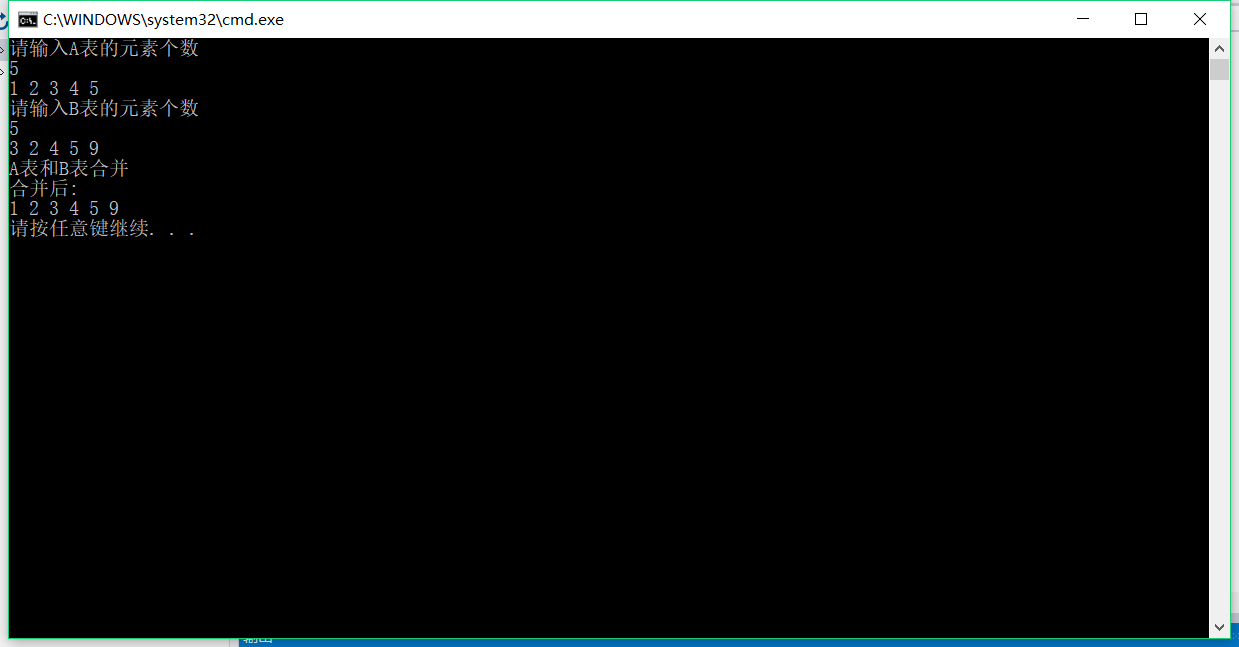
4 #include "stdafx.h" 5 #include"iostream" 6 using namespace std; 7 template <class T> 8 #define impossible 12345678 9 class List 10 { 11 private: 12 int length; 13 T *s; 14 void DestroyList(); 15 int compare(T e); 16 public: 17 List(int size); 18 List(); 19 void clearList(); 20 bool ListEmpty(); 21 void getElem(int i,T &e); 22 bool LocateElem(T e); 23 bool priorElem(T e, int &pre); 24 bool NextElem(T e, int & next); 25 bool ListInsert(int i, T e);//在指定位置插入数据 26 bool ListDelete(int i, T &e){}//数组形成的线性表,不好删除指定的元素,比较复杂,所以没有写具体的函数,如果有好的方法,可以交流一下,在评论区留下代码。 27 void ListTraverse();//用来遍历表中的元素 28 void visited(int i);//用来显示表中的元素 29 int getlength();//得到表的长度(含有用户数据的长度) 30 void Union(List &list);//没有重复元素的合并两个线性表,并且存在已经存在的一个表中 31 void mergeList(List B, List &C);//(条件:两个表已经是按照大小排好序的,然后在按照相同规则排序放入到另外一个表中 32 }; 33 34 35 template<class T> 36 void List<T>::DestroyList() 37 { 38 delete s; 39 } 40 41 template<class T> 42 int List<T>::compare(T e) 43 { 44 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) 45 { 46 if (e == s[i]) 47 { 48 return i; 49 } 50 } 51 return -1; 52 } 53 54 template<class T> 55 List<T>::List(int size) 56 { 57 s = new T[size]; 58 length = 0; 59 } 60 61 template<class T> 62 List<T>::List() 63 { 64 s = new T[100]; 65 length = 0; 66 } 67 68 69 70 template<class T> 71 void List<T>::clearList()//将线性表清空 72 { 73 length = 0; 74 } 75 76 template<class T> 77 bool List<T>::ListEmpty()//判断线性表是否为空 78 { 79 if (length == 0) 80 return true; 81 else 82 return false; 83 } 84 85 template<class T> 86 void List<T>::getElem(int i,T &e)//得到指定位置的元素 87 { 88 e = s[i]; 89 } 90 91 template<class T> 92 bool List<T>::LocateElem(T e)//元素在线性表中的位置 93 { 94 if( compare(e)!=-1) 95 return true; 96 else return false; 97 98 } 99 100 template<class T> 101 bool List<T>::priorElem(T e, int & pre)//指定元素的前驱的位置,未找到返回-1,如果是第一个元素就是它自己,则返回-2 102 { 103 if (s[0] == e) 104 { 105 pre = -2; 106 return true; 107 } 108 for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) 109 { 110 if (e == s[i]) 111 { 112 pre = i - 1; 113 return true; 114 } 115 } 116 pre = -1; 117 return false; 118 } 119 120 template<class T> 121 bool List<T>::NextElem(T e, int & next)//指定元素的后继元素的位置,未找到则next=-1,如果是最后一个元素则是-2 122 { 123 for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) 124 { 125 if (s[i] == e) 126 { 127 next = i + 1; 128 return true; 129 } 130 } 131 if (s[i] == e) 132 { 133 next = -2; 134 return true; 135 } 136 next = -1; 137 return false; 138 } 139 140 template<class T> 141 bool List<T>::ListInsert(int i, T e)//在i位置插入元素 142 { 143 s[i] = e; 144 ++length; 145 return true; 146 } 147 148 template<class T> 149 void List<T>::ListTraverse()//遍历线性表 150 { 151 152 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) 153 { 154 visited(i); 155 } 156 cout << endl; 157 } 158 159 template<class T> 160 void List<T>::visited(int i) 161 { 162 cout << s[i] << " "; 163 } 164 template<class T> 165 int List<T>::getlength() 166 { 167 return length; 168 } 169 template<class T> 170 void List<T>::Union(List & list) 171 { 172 int Len = list.getlength(); 173 int Leng = length; 174 for (int i = 0; i < Len; i++) 175 { 176 T e; 177 list.getElem(i, e); 178 if (!LocateElem(e)) 179 { 180 ListInsert(Leng++, e); 181 } 182 } 183 } 184 template<class T> 185 void List<T>::mergeList(List B, List & C) 186 { 187 int i, j, k; 188 i = j = k = 0; 189 int lenB; 190 lenB = B.getlength(); 191 T x,y;//用来接收getElem的元素 192 while (i < length&&j < lenB) 193 { 194 195 getElem(i, x); 196 B.getElem(j, y); 197 if (x > y) 198 { 199 C.ListInsert(k++, y); 200 j++; 201 } 202 else 203 { 204 C.ListInsert(k++, x); 205 i++; 206 } 207 } 208 while (i < length) 209 { 210 getElem(i, x); 211 C.ListInsert(k++, x); 212 i++; 213 } 214 while (j < lenB) 215 { 216 B.getElem(j, y); 217 C.ListInsert(k++, y); 218 j++; 219 } 220 } 221 int main() 222 { 223 List<int> A; 224 List<int> B,C; 225 cout << "请输入A表的元素个数" << endl; 226 int n; 227 cin >> n; 228 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 229 { 230 int e; 231 cin >> e; 232 A.ListInsert(i, e); 233 } 234 cout << "请输入B表的元素个数" << endl; 235 cin >> n; 236 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 237 { 238 int e; 239 cin >> e; 240 B.ListInsert(i, e); 241 } 242 243 /*A.ListTraverse(); 244 B.ListTraverse();*/ 245 246 //cout << "A表和B表合并" << endl; 247 //A.Union(B); 248 //cout << "合并后:" << endl; 249 //A.ListTraverse(); 250 251 cout << "A和B按升序方式合并" << endl; 252 A.mergeList(B, C); 253 cout << "合并后的线性表" << endl; 254 C.ListTraverse(); 255 return 0; 256 }