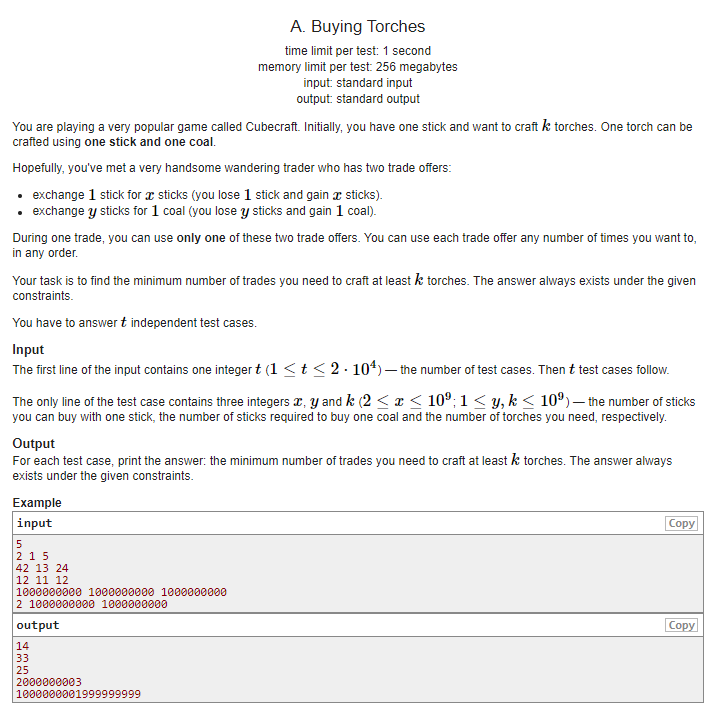
直接求最少需要多少个火柴就行
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i,j,k) for(LL i=(j); i<(k); ++i)
#define pb push_back
#define PII pair<LL,LL>
#define PLL pair<long long, long long>
#define ini(a,j) memset(a,j,sizeof a)
#define rrep(i,j,k) for(LL i=j; i>=k; --i)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define LL long long
#define beg begin()
#define ed end()
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
// #define DEBUG
#ifdef DEBUG
freopen("1.dat","r",stdin);
#endif
LL _;
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>_;
while(_--){
LL a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
LL ans = 0;
LL cur = 1;
LL need = c+b*c-1;
ans = need/(a-1) + (need%(a-1)!=0);
cout<<ans+c<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

把可以挪动的位置的值从大到小排序
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i,j,k) for(LL i=(j); i<(k); ++i)
#define pb push_back
#define PII pair<LL,LL>
#define PLL pair<long long, long long>
#define ini(a,j) memset(a,j,sizeof a)
#define rrep(i,j,k) for(LL i=j; i>=k; --i)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define LL long long
#define beg begin()
#define ed end()
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
// #define DEBUG
#ifdef DEBUG
freopen("1.dat","r",stdin);
#endif
LL _;
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>_;
while(_--){
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int> a(n+1,0),b(n+1,0);
rep(i,0,n) cin>>a[i+1];
rep(i,0,n) cin>>b[i+1];
vector<int> temp;
rep(i,0,n){
if(b[i+1])
continue;
else{
temp.push_back(a[i+1]);
}
}
sort(all(temp), std::greater<int>());
int cnt = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
if(b[i]==0)
a[i]=temp[cnt++];
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

简单的dp问题
设dp[i][0], dp[i][1] 分别是当第i个位置
是朋友和自己回合的回合的最少跳过次数
dp[i][0] = min(dp[i-1][1]+a[i], dp[i-1][1]+a[i]+a[i-1])
dp[i][1] = min(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][0])
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i,j,k) for(LL i=(j); i<(k); ++i)
#define pb push_back
#define PII pair<LL,LL>
#define PLL pair<long long, long long>
#define ini(a,j) memset(a,j,sizeof a)
#define rrep(i,j,k) for(LL i=j; i>=k; --i)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define LL long long
#define beg begin()
#define ed end()
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
// #define DEBUG
#ifdef DEBUG
freopen("1.dat","r",stdin);
freopen("ans.dat","w",stdout);
#endif
LL _;
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>_;
while(_--){
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int> a(n);
rep(i,0,n) cin>>a[i];
vector<vector<int>> dp(n+15, vector<int>(2,10000000));
dp[0][0]=0; //0 is friend`s round
dp[0][1]=0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
dp[i][0]=min(dp[i-1][1]+a[i-1], dp[i][0]);
if(i>=2)
dp[i][0]=min(dp[i-2][1]+a[i-1]+a[i-2], dp[i][0]);
if(i>1)
dp[i][1] = min(dp[i-1][0], dp[i][1]);
if(i>2)
dp[i][1] = min(dp[i-2][0], dp[i][1]);
}
cout<<min(dp[n][0], dp[n][1])<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

肯定是从两边往中间收缩
留下最大的缝隙
第一次知道迭代器还能这么玩
但是懒得写函数的写了个又臭又长的代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i,j,k) for(LL i=(j); i<(k); ++i)
#define pb push_back
#define PII pair<LL,LL>
#define PLL pair<long long, long long>
#define ini(a,j) memset(a,j,sizeof a)
#define rrep(i,j,k) for(LL i=j; i>=k; --i)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define LL long long
#define beg begin()
#define ed end()
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
// #define DEBUG
#ifdef DEBUG
freopen("1.dat","r",stdin);
// freopen("ans.dat","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int> a(n);
int q;
cin>>q;
rep(i,0,n) cin>>a[i];
int ans = 0;
sort(all(a));
map<int,int> res;
set<int> temp;
temp.insert(a[0]);
for(int i=1; i<n; i++){
temp.insert(a[i]);
ans += a[i]-a[i-1];
res[a[i]-a[i-1]]++;
}
int gg = ans;
if(res.size())
ans -= (*(--res.end())).fi;
cout<<ans<<endl;
int t,x;
while(q--){
cin>>t>>x;
auto pos = temp.lower_bound(x);
if(t==0){
// remove a new
int num = *pos;
if(temp.size()==1){
cout<<gg<<endl;
temp.erase(pos);
continue;
}
if(pos==temp.begin()){
++pos;
res[*pos-num]--;
if(res[*pos-num]==0)
res.erase(res.find(*pos-num));
gg -= *pos-num;
}else{
--pos;
int num2= *pos;
res[num-num2]--;
gg -= num-num2;
if(res[num-num2]==0)
res.erase(res.find(num-num2));
++pos;
++pos;
int num3;
if(pos!=temp.end()){
num3 = *pos;
res[num3-num]--;
gg -= num3-num;
if(res[num3-num]==0)
res.erase(res.find(num3-num));
res[num3-num2]++;
gg += num3-num2;
}
}
temp.erase(temp.lower_bound(x));
}
else{
// add a element
if(temp.size()==0){
cout<<gg<<endl;
temp.insert(x);
continue;
}
int num = *pos;
if(pos==temp.begin()){
res[*pos-x]++;
gg += *pos-x;
}else if(pos==temp.end()){
res[x-*--pos]++;
gg += x - *pos;
}else{
int num2 = *--pos;
res[x-num2]++;
res[num-x]++;
res[num-num2]--;
if(res[num-num2]==0)
res.erase(res.find(num-num2));
}
temp.insert(x);
}
ans = gg;
if(res.size())
ans -= (*(--res.end())).fi;
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}