网上学习资料:https://2d.hep.com.cn/1865445/9
numpy库内容:

| 函数 | 描述 |
| np.array([x,y,z],dtype=int) | 从Python列表和元组创造数组 |
| np.arange(x,y,i) | 创建一个从x到y,步长为 i 的数组 |
| np.linspace(x,y,n) | 创建一个从x到y,等分成 n 个元素的数组 |
| np.indices((m,n)) | 创建一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 |
| np.random.rand(m,n) | 创建一个 m 行 n 列的随机数组 |
| np.ones((m,n),dtype) | 创建一个 m 行 n 列全为 1 的数组,dtype是数据类型 |
| np.empty((m,n),dtype) | 创建一个 m 行 n 列全为0的数组,dtype是数据类型 |
实例(教材):
1 #e17.1HandDrawPic.py 2 from PIL import Image 3 import numpy as np 4 vec_el = np.pi/2.2 # 光源的俯视角度,弧度值 5 vec_az = np.pi/4. # 光源的方位角度,弧度值 6 depth = 10. # (0-100) 7 im = Image.open('fcity.jpg').convert('L') 8 a = np.asarray(im).astype('float') 9 grad = np.gradient(a) #取图像灰度的梯度值 10 grad_x, grad_y = grad #分别取横纵图像梯度值 11 grad_x = grad_x*depth/100. 12 grad_y = grad_y*depth/100. 13 dx = np.cos(vec_el)*np.cos(vec_az) #光源对x 轴的影响 14 dy = np.cos(vec_el)*np.sin(vec_az) #光源对y 轴的影响 15 dz = np.sin(vec_el) #光源对z 轴的影响 16 A = np.sqrt(grad_x**2 + grad_y**2 + 1.) 17 uni_x = grad_x/A 18 uni_y = grad_y/A 19 uni_z = 1./A 20 a2 = 255*(dx*uni_x + dy*uni_y + dz*uni_z) #光源归一化 21 a2 = a2.clip(0,255) 22 im2 = Image.fromarray(a2.astype('uint8')) #重构图像 23 im2.save('fcityHandDraw.jpg
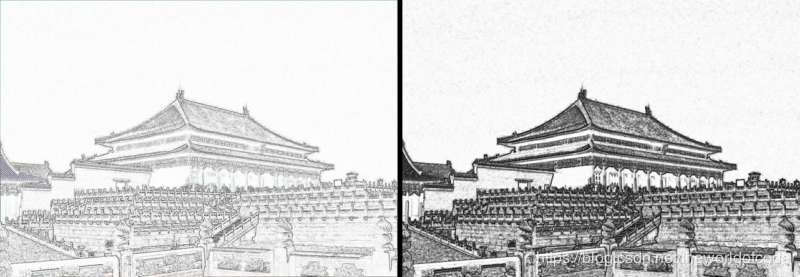
matplotlib库主要内容:

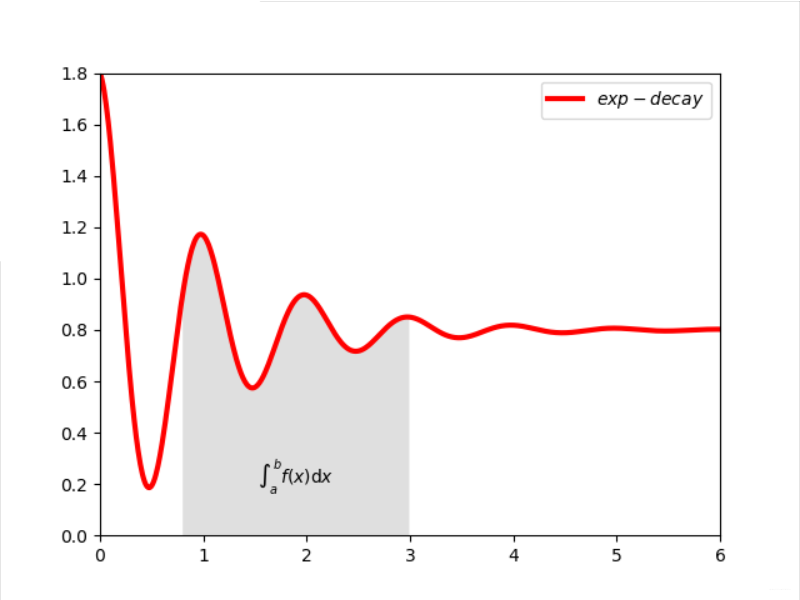
实例(教材):带阴影的坐标系
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 2 import numpy as np 3 x = np.linspace(0, 10, 1000) 4 y = np.cos(2*np.pi*x) * np.exp(-x)+0.8 5 plt.plot(x,y,'k',color='r',label="$exp-decay$",linewidth=3) 6 plt.axis([0,6,0,1.8]) 7 ix = (x>0.8) & (x<3) 8 plt.fill_between(x, y ,0, where = ix, 9 facecolor='grey', alpha=0.25) 10 plt.text(0.5*(0.8+3), 0.2, r"$int_a^b f(x)mathrm{d}x$", 11 horizontalalignment='center') 12 plt.legend() 13 plt.show()
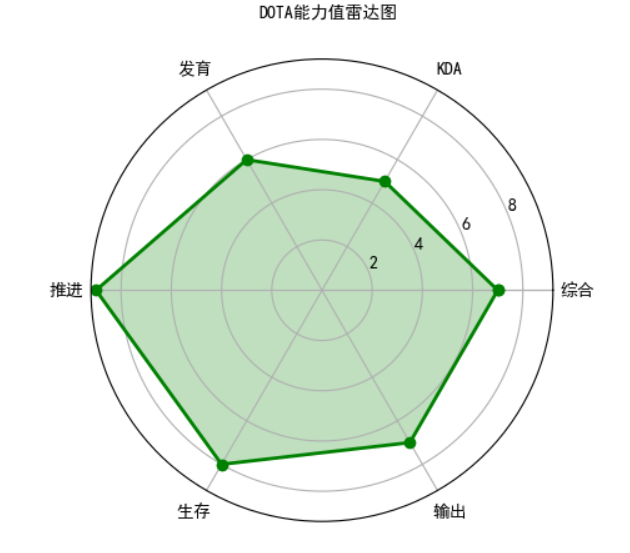
实例(教材):DOTA能力雷达图
#e19.1DrawRadar import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib matplotlib.rcParams['font.family']='SimHei' matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] labels = np.array(['综合', 'KDA', '发育', '推进', '生存','输出']) nAttr = 6 data = np.array([7, 5, 6, 9, 8, 7]) #数据值 angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, nAttr, endpoint=False) data = np.concatenate((data, [data[0]])) angles = np.concatenate((angles, [angles[0]])) fig = plt.figure(facecolor="white") plt.subplot(111, polar=True) plt.plot(angles,data,'bo-',color ='g',linewidth=2) plt.fill(angles,data,facecolor='g',alpha=0.25) plt.thetagrids(angles*180/np.pi, labels) plt.figtext(0.52, 0.95, 'DOTA能力值雷达图', ha='center') plt.grid(True) plt.show()
实例:python成绩雷达图
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 labels = np.array(['第二周','第三周','第四周','第五周','第六周']) 4 dataLenth =5 5 data = np.array([100,93.3,100,110,60]) 6 angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, dataLenth, endpoint=False) 7 data = np.concatenate((data, [data[0]])) 8 angles = np.concatenate((angles, [angles[0]])) 9 fig = plt.figure() 10 ax = fig.add_subplot(111, polar=True) 11 ax.plot(angles, data, 'ro-', linewidth=2) 12 ax.set_thetagrids(angles * 180/np.pi, labels, fontproperties="SimHei") 13 ax.set_title("呆.的python成绩雷达图", va='bottom', fontproperties="SimHei") 14 ax.grid(True) 15 plt.show()

、