题目
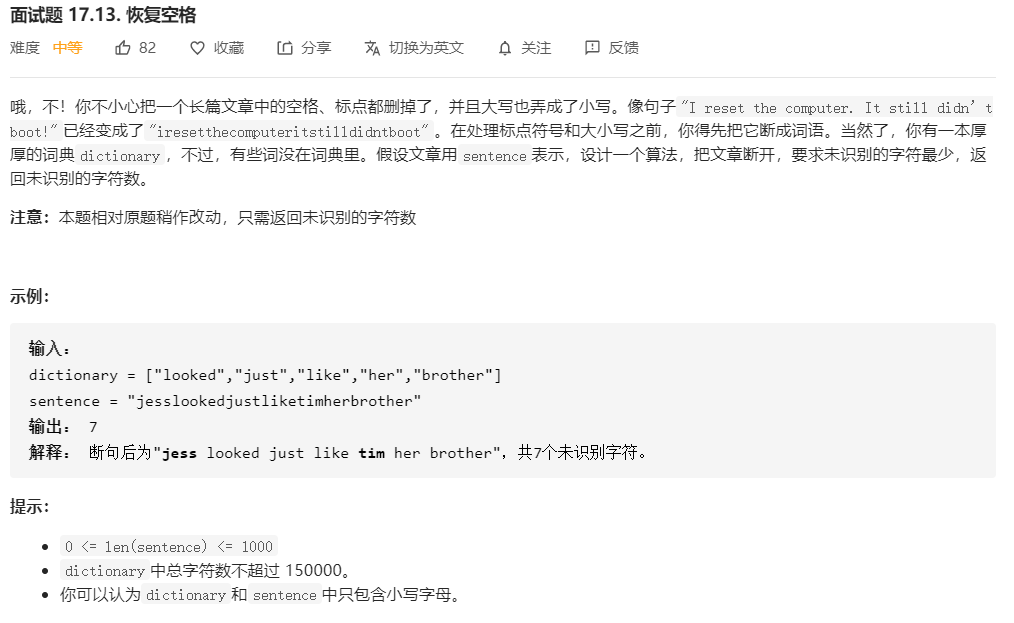
面试题 17.13. 恢复空格
我的思路
这道题还挺有难度,没有做出来。
我最初的想法是在对sentence进行多次扫描,把所有在dictionary中存在的子串记录下来。符合条件的子串用两个整数(子串的首尾在sentence中的下标)记录。可能这样就可以转化成与会议安排类似的问题:sentence的长度相当于总时间(从0到length-1),一个满足条件的子串看做是一场会议(首字符下标到尾字符下标)。
这样的思路其实并不太可行,在dictionary中查询是否存在特定字符串的过程时间复杂度过大,不经过特殊处理的话是k*n^2。(k是字典中单词个数,n是sentence长度)。同时也没有找到空余时间最少的动态规划方法。
以下实现是看了官方解答后,自己写的不使用字典树的做法。
我的实现
class Solution { public: int respace(vector<string>& dictionary, string sentence) { unordered_set<string> dictionaryMap; bool p=true; for(auto it:dictionary){ dictionaryMap.insert(it); } int unused[sentence.size()+1];unused[0]=0; for(int i=0;i<sentence.size();i++){ unused[i+1] = unused[i]+1; for(int j=0;j<=i;j++){ unordered_set<string>::iterator strIt = dictionaryMap.find(sentence.substr(j,i-j+1)); if(strIt!=dictionaryMap.end()){//在集合中找到了 unused[i+1] = min(unused[i+1] , unused[j]); }else{//没找到 //unused[i+1] = unused[i]+1; } } //printf("no.:%d %d ",i+1,unused[i+1]); } //printf("size=%d",sentence.size()); return unused[sentence.size()]; } }; /** 本题有两个关键步骤: 1.找到状态迭代转移规律 2.快速判断一个字符串,是否存在于一个大的字符串集合中 容器相关知识: 1.如何用顺序容器构造关联容器? 2.auto与iterator的区别 3.find函数对于顺序容器和相关容器 4.unordered_map或unordered_set(哈希算法)查找比vector(动态数组)和set(红黑树)快很多。各个容器的实现机制https://www.cnblogs.com/fangrong/p/5271676.html */
时间复杂度:m2+|dictionary|。|dictionary|是词典中的字符总数,m是sentence长度
空间复杂度:|dictionary|*S+m。S是字符种类数。节点数一定小于|dictionary|
使用哈希表的做法如下
class Trie { public: Trie* next[26] = {nullptr}; bool isEnd; Trie() { isEnd = false; } void insert(string s) { Trie* curPos = this; for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; --i) { int t = s[i] - 'a'; if (curPos->next[t] == nullptr) { curPos->next[t] = new Trie(); } curPos = curPos->next[t]; } curPos->isEnd = true; } }; class Solution { public: int respace(vector<string>& dictionary, string sentence) { int n = sentence.length(), inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; Trie* root = new Trie(); for (auto& word: dictionary) { root->insert(word); } vector<int> dp(n + 1, inf); dp[0] = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1; Trie* curPos = root; for (int j = i; j >= 1; --j) { int t = sentence[j - 1] - 'a'; if (curPos->next[t] == nullptr) { break; } else if (curPos->next[t]->isEnd) { dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[j - 1]); } if (dp[i] == 0) { break; } curPos = curPos->next[t]; } } return dp[n]; } }; /**作者:LeetCode-Solution 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/re-space-lcci/solution/hui-fu-kong-ge-by-leetcode-solution/ 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。*/
使用字典树(未自己独立实现)

拓展学习
转移方程
动态规划的关键是找到状态转移方程
字典树
熟悉下面的实现
class Trie { public: Trie* next[26] = {nullptr}; bool isEnd; Trie() { isEnd = false; } void insert(string s) { Trie* curPos = this; for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; --i) { int t = s[i] - 'a'; if (curPos->next[t] == nullptr) { curPos->next[t] = new Trie(); } curPos = curPos->next[t]; } curPos->isEnd = true; } }; /**作者:LeetCode-Solution 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/re-space-lcci/solution/hui-fu-kong-ge-by-leetcode-solution/ 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。*/