C#发展至今,已经从最初的1.0到了5.0版本,其进化史如下,参考了C# 5.0 IN A NUTSHEL:
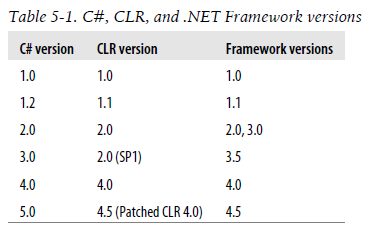
让我们来回顾一下各个版本都带来了什么:
- 1.0版本 - 基本C#语法。
- 2.0版本 - 泛型的支持,CLR进行了升级,从根本上支持了运行时泛型。
- 3.0版本 - LINQ,添加了
from/join等类SQL关键字,添加了扩展函数,添加了编译期动态类型var关键字。 - 4.0版本 - dynamic关键字,CLR进行升级,加入DLR,开始对动态进行友好的支持。同时加入动态参数、参数默认值、泛型协变等特性。
- 5.0版本-新的异步模型,新增了async/await等关键字,简化并行计算Parallel。
可以看出作为编程语言的C#已经非常强大,单随着时代的发展,C#依然在不断的前进。每一代的C#都会在语法的调整之,外带来一个新特性。从2.0的泛型、3.0的LINQ、4.0的dynamic到5.0的Async异步,每个版本的C#都有一个主导的思想,而其他细节的改进和调整则是围绕着这个主导思想给予支持。
下面我们来看下C#5.0及之前版本,异步调用方法的各种实现方法。
首先我们来看一个普通的同步方法,如下:
using System; using System.Net; namespace NoAsync { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ShowUriContent("http://www.cnblogs.com/DebugLZQ"); } static void ShowUriContent(string uri) { using (WebClient client = new WebClient()) { string text = client.DownloadString(uri); Display(text); } } static void Display(string text) { Console.WriteLine(text.Length); } } }
同步方法会造成线程的阻塞。
因此我们有了异步的方法,最早期的异步方法时Begin/End模式(其实现方法一共有四种,请参考DebugLZQ前面的博文:.NET异步编程总结----四种实现模式)。
我们用Begin/End推荐模式来封装这个同步方法以实现异步调用,如下:
using System; using System.Threading; using System.Net; namespace AsyBeginEndNoEncapsulation { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ShowUriContent("http://www.cnblogs.com/DebugLZQ");//原同步方法 ShowUriContentAsync("http://www.cnblogs.com/DebugLZQ");//封装后的异步方法 Thread.Sleep(5000); } //------进行异步封装 public delegate void ShowUriContentDelegate(string text); static void ShowUriContentAsync(string uri) { ShowUriContentDelegate showUriContentDelegate = ShowUriContent; showUriContentDelegate.BeginInvoke(uri, ShowUriContentCompleted, showUriContentDelegate); } static void ShowUriContentCompleted(IAsyncResult result) { (result.AsyncState as ShowUriContentDelegate).EndInvoke(result); } //------原同步方法 static void ShowUriContent(string uri) { using (WebClient client = new WebClient()) { string text = client.DownloadString(uri); Display(text); } } static void Display(string text) { Console.WriteLine(text.Length); } } }
最原始的封装就是这个样子。
可以利用C#新特性,如Action/Function、匿名方法、Lambda表达式等,简写(合写)如下:
using System; //using System.Collections.Generic; //using System.Linq; //using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Net; namespace AsyBeginEndNoEncapsulationSimply { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ShowUriContent("http://www.cnblogs.com/DebugLZQ");//原同步方法 ShowUriContentAsync("http://www.cnblogs.com/DebugLZQ"); //进行异步封装 ShowUriContentAsync1("http://www.cnblogs.com/DebugLZQ");//简化1:Action简化 ShowUriContentAsync2("http://www.cnblogs.com/DebugLZQ");//简化2:匿名方法简化 ShowUriContentAsync3("http://www.cnblogs.com/DebugLZQ");//简化3:Lambda简化 Thread.Sleep(50000); } //------进行异步封装 public delegate void ShowUriContentDelegate(string text); static void ShowUriContentAsync(string uri) { ShowUriContentDelegate showUriContentDelegate = ShowUriContent; showUriContentDelegate.BeginInvoke(uri, ShowUriContentCompleted, showUriContentDelegate); } static void ShowUriContentCompleted(IAsyncResult result) { (result.AsyncState as ShowUriContentDelegate).EndInvoke(result); } //------进行异步封装--简化1:Action简化 static void ShowUriContentAsync1(string uri) { Action<string> showUriContentDelegate = ShowUriContent; showUriContentDelegate.BeginInvoke(uri, ShowUriContentCompleted1, showUriContentDelegate); } static void ShowUriContentCompleted1(IAsyncResult result) { (result.AsyncState as Action<string>).EndInvoke(result); } //------简化2:匿名方法简化 static void ShowUriContentAsync2(string uri) { Action<string> showUriContentDelegate = delegate(string uri_) { using (WebClient client = new WebClient()) { string text = client.DownloadString(uri_); Display(text); } }; showUriContentDelegate.BeginInvoke(uri, delegate(IAsyncResult result) { (result.AsyncState as Action<string>).EndInvoke(result); }, showUriContentDelegate); } //------简化3:Lambda简化 static void ShowUriContentAsync3(string uri) { Action<string> showUriContentDelegate = ( uri_)=> { using (WebClient client = new WebClient()) { string text = client.DownloadString(uri_); Display(text); } }; showUriContentDelegate.BeginInvoke(uri, (result) => { (result.AsyncState as Action<string>).EndInvoke(result); }, showUriContentDelegate); } //---------------------原同步方法 static void ShowUriContent(string uri) { using (WebClient client = new WebClient()) { string text = client.DownloadString(uri); Display(text); } } static void Display(string text) { Console.WriteLine(text.Length); } } }
以上是我们最原始的实现方法,及利用新特性的各种变种写法。
但是WebClient作为WebRequest的高层封装,.NET已经帮我们把这个异步模式给封装了(也就是说有些同步方法不需要我们自己进行封装了)。
因此我们也可以如下:
using System; using System.Threading; using System.Net; namespace AsyncBeginEndEncapsulation { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ShowUriContent("http://www.cnblogs.com/DebugLZQ"); ShowUriContent2("http://www.cnblogs.com/DebugLZQ"); Console.WriteLine("Main thread continue..."); Thread.Sleep(5000); } static void ShowUriContent(string uri) { using (WebClient client = new WebClient()) { client.DownloadStringCompleted += new DownloadStringCompletedEventHandler(Display); client.DownloadStringAsync(new Uri(uri)); } } static void Display(object sender, DownloadStringCompletedEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine(e.Result.Length); } //-------简化的写法 static void ShowUriContent2(string uri) { using (WebClient client = new WebClient()) { client.DownloadStringCompleted += (s, e) => { Console.WriteLine(e.Result.Length); }; client.DownloadStringAsync(new Uri(uri)); } } } }
从上面.NET对Begin/End模式的主动封装可以看出,其目的是为了简化异步方法的调用,最终的目的是让异步方法调用像我们最熟悉的同步方法调用那么简单。
C#5.0引入了两个关键字async、await以提供一种更为简洁的异步方法调用模式。
我们实现如下(控制台入口点Main方法无法标记为async,因此我们用Winform程序演示):
using System; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Net; namespace AsyncAwaitWinForm { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private async void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { int length = await ShowUriContentAsyncAwait("http://www.cnblogs.com/DebugLZQ"); textBox1.Text = length.ToString(); } // async Task<int> ShowUriContentAsyncAwait(string uri) { using (WebClient client = new WebClient()) { string text = client.DownloadString(uri); return text.Length; } } } }
需要说明的是async、await需要:Visual Studio 2010 + SP1+Visual Studio Async CTP,或是Visual Studio 2012.
Update: 关于 Parallel---Task,请参考DebugLZQ后续博文:Task and Parallel
update:关于Async await详细,请参考DebugLZQ后续博文:
async wait
以上所有示例程序均由DebugLZQ动手编写,可以正常运行,其结果显而易见,因此没有附上运行截图。
科技不断向前发展,期待以后版本的C#6,7,8,X....带来的更多精彩~
把自己的理解分享给大家,共同交流进步,认识不断提升~
Update: Read more
Difference between Delegate.BeginInvoke and Thread.Start
Differences in the different ways to make concurrent programs