/**
* 测试FileInputStream和FileOutputStream的使用
*
* 结论:
* 1. 对于文本文件(.txt,.java,.c,.cpp),使用字符流处理
* 2. 对于非文本文件(.jpg,.mp3,.mp4,.avi,.doc,.ppt,...),使用字节流处理
* @author CH
* @create 2021 下午 2:13
*/
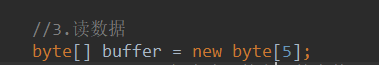
//使用字节流FileInputStream处理文本文件,可能出现乱码。 @Test public void testFileInputStream() { FileInputStream fis = null; try { //1. 造文件 File file = new File("hello.txt"); //2.造流 fis = new FileInputStream(file); //3.读数据 byte[] buffer = new byte[5]; int len;//记录每次读取的字节的个数 while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){ String str = new String(buffer,0,len); System.out.print(str); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(fis != null){ //4.关闭资源 try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
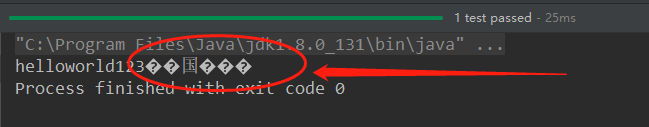
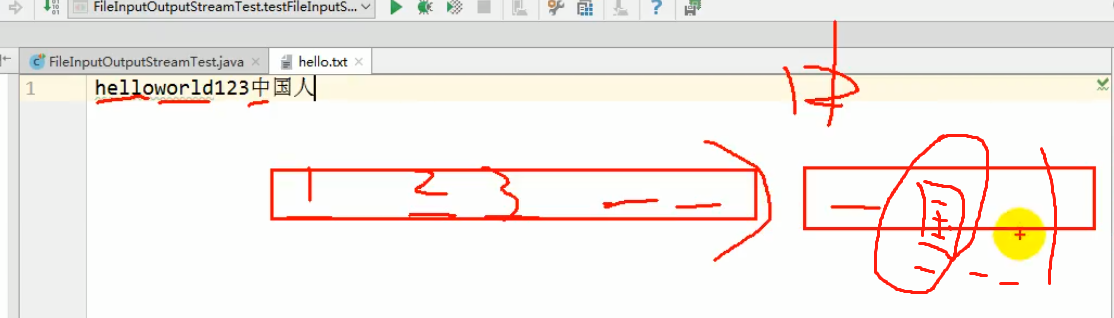
分析:输出流buffer五个字节,国字正好夹在中间,所以没有乱码
/* 实现对图片的复制操作 */ @Test public void testFileInputOutputStream() { FileInputStream fis = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; try { // File srcFile = new File("爱情与友情.jpg"); File destFile = new File("爱情与友情2.jpg"); // fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile); fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //复制的过程 byte[] buffer = new byte[5]; int len; while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){ fos.write(buffer,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(fos != null){ // try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(fis != null){ try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }

//指定路径下文件的复制 public void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath){ FileInputStream fis = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; try { // File srcFile = new File(srcPath); File destFile = new File(destPath); // fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile); fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //复制的过程 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){ fos.write(buffer,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(fos != null){ // try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(fis != null){ try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
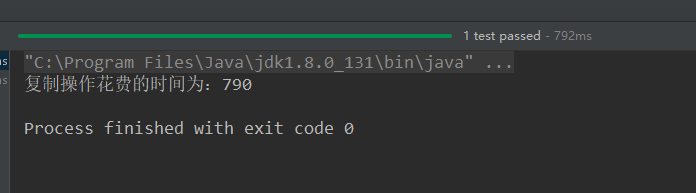
@Test public void testCopyFile(){ long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); String srcPath = "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\01.jvm结构_1.avi"; String destPath = "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\0111.jvm结构_1.avi"; // String srcPath = "hello.txt"; // String destPath = "hello3.txt"; copyFile(srcPath,destPath); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("复制操作花费的时间为:" + (end - start));//618 }