前言
一个表和多个表进行关联,但具体随着业务的加深,表不断的增加,关联的数量不断的增加,怎么通过一开始通过表的设计后,不在后期在修改表,彻底的解决这个问题呢呢
django中的一个组件content-type可以帮助我们解决这样的一个问题
在这里我先设计了3张表 学位表 普通课程 和价格策略表 大致的设计如下
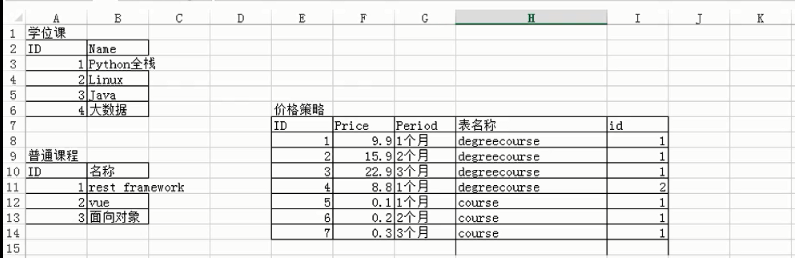
在上图中我们可以看到价格策略表和其他的两个表进行了关联,可以根据表明
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey, GenericRelation
from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType
class Course(models.Model):
"""
普通课程
"""
title = models.CharField(max_length=32)
# 仅用于反向查找 不在数据库中添加字段
price_policy_list = GenericRelation("PricePolicy")
class DegreeCourse(models.Model):
"""
学位课程
"""
title = models.CharField(max_length=32)
# 仅用于反向查找
price_policy_list = GenericRelation("PricePolicy")
class PricePolicy(models.Model):
"""
价格策略
"""
price = models.IntegerField()
period = models.IntegerField()
# 关联表
content_type = models.ForeignKey(ContentType, verbose_name='关联的表名称') # 7,8 表名称
object_id = models.IntegerField(verbose_name='关联的表中的数据行的ID') #
# 帮助你快速实现content_type操作 ,快速插入数据 不生成数据库中的字段
content_object = GenericForeignKey('content_type', 'object_id')
进行插入数据的类视图
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from app01 import models
def test(request):
# 1. 为学位课“Python全栈”添加一个价格策略:一个月 9.9
# obj1 = models.DegreeCourse.objects.filter(title='Python全栈').first()
# models.PricePolicy.objects.create(price=9.9, period=30, content_object=obj1)
#
# obj2 = models.DegreeCourse.objects.filter(title='Python全栈').first()
# models.PricePolicy.objects.create(price=19.9, period=60, content_object=obj2)
#
# obj3 = models.DegreeCourse.objects.filter(title='Python全栈').first()
# models.PricePolicy.objects.create(price=29.9, period=90, content_object=obj3)
# 2. 为学位课“rest”添加一个价格策略:一个月 9.9
# obj1 = models.Course.objects.filter(title='rest framework').first()
# models.PricePolicy.objects.create(price=9.9, period=30, content_object=obj1)
#
# obj2 = models.Course.objects.filter(title='rest framework').first()
# models.PricePolicy.objects.create(price=19.9, period=60, content_object=obj2)
#
# obj3 = models.Course.objects.filter(title='rest framework').first()
# models.PricePolicy.objects.create(price=29.9, period=90, content_object=obj3)
# 3. 根据课程ID获取课程, 并获取该课程的所有价格策略
# course = models.Course.objects.filter(id=1).first()
#
# price_policys = course.price_policy_list.all()
#
# print(price_policys)
return HttpResponse('...')
为其添加路由
from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^test/', views.test), ]
我们自己进行插入数据可能会这样写
# 1. 为学位课“Python全栈”添加一个价格策略:一个月 9.9 """ obj = DegreeCourse.objects.filter(title='Python全栈').first() # obj.id cobj = ContentType.objects.filter(model='course').first() # cobj.id PricePolicy.objects.create(price='9.9',period='30',content_type_id=cobj.id,object_id=obj.id) """ # obj = DegreeCourse.objects.filter(title='Python全栈').first() # PricePolicy.objects.create(price='9.9',period='30',content_object=obj)