转自:https://www.tutorialspoint.com/python_pandas/python_pandas_dataframe.htm
1.数据框4特性

-
列是不同类型的数据元素。
-
每列的长度可变
-
行和列都有标签
-
对行和列可进行算术运算。
可将其视为SQL表。//这个十分容易理解了。
2.创建
pandas.DataFrame( data, index, columns, dtype, copy)
其中Data可以是list,dict,array,series,map,等。
- Lists
- dict
- Series
- Numpy ndarrays
- Another DataFrame
index是对行的索引,column是列名。
空
从List

从dict

3.列操作
选择列,直接用列名即可。
添加列:

删除列,
使用del函数或者pop函数:

4.行操作
对行索引,
可以通过label来进行,那么使用loc;通过行数字来进行,使用iloc:
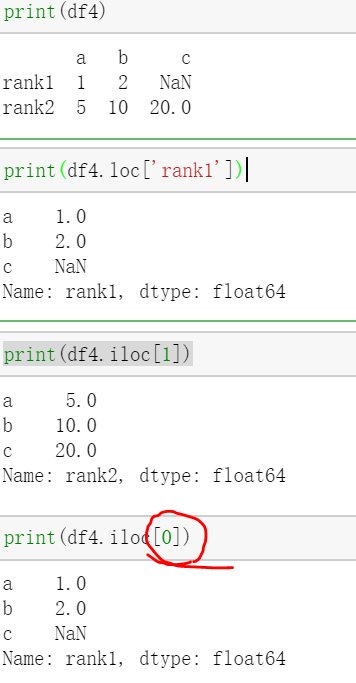
//行号是从0开始的。
对行进行数据切片:

//直接使用冒号即可,并且右边的数是取不到的。
添加行,使用append函数
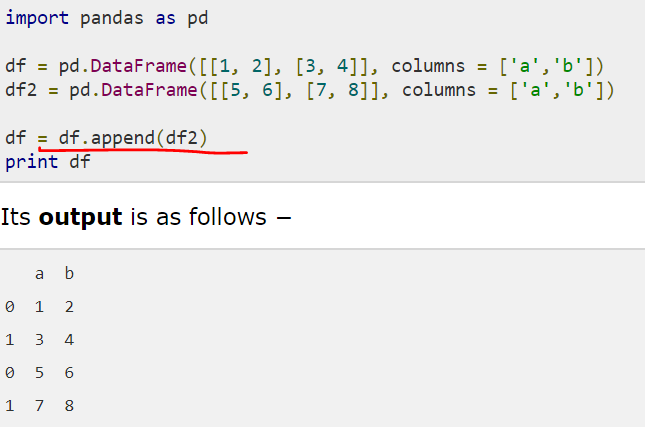
//注意上述,append了之后,index是仍旧保持原来的,会有相同的index。
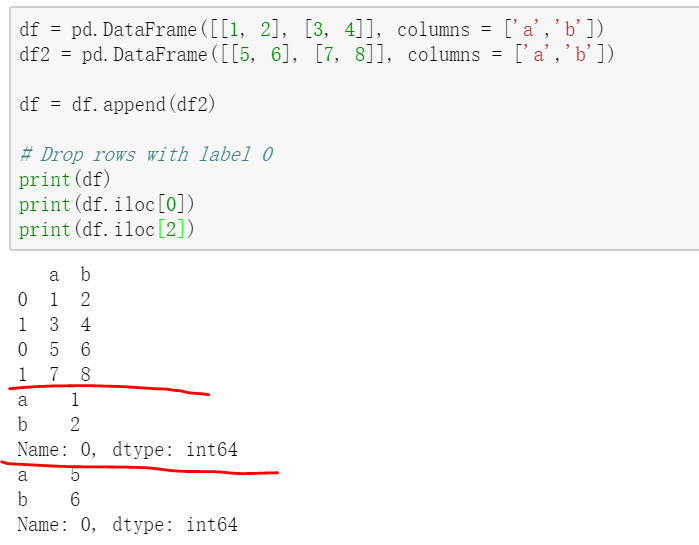
对于相同的index,如果使用整数去iloc的话,实际上并不是一列,从上述结果可以看书,那么如果是使用loc呢?
print(df.loc['0'])
报错:KeyError: 'the label [0] is not in the [index]'
那么就只能用iloc去索引了

//去掉引号之后可以了。
这说明,对于不指定index的,自动生成的0,1,2,3.是label,使用loc索引。
删除行:

使用pop函数,会将具有相同label的行删除。
2020-3-3————————————
1.行遍历数据框
import pandas as pd import numpy as np b=pd.read_csv("a.txt",names=['1','2','3','4','5'],skiprows=3,sep=' ') a=np.zeros((4,2)) for i,v in b.iterrows():#这样就可以直接遍历行 a[i,0]=v[0]#下面可以直接访问列对另一个矩阵赋值 a[i,1]=v[2]
a.txt:
S.No Name Age City Salary df dfs
1 Tom 28 Toronto 20000.0
2 Lee 32 HongKong 3000.0
3 Steven 43 BayArea 8300.0
4 Ram 38 Hyderabad 3900.0
2.对行按照行名进行重新放置
import pandas as pd import numpy as np b=pd.read_csv("a.txt",sep=' ') b.index=['a','b','c','d'] #直接这样就ok的啊。
也是非常的简单,直接b.reindex([....])即可,也可以是别的df的index