1、利用字符重复出现的次数,编写一个方法,实现基本的字符串压缩功能。
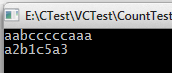
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<conio.h> 4 #include <string.h> 5 6 /* 7 重复字符压缩 8 */ 9 void RepeatCharReduce(char *str, int n, char *s){ 10 11 // char s[20]; 12 char tmp = str[0]; 13 s[0] = tmp; 14 int j = 1; 15 int count = 1; 16 for(int i = 1; i <n; i++){ 17 if(str[i] == tmp){ 18 count++; 19 } 20 else{ 21 s[j] = count; 22 j++; 23 tmp = str[i]; 24 s[j] = str[i]; 25 count = 1; 26 j++; 27 } 28 } 29 s[j] = count; 30 31 } 32 33 int main(){ 34 char str[] = "aabcccccaaa"; 35 char s[20] = "0"; 36 RepeatCharReduce(str, 11, s); 37 for(int j = 0; j < 11; j++){ 38 printf("%c", str[j]); 39 } 40 printf(" "); 41 for(int i = 0; i < 11; i += 2){ 42 printf("%c%d", s[i], s[i+1]); 43 } 44 printf(" "); 45 getch(); 46 return 0; 47 }
2、给定一个字符串,要求把字符串前面的若干个字符移动到字符串的尾部,如把字符串“abcdef”前面的2个字符'a'和'b'移动到字符串的尾部,使得原字符串变成字符串“cdefab”。请写一个函数完成此功能,要求对长度为n的字符串操作的时间复杂度为 O(n),空间复杂度为 O(1)。
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<conio.h> 4 #include<math.h> 5 #include<time.h> 6 #include <string.h> 7 8 void ReverseString(char *s, int from, int to) 9 { 10 while(from < to){ 11 char t = s[from]; 12 s[from++] = s[to]; 13 s[to--] = t; 14 } 15 } 16 17 void LeftRotateString(char *s, int n, int m) 18 { 19 m %= n; 20 ReverseString(s, 0, m-1); 21 ReverseString(s, m, n-1); 22 ReverseString(s, 0, n-1); 23 } 24 25 int main(){ 26 char s[] = "abcdefgh"; 27 for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++){ 28 printf("%c ", s[i]); 29 } 30 printf(" "); 31 LeftRotateString(s, 8, 3); 32 for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++){ 33 printf("%c ", s[i]); 34 } 35 printf(" "); 36 getch(); 37 return 0; 38 }

3、链表翻转。给出一个链表和一个数k,比如,链表为1→2→3→4→5→6,k=2,则翻转后2→1→6→5→4→3,若k=3,翻转后3→2→1→6→5→4,若k=4,翻转后4→3→2→1→6→5,用程序实现。
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<conio.h> 4 #include<math.h> 5 #include<time.h> 6 #include <string.h> 7 8 #define OK 1 9 #define ERROR 0 10 #define TRUE 1 11 #define FALSE 0 12 13 #define MAXSIZE 20 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */ 14 15 typedef int Status;/* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */ 16 typedef int ElemType;/* ElemType类型根据实际情况而定,这里假设为int */ 17 18 typedef struct Node{ 19 int data; 20 struct Node *next; 21 }Node, *LinkList; 22 23 /* 初始化顺序线性表 */ 24 Status InitList(LinkList *L) 25 { 26 *L=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(Node)); /* 产生头结点,并使L指向此头结点 */ 27 if(!(*L)) /* 存储分配失败 */ 28 { 29 return ERROR; 30 } 31 (*L)->next=NULL; /* 指针域为空 */ 32 return OK; 33 } 34 35 36 /* 随机产生n个元素的值,建立带表头结点的单链线性表L(头插法) */ 37 void CreateListHead(LinkList *L, int n) 38 { 39 LinkList p; 40 int i; 41 srand(time(0)); /* 初始化随机数种子 */ 42 *L = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(Node)); 43 (*L)->next = NULL; /* 先建立一个带头结点的单链表 */ 44 for (i=0; i < n; i++) 45 { 46 p = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(Node)); /* 生成新结点 */ 47 p->data = rand()%100+1; /* 随机生成100以内的数字 */ 48 printf("%d ", p->data); 49 p->next = (*L)->next; 50 (*L)->next = p; /* 插入到表头 */ 51 } 52 } 53 /* 初始条件:顺序线性表L已存在。操作结果:返回L中数据元素个数 */ 54 int ListLength(LinkList L) 55 { 56 int i=0; 57 LinkList p=L->next; /* p指向第一个结点 */ 58 while(p) 59 { 60 i++; 61 p=p->next; 62 } 63 return i; 64 } 65 Status visit(ElemType c) 66 { 67 printf("-> %d ",c); 68 return OK; 69 } 70 /* 初始条件:顺序线性表L已存在 */ 71 /* 操作结果:依次对L的每个数据元素输出 */ 72 Status ListTraverse(LinkList L) 73 { 74 LinkList p=L->next; 75 while(p) 76 { 77 visit(p->data); 78 p=p->next; 79 } 80 printf(" "); 81 return OK; 82 } 83 84 LinkList ListReverse2(LinkList L) 85 { 86 LinkList current, p; 87 if (L == NULL) 88 { 89 return NULL; 90 } 91 current = L->next; 92 while (current->next != NULL) 93 { 94 p = current->next; 95 current->next = p->next; 96 p->next = L->next; 97 L->next = p; 98 } 99 ListTraverse(L); 100 return L; 101 } 102 /* 103 1、链表翻转。给出一个链表和一个数k, 104 比如,链表为1→2→3→4→5→6,k=2,则翻转后2→1→6→5→4→3, 105 若k=3,翻转后3→2→1→6→5→4, 106 若k=4,翻转后4→3→2→1→6→5,用程序实现。 107 108 对于链表而言只是对指针的指向调换,所以不会耗费额外存储空间,空间复杂度O(1) 109 时间复杂度此处看来也是线性的 110 */ 111 112 LinkList ReverseSpecArea(LinkList L, int k){ 113 LinkList current, p, q; 114 LinkList temp; 115 int i = 1; 116 if (L == NULL) 117 { 118 return NULL; 119 } 120 current = L->next; 121 122 while (current->next != NULL) 123 { 124 p = current->next; 125 current->next = p->next; 126 p->next = L->next; 127 L->next = p; 128 if(++i >= k){ 129 break; 130 } 131 }//current始终指向起先除去头结点的第一个元素 132 temp = current; 133 current = current->next; 134 while(current->next != NULL){ 135 p = current->next; 136 current->next = p->next; 137 p->next = temp->next; 138 temp->next = p; 139 } 140 ListTraverse(L); 141 142 return L; 143 } 144 145 146 void ReverseString(char *s, int from, int to) 147 { 148 while(from < to){ 149 char t = s[from]; 150 s[from++] = s[to]; 151 s[to--] = t; 152 } 153 } 154 155 void LeftRotateString(char *s, int n, int k) 156 { 157 k %= n; 158 ReverseString(s, 0, k-1); 159 ReverseString(s, k, n-1); 160 } 161 162 int main(){ 163 LinkList L; 164 LinkList h; 165 Status i; 166 int j,k,pos,value; 167 int length; 168 char opp; 169 ElemType e; 170 i=InitList(&L); 171 printf("%d ", i); 172 173 CreateListHead(&L,10); 174 printf(" "); 175 length = ListLength(L); 176 printf("%d ", length); 177 printf("整体创建L的元素(头插法): "); 178 ListTraverse(L); 179 printf(" "); 180 h = L->next; 181 while(h){ 182 printf("%d ", h->data); 183 h = h->next; 184 } 185 printf(" "); 186 ListReverse2(L); 187 // printf("反转指定位置3的元素 "); 188 // ReverseSpecArea(L, 3); 189 printf("反转指定位置5的元素 "); 190 ReverseSpecArea(L, 5); 191 192 getch(); 193 return 0; 194 }

4、判断一个栈是不是“回文”(判断一个字符串是不是回文)
思路:将一个字符串依次全部入栈,然后再出栈,依次比较每个字符是否相等,若存在一个不等即不是回文,当全部相等时即为回文

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<conio.h> 4 #include<math.h> 5 #include<time.h> 6 #include <string.h> 7 8 typedef int Status;/* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */ 9 typedef int ElemType;/* ElemType类型根据实际情况而定,这里假设为int */ 10 typedef int SElemType; 11 12 #define MAXSIZE 20 13 #define OK 1 14 #define ERROR 0 15 #define TRUE 1 16 #define FALSE 0 17 //定义栈对象 18 typedef struct{ 19 SElemType data[MAXSIZE]; 20 int top;//指示栈顶元素 21 }SqStack; 22 //初始化栈 23 Status initStack(SqStack* S){ 24 S->top = -1; 25 return OK; 26 } 27 Status visit(SElemType c) 28 { 29 printf("%d ",c); 30 return OK; 31 } 32 /* 从栈底到栈顶依次对栈中每个元素显示 */ 33 Status StackTraverse(SqStack S) 34 { 35 int i; 36 i=0; 37 while(i<=S.top) 38 { 39 visit(S.data[i++]); 40 } 41 printf(" "); 42 return OK; 43 } 44 //入栈 45 Status push(SqStack* S, SElemType e){ 46 //首先判断是否栈满 47 if(S->top == MAXSIZE - 1){ 48 return ERROR; 49 } 50 S->top++; /* 栈顶指针增加一 */ 51 S->data[S->top] = e; 52 return OK; 53 } 54 /* 若栈不空,则删除S的栈顶元素,用e返回其值,并返回OK;否则返回ERROR */ 55 Status Pop(SqStack *S,SElemType *e) 56 { 57 if(S->top==-1)//为空 58 return ERROR; 59 *e=S->data[S->top]; /* 将要删除的栈顶元素赋值给e */ 60 S->top--; /* 栈顶指针减一 */ 61 return OK; 62 } 63 ElemType Pop1(SqStack *S) 64 { 65 if(S->top==-1)//为空 66 return ERROR; 67 ElemType temp; 68 temp = S->data[S->top]; /* 将要删除的栈顶元素赋值给e */ 69 S->top--; /* 栈顶指针减一 */ 70 return temp; 71 } 72 73 /* 若栈不空,则用e返回S的栈顶元素,并返回OK;否则返回ERROR */ 74 ElemType GetTop(SqStack S) 75 { 76 ElemType topElement; 77 if (S.top==-1) 78 return ERROR; 79 else 80 return S.data[S.top]; 81 82 } 83 84 int main() 85 { 86 SqStack s1; 87 SqStack s2; 88 SqStack temps; 89 bool flag = true; 90 int opp = 0; 91 int j; 92 if(initStack(&s1)==OK && initStack(&s2)==OK && initStack(&temps)==OK) 93 { 94 printf("顺序栈初始化成功。"); 95 StackTraverse(s1); 96 StackTraverse(s2); 97 StackTraverse(temps); 98 } 99 char* str = "asfdasegf"; 100 char* str1 = "adfghgfda"; 101 for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++){ 102 push(&s1, str1[i]); 103 push(&temps, str1[i]); 104 } 105 StackTraverse(s1); 106 while((&temps)->top != -1){//不为空 107 push(&s2, Pop1(&temps)); 108 } 109 StackTraverse(s2); 110 while((&s1)->top != -1){ 111 ElemType temp1 = Pop1(&s1); 112 ElemType temp2 = Pop1(&s2); 113 if(temp1 != temp2){ 114 printf("temp1 = %d ", temp1); 115 printf(" "); 116 printf("temp2 = %d ", temp2); 117 printf(" "); 118 printf("不是回文!"); 119 flag = false; 120 break; 121 } 122 } 123 if(flag){ 124 printf("是回文!"); 125 } 126 getch(); 127 }

此处采用的是顺序栈的数据结构来实现的,也可以采用链栈的结构处理
对于判断一个字符串是否是回文的问题可以采用分别从字符串两端遍历的方式,逐个比较来判定
实现时需采用两个指针变量分别指向头和尾:front和rear

1 bool IsPalindrome(const char *s, int n) 2 { 3 //非法输入 4 if (s == NULL || n < 1) 5 return false; 6 char *front, *back; 7 8 //初始化头指针和尾指针 9 front = s; 10 back = s + n - 1; 11 12 while (front < back) 13 { 14 if (*front != *back) 15 return false; // 不是回文,立即返回 16 ++front; 17 --back; 18 } 19 return true; // 是回文 20 }
此方法效率较高,时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(1)
当然,从中间向两边扫也是可行的:

1 bool IsPalindrome2(const char *s, int n) 2 { 3 if (s == NULL || n < 1) 4 return false; // 非法输入 5 char *first, *second; 6 7 int m = ((n >> 1) - 1) >= 0 ? (n >> 1) - 1 : 0; // m is themiddle point of s 右移一位相当于除以2 8 first = s + m; 9 second = s + n - 1 - m; 10 11 while (first >= s) 12 if (s[first--] != s[second++]) 13 return false; // not equal, so it's not apalindrome 14 return true; // check over, it's a palindrome 15 }
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(1)
1、判断一条单向链表是不是“回文”
分析:对于单链表结构,可以用两个指针从两端或者中间遍历并判断对应字符是否相等。但这里的关键就是如何朝两个方向遍历。由于单链表是单向的,所以要向两个方向遍历的话,可以采取经典的快慢指针的方法,即先位到链表的中间位置,再将链表的后半逆置,最后用两个指针同时从链表头部和中间开始同时遍历并比较即可。
后面会具体实现
