题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/734/problem/D
Anton likes to play chess. Also, he likes to do programming. That is why he decided to write the program that plays chess. However, he finds the game on 8 to 8 board to too simple, he uses an infinite one instead.
The first task he faced is to check whether the king is in check. Anton doesn't know how to implement this so he asks you to help.
Consider that an infinite chess board contains one white king and the number of black pieces. There are only rooks, bishops and queens, as the other pieces are not supported yet. The white king is said to be in check if at least one black piece can reach the cell with the king in one move.
Help Anton and write the program that for the given position determines whether the white king is in check.
Remainder, on how do chess pieces move:
- Bishop moves any number of cells diagonally, but it can't "leap" over the occupied cells.
- Rook moves any number of cells horizontally or vertically, but it also can't "leap" over the occupied cells.
- Queen is able to move any number of cells horizontally, vertically or diagonally, but it also can't "leap".
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 500 000) — the number of black pieces.
The second line contains two integers x0 and y0 ( - 109 ≤ x0, y0 ≤ 109) — coordinates of the white king.
Then follow n lines, each of them contains a character and two integers xi and yi ( - 109 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 109) — type of the i-th piece and its position. Character 'B' stands for the bishop, 'R' for the rook and 'Q' for the queen. It's guaranteed that no two pieces occupy the same position.
The only line of the output should contains "YES" (without quotes) if the white king is in check and "NO" (without quotes) otherwise.
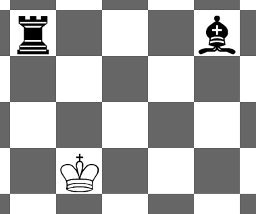
2 4 2 R 1 1 B 1 5
YES
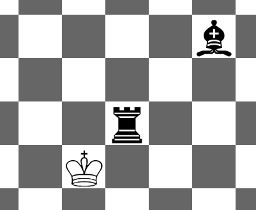
2 4 2 R 3 3 B 1 5
NO
Picture for the first sample:
Picture for the second sample:
题解:
1.在King的八个方向上,分别记录离其最近的棋子。
2.如果在横、竖线上,存在Rook或者Queen,则King in check; 如果在对角线上,存在Bishop或者Queen, 则King in check。
学习之处:
对角线的表示:
1.左上右下: x-y (注意:如果需要用非负数表示,则x-y+n)
2.右上左下:x+y
代码如下;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const double eps = 1e-6;
const int INF = 2e9;
const LL LNF = 9e18;
const int mod = 1e9+7;
const int maxn = 1e5+10;
int n, xo, yo;
int a[10][5];
map<string, int>m;
void f(int x, int y, int id) //分别在八个方向上取最近的棋
{
if(x==xo)
{
if(y<yo && (a[1][1]==INF || y>a[1][2]) )
a[1][1] = x, a[1][2] = y, a[1][3] = id;
if(y>yo && ( a[2][1]==INF || y<a[2][2]) )
a[2][1] = x, a[2][2] = y, a[2][3] = id;
}
else if(y==yo)
{
if(x<xo && ( a[3][1]==INF || x>a[3][1] ) )
a[3][1] = x, a[3][2] = y, a[3][3] = id;
if(x>xo && ( a[4][1]==INF || x<a[4][1]) )
a[4][1] = x, a[4][2] = y, a[4][3] = id;
}
else if(x-y==xo-yo)
{
if(x<xo && ( a[5][1]==INF || x>a[5][1]) )
a[5][1] = x, a[5][2] = y, a[5][3] = id;
if(x>xo && ( a[6][1]==INF || x<a[6][1]) )
a[6][1] = x, a[6][2] = y, a[6][3] = id;
}
else if(x+y==xo+yo)
{
if(x>xo && ( a[7][1]==INF || x<a[7][1]) )
a[7][1] = x, a[7][2] = y, a[7][3] = id;
if(x<xo && ( a[8][1]==INF || x>a[8][1]) )
a[8][1] = x, a[8][2] = y, a[8][3] = id;
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&xo, &yo);
m["B"] = 1; m["R"] = 2; m["Q"] = 3;
for(int i = 0; i<10; i++)
a[i][1] = INF;
string s; int x, y;
for(int i = 1; i<=n; i++)
{
cin>>s>>x>>y;
f(x, y, m[s]);
}
int B = 0;
for(int i = 1; i<=4; i++) //横、竖
if(a[i][1]!=INF && ( a[i][3]==2 || a[i][3]==3))
B = 1;
for(int i = 5; i<=8; i++) //对角线
if(a[i][1]!=INF && ( a[i][3]==1 || a[i][3]==3))
B = 1;
printf("%s
", B? "YES" : "NO");
}