二叉树的遍历-链式存储
利用指针域我们便可以完美的存储非完全二叉树,如下:
结构体
struct TreeNode
{
TreeNode*left;
TreeNode*right;
char data;
};
typedef TreeNode* BTree;
建树
BTree CreateBTree()
{
BTree bt = NULL;
char ch;
cin>>ch;
if (ch != '#')
{
bt = new TreeNode;
bt->data = ch;
bt->left = CreateBTree();
bt->right = CreateBTree();
}
return bt;
}
前序访问的递归写法
void PreOrder(TreeNode*root){
if (root==NULL)
{
return; //若结点为空
}
cout<<root->data; //输出根节点的值
PreOrder(root->left); //前序访问左子树
PreOrder(root->right); //前序访问右子树
}
前序访问的非递归写法 ---先根次序周游
void PreOrderLoop(TreeNode*root){
stack<TreeNode*>s;
TreeNode*cur,*top;
cur = root;
while(cur!=NULL||!s.empty()){
while (cur!=NULL)
{
cout<<cur->data;
s.push(cur);
cur=cur->left;
}
top=s.top();
s.pop();
cur =top->right;
}
}
中序遍历的递归写法
void InOrder(TreeNode*root){
if(root==NULL){
return; //判断节点是否为空
}
InOrder(root->left); //中序遍历左子树
cout<<root->data; //访问节点值
InOrder(root->right); //中序遍历右子树
}
中序访问的非递归写法 ---对称周游
void InOrderLoop(TreeNode *root){
stack<TreeNode *>s;
TreeNode *cur;
cur=root;
while (cur!=NULL||!s.empty()){
while(cur!=NULL){
s.push(cur);
cur=cur->left;
}
cur = s.top();
s.pop();
cout<<cur->data;
cur=cur->right;
}
}
后序遍历的递归写法
void PostOrder(TreeNode*root){
if(root==NULL){
return; //判断节点是否为空
}
InOrder(root->left); //后序遍历左子树
InOrder(root->right); //后序遍历右子树
cout<<root->data; //访问节点值
}
后序访问的非递归写法 --后跟周游
void PostOrderLoop(TreeNode *root){
stack<TreeNode *>s;
TreeNode *cur,*top,*last=NULL;
cur=root;
while (cur!=NULL||!s.empty()){
while(cur!=NULL){
s.push(cur);
cur=cur->left;
}
top = s.top();
if(top->right==NULL||top->right==last){
s.pop();
cout<<top->data;
last=top;
}else{
cur =top->right;
}
}
}
层序遍历 -- -广度优先周游
void LevelOrder(TreeNode* root){
queue<TreeNode*>q;
TreeNode *front;
if(root==NULL)return;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty())
{
front = q.front();
q.pop();
if (front->left)
{
q.push(front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
q.push(front->right);
}
cout<<front->data;
}
}
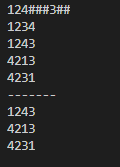
测试结果
124###3##
统计叶子结点的数目,方法一
int leftCount=0;
void leaf1(BTree root){
if(root!=NULL){
leaf1(root->left);
leaf1(root->right);
if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL){
leftCount++;
}
}
}
统计叶子结点的数目,方法二
int leaf2(BTree root){
int leftC=0;
if(root==NULL)leftCount=0;
else if (root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL)
{
leftC=1;
}else
{
leftC=leaf2(root->left)+leaf2(root->right);
}
return leftC;
}
求二叉树的高度
int TreeDepth(BTree bt)
{
int hl,hr,max;
if(bt!=NULL)
{
hl=TreeDepth(bt->left);
hr=TreeDepth(bt->right);
max=hl>hr?hl:hr;
return(max+1);
}
else return(0);
}