Description
给一个数字串s和正整数d, 统计s有多少种不同的排列能被d整除(可以有前导0)。例如123434有90种排列能
被2整除,其中末位为2的有30种,末位为4的有60种。
Input
输入第一行是一个整数T,表示测试数据的个数,以下每行一组s和d,中间用空格隔开。s保证只包含数字0, 1
, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
Output
每个数据仅一行,表示能被d整除的排列的个数。
Sample Input
7
000 1
001 1
1234567890 1
123434 2
1234 7
12345 17
12345678 29
000 1
001 1
1234567890 1
123434 2
1234 7
12345 17
12345678 29
Sample Output
1
3
3628800
90
3
6
1398
3
3628800
90
3
6
1398
HINT
在前三个例子中,排列分别有1, 3, 3628800种,它们都是1的倍数。
【限制】
100%的数据满足:s的长度不超过10, 1<=d<=1000, 1<=T<=15
题解
暴力可以过,但状压dp才是正解。
设f[s][j]表示状态s下【s表示已经选择了哪些数】余数为j的方案数,那么f[s | (1<<i-1)][(j * 10 + a[i])%d] += f[s][j]
很明显,状态s下可以通过在末尾添加一个不在状态中的i号数来转移到s|(1<<i-1)这个状态
设立一个状态(突然不知道怎么用语言描述这个状态)DP(I,J),IDP(I,J),I表示当前枚举的状态,JJ表示状态I对应的数字的数值,这样设立状态后很容易得出下面的状态转移方程:
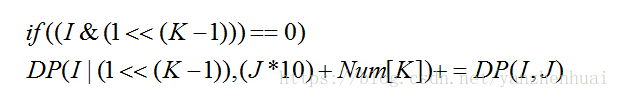
其中判断语句的含义是在II状态中,KK号没有选择出来。
状态转移结束后,由于数串中可能存在重复的数字(样例已经给出来了),这个时候我们就会有许多重复的计算。这个问题很好解决,我们根据排列的知识将最后的Ans/=Cnt[I] Cnt[I] 记录数字I在数串中出现的次数)就可以了。
C++代码/暴力
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int a[100],b[100]; int n ,d; int ans ; void dfs(int i,long long x){ if(i > n){ if(x % d == 0) ans ++; return; } for(int j = 0;j <= 9;j ++){ if(b[j]) { --b[j]; dfs(i + 1,x * 10 + j); ++b[j]; } } } int main(){ int t; cin >> t; while(t--){ string str; cin >> str; ans = 0; n = str.size(); memset(a,0,sizeof a); memset(b,0,sizeof b); for(int i = 0; i < str.size() ; i++){ a[i] = str[i] - '0'; b[a[i]]++; } cin >> d; dfs(1,0); cout << ans << endl; } }
C++代码/状压
#include <cmath> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #define DB double #define SG string #define LL long long #define DP(A,B) DP[A][B] #define Fp(A,B,C,D) for(A=B;A<=C;A+=D) #define Fm(A,B,C,D) for(A=B;A>=C;A-=D) #define Clear(A) memset(A,0,sizeof(A)) using namespace std; const LL Mod=1e9+7; const LL Max=2e3+5; const LL Inf=1e18; LL T,M,Num[Max],Cnt[Max],DP[Max][Max]; inline LL Read(){ LL X=0;char CH=getchar();bool F=0; while(CH>'9'||CH<'0'){if(CH=='-')F=1;CH=getchar();} while(CH>='0'&&CH<='9'){X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+CH-'0';CH=getchar();} return F?-X:X; } inline void Write(LL X){ if(X<0)X=-X,putchar('-'); if(X>9)Write(X/10); putchar(X%10+48); } int main(){ LL I,J,K,L; T=Read(); while(T--){ Clear(Cnt);Clear(DP); char CH[15];scanf("%s",CH+1); LL Length=strlen(CH+1);M=Read(); Fp(I,1,Length,1){ Num[I]=CH[I]-'0'; Cnt[Num[I]]++; }DP(0,0)=1; K=(1<<Length)-1; Fp(I,0,K,1){ Fp(J,0,M-1,1){ Fp(L,1,Length,1){ if((I&(1<<(L-1)))==0){ DP(I|(1<<(L-1)),((J<<1)+(J<<3)+Num[L])%M)+=DP(I,J); } } } }LL Ans=DP(K,0); Fp(I,0,9,1){ Fp(J,1,Cnt[I],1){ Ans/=J; } }Write(Ans);putchar(' '); } return 0; }