https://echo360.org.au/lesson/9750cbfe-6500-42f7-b024-45c5cf2a69b0/classroom#sortDirection=desc
Tracking :
1. Bayesian inference Using probabilistic models to perform tracking
1). • A moving object has a state which evolves over time; Random variable Xi can contain any quantities of interest (position, velocity, acceleration, shape, intensity, colour, …)
2) The state is measured at each time point ; Random variable Yi measurements are typical features computed from the images
3) 贝叶斯预测三步

(1)Prediction 基于前i-1步的measurements预测第i步的state

(2)Assiciation:如果有不同的objects 则需要选择不同的 object-related measurements (这里预测单个object 没有这一步)
(3) Correction: 用正确的Yi更新之前的预测
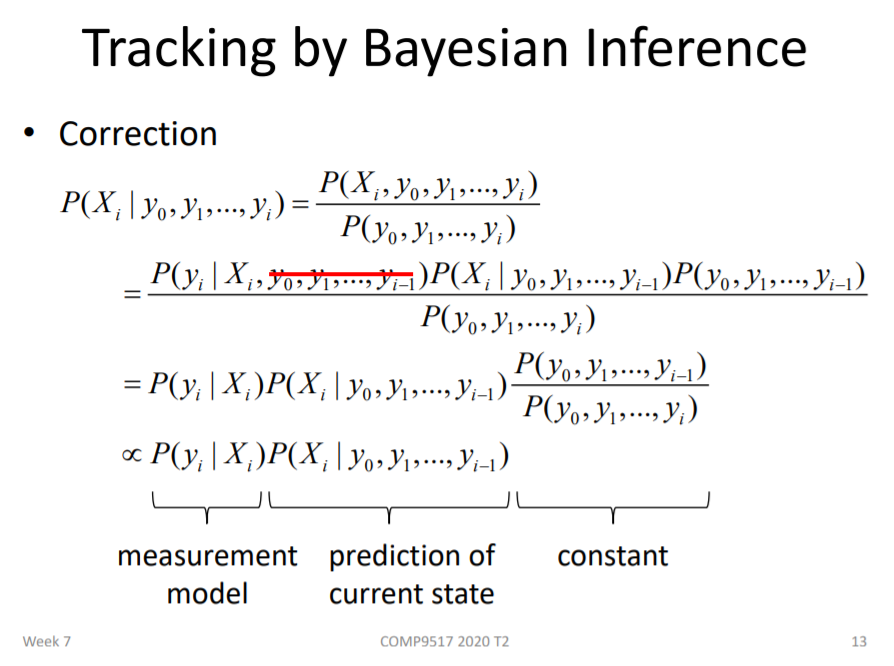
4) Current state only depends on the immediate past; Measurements depend only on the current state
隐马尔可夫模型

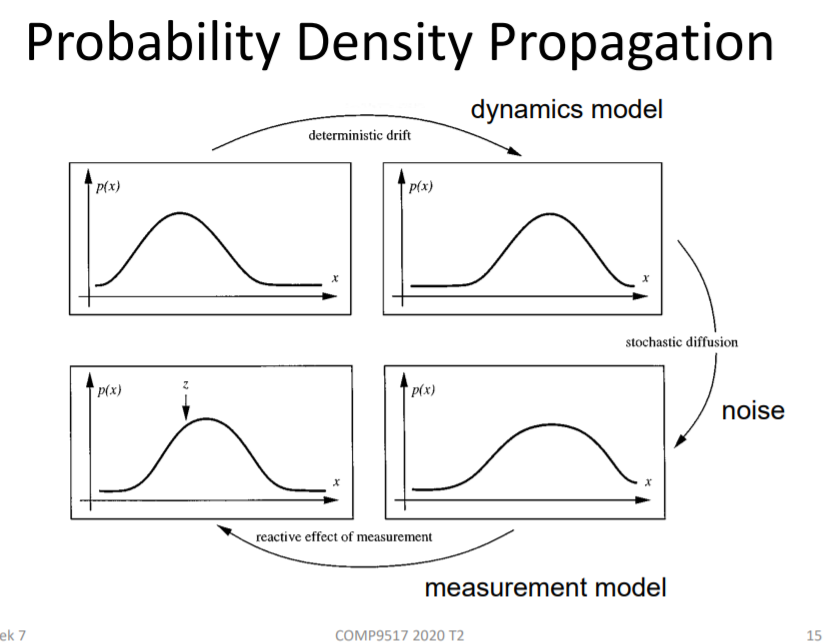
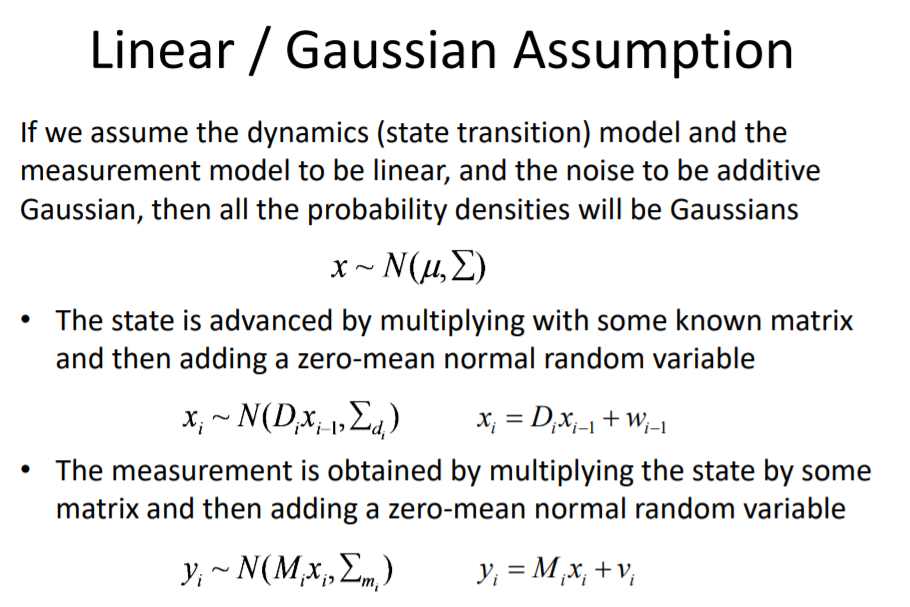
2.• Kalman filtering Using linear model assumptions for tracking
假设object线性运用,noise成高斯分布

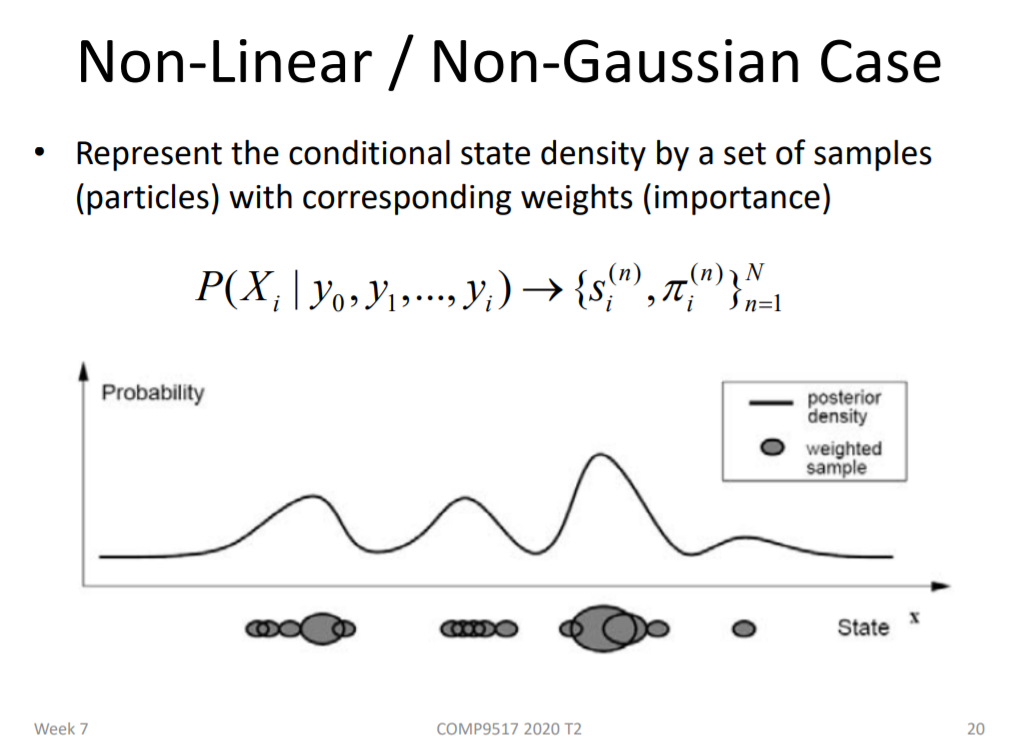
3.• Particle filtering Using nonlinear models for tracking