通过上篇博客知道,二叉搜索树的局限在于不能完成自平衡,从而导致不能一直保持高性能。
AVL树则定义了平衡因子绝对值不能大于1,使二叉搜索树达到了严格的高度平衡。
还有一种能自我调整的二叉搜索树,
红黑树 : 通过标记节点的颜色(红/黑),使其拥有自平衡的二叉搜索树。
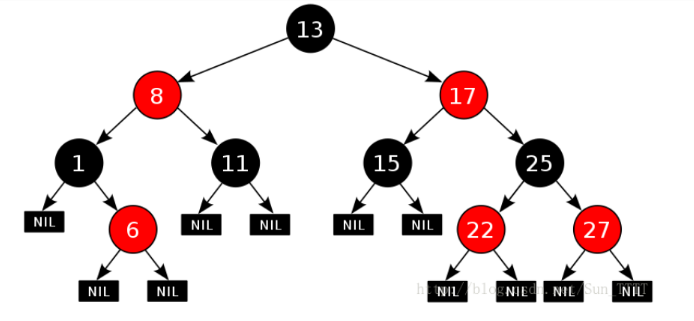
红黑树性质 :
- 性质1:每个节点要么是黑色,要么是红色。
- 性质2:根节点是黑色。
- 性质3:每个叶子节点(NIL)是黑色。
- 性质4:每个红色结点的两个子结点一定都是黑色。
- 性质5:所有路径都包含数量相同的黑结点
这些约束强制了红黑树的关键性质: 红黑树没有一条路径会比其他路径的两倍长(同一起点)。所以这个树大致上是平衡的,不会像二叉搜索树出现极端情况。
是性质4和5导致路径上确保了这个结果。最短的路径只有黑色节点,最长路径有交替的红色和黑色节点。因为所有的路径黑色节点数量相同,所以没有路径能多于任何其他路径的两倍长。
红黑树节点定义:
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK,
};
template<class K,class V>
class RBtreeNode
{
RBtree<K,V>* _left;
RBtree<K,V>* _right;
RBtree<K,V>* _parent;
pair<K,V> _kv;
Colour _col;
};
template<class K,class V>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBtreeNode<K,V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K,V>& kv);
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
}
红黑树的插入:
在结点插入后,需要遵循红黑树性质
新结点默认是红色,所以需要判断红黑树的性质是否遭到破坏(插入节点与父亲节点都为红色,违反性质4)
有以下三种情况:
1.u为红 ---> p,u-->黑 g-->红 cur=g,向上调整
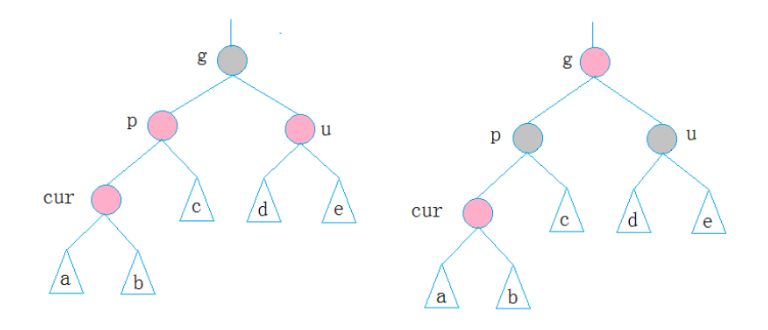
2.cur和p在g的同一边,u不存在/为黑 --- cur,p在g左--- 左左 : g右旋, g--->红, p-->黑
cur,p在g右 --- 右右 : g左旋, g--->红,p--->黑

3.cur和p不在g的同一边,u不存在/为黑 --- p在g左,cur在p右--- 左右: p左旋
p在g右,cur在p左--- 右左: p右旋
--->变成情况2处理

插入结点代码:
bool Insert(const pair<K,V> _kv)
{
//插入结点
if(root == nullptr)
{
root=new Node(kv);
root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = root;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->kv.first < kv.first)
else if(cur->kv.first > kv.first)
else
return false;
}
cur = new Node(kv);
cur->_col = RED;
//父节点连接插入的结点
if(parent->kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent->_right = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
}
else
{
...
}
//颜色调整
//红黑树遭到破坏: 红红相连
while(parent && parent->_col==RED)
{
Node* g = parent->_parent;
//叔叔在右边
if(parent == g->_left)
{
Node* u = g->_right;
//叔叔为红,变色调整
if(u && u->_col==RED)
{
parent->_col = BLACK;
u->_col = BLACK;
g->_col = RED;
cur = g;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//叔叔非红,旋转调整
else
{
//父亲和孩子没有对齐,左旋变齐
if(cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(parent);
swap(parent,cur);
}
//对齐,右旋并调色,完成调整
RotateR(g);
parent->_col = BLACK;
g->_col = RED;
break;
}//end of 叔非红处理
}
//叔叔在左边
else
{
//....
}
}//end of 红红相连
//按规定将其根置为黑 : 防止根为cur情况
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
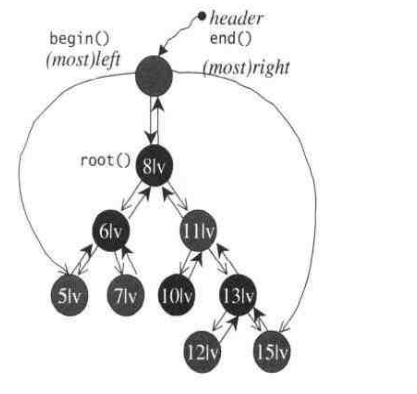
STL标准的红黑树是这样的, 根的父亲不是nullptr而是header,使红黑树构成了闭环.
header->_left = rbtree.begin(), header->_right = rbtree.end(), header->_parent = root.
利用性质验证红黑树代码:
//判断是否为红黑树
bool isRBTree()
{
pNode root = _header->_parent;
if(root == nullptr) return true;
//1.根是否黑色
if(root->_color == RED)
{
cout<<"根节点必须是黑色!"<<endl;
return false;
}
//2.每条路径黑色个数相同?
//可以任意遍历一条(最右)路径获取黑色节点数量
pNode cur = root;
int black_count = 0;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_color == BLACK)
++black_count;
cur = cur->_right;
}
int k = 0;
return _isRBTree(root,k,black_count);
}
//看每一条路径是否和基准值相同
bool _isRBTree(pNode root,int curCount,int count)
{
//终止条件: 一条路径走完
if(root==nullptr){
if(curCount != count)
{
cout<<"每个路径黑色节点个数不同"<<endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
if(root->_color == BLACK)
++curCount;
//3.没有红色连续的?
pNode parent = root->_parent;
if(parent && parent->_color == RED && root->_color == RED)
{
cout<<"有红色连续的节点"<<endl;
return fasle;
}
return _isRBTree(root->_left,curCount,count)
&& _isRBTree(root->_right,curCount,count);
}
