323846264338327;
const double E = exp(1);
const double eps = 1e-30;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
struct Node
{
char c;
int l, r;
}tree[2][10];
string s[2];
queue <int> q;
void bfs(int index)
{
int len = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
int num = q.front();
q.pop();
s[index] += tree[index][num].c;
if (tree[index][num].l != -1 && tree[index][num].r != -1)
{
if (tree[index][tree[index][num].l].c < tree[index][tree[index][num].r].c)
{
q.push(tree[index][num].l);
q.push(tree[index][num].r);
}
else
{
q.push(tree[index][num].r);
q.push(tree[index][num].l);
}
}
else if (tree[index][num].l != -1)
q.push(tree[index][num].l);
else if (tree[index][num].r != -1)
q.push(tree[index][num].r);
}
while (q.size())
bfs(index);
}
int main()
{
int n[2];
map <int, int> m;
char a, b, c;
int root[2];
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++)
{
m.clear();
scanf("%d", &n[k]);
for (int i = 0; i < n[k]; i++)
{
scanf(" %c %c %c", &a, &b, &c);
tree[k][i].c = a;
if (isdigit(b))
{
tree[k][i].l = b - '0';
m[b - '0'] = 1;
}
else
tree[k][i].l = -1;
if (isdigit(c))
{
tree[k][i].r = c - '0';
m[c - '0'] = 1;
}
else
tree[k][i].r = -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n[k]; i++)
{
if (m[i] == 0)
{
root[k] = i;
break;
}
}
}
if (n[0] && n[1])
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
s[i].clear();
while (!q.empty())
q.pop();
q.push(root[i]);
bfs(i);
}
if (s[0] == s[1])
printf("Yes
");
else
printf("No
");
}
else
printf("Yes
");
}