线性表的顺序表示和实现
时间:2006/02/14
测试环境:TC2.0
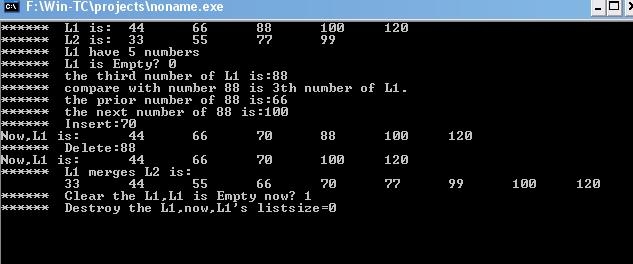
#include "stdio.h" #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 #define List_Init_Size 30 #define List_Increment 10 typedef int ElemType; typedef struct { ElemType *elem; int length; int listsize; }Sqlist; /*初始化一个线性表*/ int InitList_Sq(Sqlist *L) { L->elem=(ElemType *)malloc(List_Init_Size*sizeof(ElemType)); if(!L->elem) return TRUE; L->length=0; L->listsize=List_Init_Size; return FALSE; } /*销毁一个线性表*/ void DestroyList(Sqlist *L) { if(L->elem) { free(L->elem); L->length=0; L->listsize=0; } } /*清空线性表*/ void ClearList(Sqlist *L) { L->length=0; } /*判断是否为空表*/ int ListEmpty(Sqlist L) { if(L.length==0) return TRUE; else return FALSE; } /*返回元素个数*/ int ListLength(Sqlist L) { return L.length; } /*返回某一元素的值*/ int GetElem(Sqlist L,int i,ElemType *e) { if(i<1 || i>(L.length)) return FALSE; *e=L.elem[i-1]; } /*比较两个元素*/ int compare(ElemType x,ElemType y) { if(x==y) return TRUE; else return FALSE; } /*返回线性表中第一个与e满足关系compare()的元素的位序*/ int LocateElem(Sqlist L,ElemType e) { int i; for(i=0;i<L.length;i++) { if(compare(L.elem[i],e)) return i+1; } return FALSE; } /*若cur_e是线性表的元素,且不是第一个,则返回它的前驱*/ int PriorElem(Sqlist L,ElemType cur_e,ElemType *e) { int i; if(cur_e==L.elem[0]) return FALSE; for(i=1;i<L.length;i++) { if(L.elem[i]==cur_e) *e=L.elem[i-1]; } } /*若cur_e是线性表的元素,且不是最后一个,则返回它的后继*/ int NextElem(Sqlist L,ElemType cur_e,ElemType *e) { int i; if(cur_e==L.elem[L.length-1]) return FALSE; for(i=0;i<L.length-1;i++) { if(L.elem[i]==cur_e) *e=L.elem[i+1]; } } /*在线性表的第i个位置前插入新元素e*/ int ListInsert(Sqlist *L,int i,ElemType e) { ElemType *p,*q,*newbase; if(i<1 || i>(L->length+1)) return FALSE; if((L->length) >= (L->listsize)) { newbase=(ElemType *)realloc(L->elem, (List_Init_Size+List_Increment)*sizeof(ElemType)); if(!newbase) return FALSE; L->elem = newbase; L->listsize+=List_Increment; } p=&(L->elem[i-1]); for(q=&(L->elem[L->length-1]);q>=p;--q) *(q+1)=*q; *p=e; ++(L->length); } /*删除线性表的第i个元素,并用e返回其值*/ int ListDelete(Sqlist *L,int i,ElemType *e) { ElemType *p,*q; if(i<1 || i>(L->length)) return FALSE; p=&(L->elem[i-1]); *e=*p; q=L->elem+L->length-1; for(++p;p<=q;p++) *(p-1)=*p; --(L->length); } /*两个线性表的合并*/ void MergeList(Sqlist La,Sqlist Lb,Sqlist *Lc) { int La_len,Lb_len; int i,j,k; ElemType ai,bj; i=j=1; k=0; InitList_Sq(Lc); La_len=ListLength(La); Lb_len=ListLength(Lb); while(i<=La_len && j<=Lb_len) { GetElem(La,i,&ai); GetElem(Lb,j,&bj); if(ai<=bj) { ListInsert(Lc,++k,ai); ++i; } else { ListInsert(Lc,++k,bj); ++j; } } while(i<=La_len) { GetElem(La,i++,&ai); ListInsert(Lc,++k,ai); } while(j<=Lb_len) { GetElem(Lb,j++,&bj); ListInsert(Lc,++k,bj); } } void main() { Sqlist L1,L2,L3; ElemType e; /*初始化一个线性表*/ InitList_Sq(&L1); InitList_Sq(&L2); /*L1插入元素*/ ListInsert(&L1,1,44); ListInsert(&L1,2,66); ListInsert(&L1,3,88); ListInsert(&L1,4,100); ListInsert(&L1,5,120); /*L2插入元素*/ ListInsert(&L2,1,33); ListInsert(&L2,2,55); ListInsert(&L2,3,77); ListInsert(&L2,4,99); /*打印出L1和L2的值*/ printf("******/tL1 is:"); for(e=0;e<L1.length;e++) printf("/t%d",L1.elem[e]); printf("/n******/tL2 is:"); for(e=0;e<L2.length;e++) printf("/t%d",L2.elem[e]); /*返回元素个数*/ printf("/n******/tL1 have %d numbers",ListLength(L1)); /*判断线性表是否为空*/ printf("/n******/tL1 is Empty? %d",ListEmpty(L1)); /*返回第i个元素的值*/ GetElem(L1,3,&e); printf("/n******/tthe third number of L1 is:%d",e); /*返回线性表中第一个与e满足关系compare()的元素的位序*/ printf("/n******/tcompare with number 88 is %dth number of L1./n",LocateElem(L1,88)); /*若cur_e是线性表的元素,且不是第一个,则返回它的前驱*/ PriorElem(L1,88,&e); printf("******/tthe prior number of 88 is:"); printf("%d/n",e); /*若cur_e是线性表的元素,且不是最后一个,则返回它的后继*/ NextElem(L1,88,&e); printf("******/tthe next number of 88 is:"); printf("%d/n",e); /*在线性表的第i个位置前插入新元素e*/ ListInsert(&L1,3,70); GetElem(L1,3,&e); printf("******/tInsert:%d/n",e); printf("Now,L1 is:"); for(e=0;e<L1.length;e++) printf("/t%d",L1.elem[e]); /*删除线性表的第i个元素,并用e返回其值*/ ListDelete(&L1,4,&e); printf("/n******/tDelete:%d/n",e); printf("Now,L1 is:"); for(e=0;e<L1.length;e++) printf("/t%d",L1.elem[e]); printf("/n"); /*合并两个线性表L1,L2*/ MergeList(L1,L2,&L3); printf("******/tL1 merges L2 is:/n"); for(e=0;e<L3.length;e++) printf("/t%d",L3.elem[e]); /*清空线性表*/ ClearList(&L1); printf("/n******/tClear the L1,L1 is Empty now? %d",ListEmpty(L1)); /*销毁线性表*/ DestroyList(&L1); printf("/n******/tDestroy the L1,"); printf("now,L1's listsize=%d",L1.listsize); getch(); }
运行后结果: