本文部分照片和代码分析来自文末参考资料
java8中的concurrenthashmap的方法逻辑和注解有些问题,建议看最新的JDK版本
建议阅读 concurrenthashmap 源码前过一遍源码前面的注释,参考资料第二篇的博客有注释翻译
概述
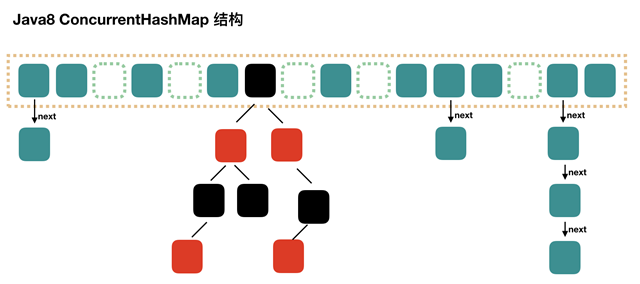
java8 的 concurrenthashmap 主要工作方式如下 :
可以看到总体就是链表+红黑树。当链表数量达到一定值(默认是8)时,我们就会将链表转化为红黑树。concurrenthash的特点就是并发,那么是如何并发的呢?下面是几个concurrenthash 的工作过程。
源码阅读
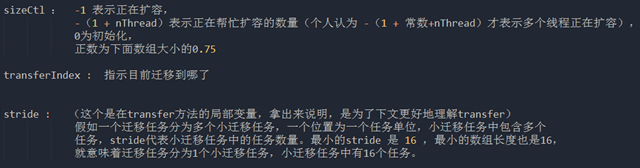
控制信号
put
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(key, value, false); } /** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */ final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); //计算 hash 值 int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); int binCount = 0; //for 循环 for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; // 首次加入或是 tab 里面没元素 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) tab = initTable(); //初始化 Table,然后继续循环 //发现在列表中没有 else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { //CAS 放进去,成功后 break退出循环 if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null))) break; // no lock when adding to empty bin } //在列表中存在,hash 值为 MOVED(-1) else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); else { //进到这里 f , fh 分别都被赋值了,列表中存在该值 V oldVal = null; //直接加锁操作 synchronized (f) { if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { //如果为链表 if (fh >= 0) { binCount = 1; for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { K ek; //找到,更新 if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { oldVal = e.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) e.val = value; break; } //找不到,e指向e后面那个 Node<K,V> pred = e; if ((e = e.next) == null) { //最后这条链表没有,就加在后面 pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null); break; } } } //如果为红黑树 else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { Node<K,V> p; binCount = 2; if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null) { //存在一样的 key , 更新 oldVal = p.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) p.val = value; } } } } if (binCount != 0) { if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) //判断是否应该变为红黑树,treeifyBin 也有可能是扩展了数组大小。 treeifyBin(tab, i); if (oldVal != null) return oldVal; break; } } } addCount(1L, binCount); return null; }
初始化数组
/** * Initializes table, using the size recorded in sizeCtl. * * 这里假如有多个线程执行put 操作,那么初始化线程的操作应该只能执行一次 */ private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() { Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc; while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0) Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin //CAS 将 sizeCtl 赋值为 -1 ,那么CAS失败的线程进行循环要不让步,要不就tab得到赋值退出 else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) { try { if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n]; table = tab = nt; //这里就是 0.75*n sc = n - (n >>> 2); } } finally { // sizeCtl = sc = 0.75*n sizeCtl = sc; } break; } } return tab; }
扩容和迁移
假如上面的put 方法进入了treeifyBin 方法,那么接下来要进行扩容。
/** * Replaces all linked nodes in bin at given index unless table is * too small, in which case resizes instead. */ private final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int index) { Node<K,V> b; int n; if (tab != null) { if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) //扩容迁移 tryPresize(n << 1); //生成红黑树 else if ((b = tabAt(tab, index)) != null && b.hash >= 0) { synchronized (b) { if (tabAt(tab, index) == b) { TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null; for (Node<K,V> e = b; e != null; e = e.next) { TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>(e.hash, e.key, e.val, null, null); if ((p.prev = tl) == null) hd = p; else tl.next = p; tl = p; } setTabAt(tab, index, new TreeBin<K,V>(hd)); } } } } } /** * Tries to presize table to accommodate the given number of elements. * * @param size number of elements (doesn't need to be perfectly accurate) */ private final void tryPresize(int size) { int c = (size >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor(size + (size >>> 1) + 1); int sc; while ((sc = sizeCtl) >= 0) { Node<K,V>[] tab = table; int n; //和initTable一样 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) { n = (sc > c) ? sc : c; if (U.compareAndSetInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) { try { if (table == tab) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n]; table = nt; sc = n - (n >>> 2); } } finally { sizeCtl = sc; } } } else if (c <= sc || n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) break; else if (tab == table) { //扩容迁移 int rs = resizeStamp(n); if (U.compareAndSetInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, (rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2)) transfer(tab, null); } } }
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) { int n = tab.length, stride; // stride 在单核下直接等于 n,多核模式下为 (n>>>3)/NCPU,最小值是 16 // stride 可以理解为”步长“,有 n 个位置是需要进行迁移的, // 将这 n 个任务分为多个任务包,每个任务包有 stride 个任务 if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE) stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range // 如果 nextTab 为 null,先进行一次初始化 // 前面我们说了,外围会保证第一个发起迁移的线程调用此方法时,参数 nextTab 为 null // 之后参与迁移的线程调用此方法时,nextTab 不会为 null if (nextTab == null) { try { // 容量翻倍 Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1]; nextTab = nt; } catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } // nextTable 是 ConcurrentHashMap 中的属性 nextTable = nextTab; // transferIndex 也是 ConcurrentHashMap 的属性,用于控制迁移的位置 transferIndex = n; } int nextn = nextTab.length; // ForwardingNode 翻译过来就是正在被迁移的 Node // 这个构造方法会生成一个Node,key、value 和 next 都为 null,关键是 hash 为 MOVED // 后面我们会看到,原数组中位置 i 处的节点完成迁移工作后, // 就会将位置 i 处设置为这个 ForwardingNode,用来告诉其他线程该位置已经处理过了 // 所以它其实相当于是一个标志。 ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab); // advance 指的是做完了一个位置的迁移工作,可以准备做下一个位置的了 boolean advance = true; boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab /* * 下面这个 for 循环,最难理解的在前面,而要看懂它们,应该先看懂后面的,然后再倒回来看 * */ // i 是位置索引,bound 是边界,注意是从后往前 for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) { Node<K,V> f; int fh; // 下面这个 while 真的是不好理解 // advance 为 true 表示可以进行下一个位置的迁移了 // 简单理解结局:i 指向了 transferIndex,bound 指向了 transferIndex-stride // 下面这个while 的作用是 i 和 bound 进行 赋值 (为每个线程划定任务区) while (advance) { int nextIndex, nextBound; if (--i >= bound || finishing) advance = false; // 将 transferIndex 值赋给 nextIndex // 这里 transferIndex 一旦小于等于 0,说明原数组的所有位置都有相应的线程去处理了 else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) { i = -1; advance = false; } //一次小迁移任务完成后(此时还有得分配),迁移的线程继续来到这里,和想帮忙的线程一起抢 else if (U.compareAndSetInt (this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex, nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ? nextIndex - stride : 0))) { // 看括号中的代码,nextBound 是这次迁移任务的边界,注意,是从后往前 bound = nextBound; i = nextIndex - 1; advance = false; } //抢不到就继续循环,直到退出 } //这个if里面的作用是对所有的迁移操作是否完成进行判断 (判断所有任务是否 OK ) // 或是从 上面第二个 else if 过来的 if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) { int sc; if (finishing) { // 所有的迁移操作已经完成 nextTable = null; // 将新的 nextTab 赋值给 table 属性,完成迁移 table = nextTab; // 重新计算 sizeCtl:n 是原数组长度,所以 sizeCtl 得出的值将是新数组长度的 0.75 倍 sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1); return; } // 之前我们说过,sizeCtl 在迁移前会设置为 (rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2 // 然后,每有一个线程参与迁移就会将 sizeCtl 加 1, // 这里使用 CAS 操作对 sizeCtl 进行减 1,代表做完了属于自己的任务 if (U.compareAndSetInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) { if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) //进来这里就是说明迁移完成,有其他线程在帮忙迁移 //(假如一个次迁移完成,没人帮忙,等号两边应该是相等的) return; //最后一批迁移任务完成 // 到这里,说明 (sc - 2) == resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT, // 也就是说,所有的迁移任务都做完了,也就会进入到上面的 if(finishing){} 分支了 finishing = advance = true; i = n; // recheck before commit } } //下面的 else if 是对分到的任务区进行判断,是否已经迁移过了(是否迁移过的标志就是 ForwardingNode) //要是都不是,那么就是还没迁移咯,开始自己任务区的迁移工作!! // 如果位置 i 处是空的,没有任何节点,那么放入刚刚初始化的 ForwardingNode ”空节点“, //表明这个区域正在迁移 else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null) advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd); // 该位置处是一个 ForwardingNode,代表该位置已经迁移过了 else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) advance = true; // already processed else { // 对数组该位置处的结点加锁,开始处理数组该位置处的迁移工作 synchronized (f) { if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { Node<K,V> ln, hn; // 头结点的 hash 大于 0,说明是链表的 Node 节点 if (fh >= 0) { // 下面这一块和 Java7 中的 ConcurrentHashMap 迁移是差不多的, // 需要将链表一分为二, // 找到原链表中的 lastRun,然后 lastRun 及其之后的节点是一起进行迁移的 // lastRun 之前的节点需要进行克隆,然后分到两个链表中 // 文档中说到大概只有六分之一需要复制 int runBit = fh & n; Node<K,V> lastRun = f; for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) { int b = p.hash & n; if (b != runBit) { runBit = b; lastRun = p; } } if (runBit == 0) { ln = lastRun; hn = null; } else { hn = lastRun; ln = null; } for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) { int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val; if ((ph & n) == 0) ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln); else hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn); } // 其中的一个链表放在新数组的位置 i setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln); // 另一个链表放在新数组的位置 i+n setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn); // 将原数组该位置处设置为 fwd,代表该位置已经处理完毕, // 他线程一旦看到该位置的 hash 值为 MOVED,就不会进行迁移了 setTabAt(tab, i, fwd); // advance 设置为 true,代表该位置已经迁移完毕,进行下一个循环 advance = true; } else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { // 红黑树的迁移 TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f; TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null; TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null; int lc = 0, hc = 0; for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) { int h = e.hash; TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V> (h, e.key, e.val, null, null); if ((h & n) == 0) { if ((p.prev = loTail) == null) lo = p; else loTail.next = p; loTail = p; ++lc; } else { if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null) hi = p; else hiTail.next = p; hiTail = p; ++hc; } } // 如果一分为二后,节点数少于 8,那么将红黑树转换回链表 ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) : (hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t; hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) : (lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t; // 将 ln 放置在新数组的位置 i setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln); // 将 hn 放置在新数组的位置 i+n setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn); // 将原数组该位置处设置为 fwd,代表该位置已经处理完毕, // 其他线程一旦看到该位置的 hash 值为 MOVED,就不会进行迁移了 setTabAt(tab, i, fwd); // advance 设置为 true,代表该位置已经迁移完毕 advance = true; }else if (f instanceof ReservationNode) throw new IllegalStateException("Recursive update"); } } } } }
其中要说一下,当进行transfer 前都会 传入一个 rs 进行CAS ,让我们来看一下 rs 表示什么东西.
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
/** * Returns the stamp bits for resizing a table of size n. * Must be negative when shifted left by RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT. * * Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n) 返回的是 n 前面有多少个零 * */ static final int resizeStamp(int n) { return Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n) | (1 << (RESIZE_STAMP_BITS - 1)); }
我们知道上面代码中的 n 就是数组大小,都是2的N 次方大小,二进制由一个1和多个0组成,即是说,n不同,返回的值(即rs)必定不同。这有什么作用呢?
文档中是这么说的 :
A generation stamp in field sizeCtl ensures that resizings do not overlap.
我们想想要是 sizeCtl 里面就表示包含了扩容的线程数,假如一个线程把 n 变到 2n , 一个线程 把2n 变到 4n 的时候,有可能值就把后面生成的新的数组覆盖掉,那为什么用了 rs 就不会呢?前面说了 n不同,返回的值(即rs)必定不同。
帮助迁移
final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) { Node<K,V>[] nextTab; int sc; if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) && (nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) { int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT; while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab && (sc = sizeCtl) < 0) { // sc == rs + 1 不知是什么意思 if (sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || sc == rs + 1 || transferIndex <= 0) break; //到这里就表示条件满足了, CAS 后进入帮助迁移 //可以知道 nextTab 此时不为空了,要是进入是空的话,方法内部也会创建 if (U.compareAndSetInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) { transfer(tab, nextTab); break; } } return nextTab; } return table; }
get
public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek; int h = spread(key.hashCode()); if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) { //存在返回 if ((eh = e.hash) == h) { if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))) return e.val; } //有可能在迁移 else if (eh < 0) //有可能是红黑树节点,或是其他节点,find 方法在每种节点有重写 return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null; while ((e = e.next) != null) { if (e.hash == h && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) return e.val; } } return null; }