题意:
输入共三行,每行为一个长度在1到100之间的字符串,第1行为一条加密信息,第2行为第1行的加密信息所对应的原信息,第3行则是要求翻译的加密信息。比如
第一行:ABA
第二行:ACA
第三行:BA
的情况下,输入的结果则是 CA
但,还有条件限制,
① :第二行里A~Z这26个字母一定都出现过
② :加密信息与原文信息不能有重复,比如(密文->原信息)A->A,A->B这样是不行的
③ :在②的同理下,X->A,Z->A也是不行的
当不符合以上条件之一时,就输出Failed,否则输出利用密码翻译加密信息后得到的原信息
(分析下3个输入输出样例就很清晰明了了)
分析:
字符一一映射,这时候应该吹一波map大法好了。若对map还不了解的赶紧去学习,超级好用!个人觉得map算是加强版的数组。
如果你会用map,这题已经可以AC一大半了。
我添加了两个bool数组,一个是判断密文里是否已经映射了原信息,另一个是判断A~Z是否全都出现了。
提交代码时,洛谷警告了下语法就AC了。

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<map> 4 #include<string> 5 #include<cstring> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 string str1, str2, str3; 9 map<char, char> mymap; 10 bool ch[27], have[27]; 11 12 int main() 13 { 14 while(cin >> str1 >> str2 >> str3){ 15 int count = 0; 16 memset(ch, false, sizeof(ch)); 17 memset(have, false, sizeof(have)); 18 for(int i = 0; i < str1.size(); i++){ 19 if(!have[str1[i]-'A']) { 20 mymap[str1[i]] = str2[i]; 21 have[str1[i]-'A'] = true; 22 } 23 else break; 24 if(!ch[str2[i]-'A']) { count++; ch[str2[i]-'A'] = true; } 25 } 26 27 if(count != 26) { cout << "Failed" << endl; continue; } 28 else { 29 for(int i = 0; i < str3.size(); i++){ 30 cout << mymap.find(str3[i])->second; 31 } 32 cout << endl; 33 } 34 } 35 return 0; 36 }
下一题:
题意:
输入一个k表示数的大小,下一行输入的字符串表示要表演的姿态。
分析:
也许刚看到这个输出时你跟我一样一脸懵圈,但只要把输出样例复制到记事本上就很清晰了。(如图)
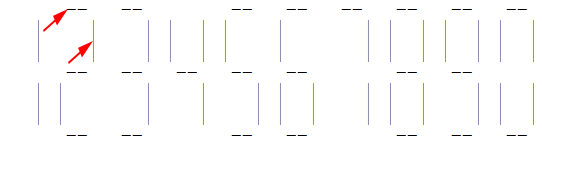
K = 2表示箭头所指的长度分别为2。
结果分析发现是一道模拟题,需要一点耐心去规划每一步的输出。
详细分析贴在代码里:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 string str; 7 int k; 8 9 int main() 10 { 11 while(cin >> k){ 12 cin >> str; 13 14 // 开始模拟 15 for(int j = 0; j < 2*k + 3; j++){ 16 for(int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++){ 17 // k +2 是输出角落那个空格,如果还不清楚请再研究下输出样例 18 if(j == 0 || j == k+1 || j == 2*k+2){ // 输出 '-' 19 // 1,4,7,0 的 '-'输出部分要特殊处理 20 if(str[i] != '1' && (str[i] != '4' || j == k+1) && (str[i] != '7' || j == 0) && (str[i] != '0' || j == 0 || j == 2*k+2)){ 21 for(int h = 0; h < k+2; h++){ 22 if(h == 0 || h == k+1) cout << ' '; 23 else cout << '-'; 24 } 25 } 26 else for(int h = 0; h < k+2; h++) cout << ' '; 27 } 28 29 else { // 输出 '|', 分了两部分,由中间线分开,比如数字 2 的上半部分与下半部分就不一样, 上半部分相同的就放在一起判断输出 30 if(j < k+1){ // 上半部分 31 if(str[i] == '1') for(int h = 0; h < k+2; h++){ 32 if(h == k+1) cout << '|'; 33 else cout << ' '; 34 } 35 else if(str[i] == '2' || str[i] == '3' || str[i] == '7') { 36 for(int h = 0; h < k+2; h++){ 37 if(h == k+1) cout << '|'; 38 else cout << ' '; 39 } 40 } 41 else if(str[i] == '5' || str[i] == '6'){ 42 for(int h = 0; h < k+2; h++){ 43 if(h == 0) cout << '|'; 44 else cout << ' '; 45 } 46 } 47 else if(str[i] == '4' || str[i] == '8' || str[i] == '9' || str[i] == '0'){ 48 for(int h = 0; h < k+2; h++){ 49 if(h == 0 || h == k+1) cout << '|'; 50 else cout << ' '; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 else if(j > k+1){ // 下半部分,同理 55 if(str[i] == '1') for(int h = 0; h < k+2; h++) { 56 if(h == k+1) cout << '|'; 57 else cout << ' '; 58 } 59 else if(str[i] == '2') { 60 for(int h = 0; h < k+2; h++){ 61 if(h == 0) cout << '|'; 62 else cout << ' '; 63 } 64 } 65 else if(str[i] == '3' || str[i] == '4' || str[i] == '5' || str[i] == '7' || str[i] == '9'){ 66 for(int h = 0; h < k+2; h++){ 67 if(h == k+1) cout << '|'; 68 else cout << ' '; 69 } 70 } 71 else if(str[i] == '6' || str[i] == '8' || str[i] == '0'){ 72 for(int h = 0; h < k+2; h++){ 73 if(h == 0 || h == k+1) cout << '|'; 74 else cout << ' '; 75 } 76 } 77 } 78 } 79 cout << ' '; // 每输出完一个数字就空出一格 80 } 81 cout << endl; // 一行数字遍历完毕,换行继续输出 82 } 83 } 84 return 0; 85 }
下一题:
题意:
找到句子里与数字有关的单词,平方后排列,输出排列后最小的数字。
分析:
暴力解决。因为输入只有6个单词,所以是可以暴力解决的(笑)
然后再用排序算法把小的放前面,输出结果去掉开头的0即可。
注意,个位数前面保留0的这一性质!

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 string cha[7]; 8 string ch[7]; 9 int n = 0; 10 for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++){ // 暴力找出平方后的数字 11 cin >> ch[i]; 12 if(ch[i] == ".") break; 13 if(ch[i] == "one" || ch[i] == "a" || ch[i] == "another" || ch[i] == "first") 14 cha[n++] = "01"; 15 else if(ch[i] == "two" || ch[i] == "both" || ch[i] == "second") cha[n++] = "04"; 16 else if(ch[i] == "three" || ch[i] == "third") cha[n++] = "09"; 17 else if(ch[i] == "four") cha[n++] = "16"; 18 else if(ch[i] == "five") cha[n++] = "25"; 19 else if(ch[i] == "six") cha[n++] = "36"; 20 else if(ch[i] == "seven") cha[n++] = "49"; 21 else if(ch[i] == "eight") cha[n++] = "64"; 22 else if(ch[i] == "nine") cha[n++] = "81"; 23 else if(ch[i] == "ten" || ch[i] == "twenty") cha[n++] = "00"; 24 else if(ch[i] == "eleven") cha[n++] = "21"; 25 else if(ch[i] == "twelve") cha[n++] = "44"; 26 else if(ch[i] == "thirteen") cha[n++] = "69"; 27 else if(ch[i] == "fourteen") cha[n++] = "96"; 28 else if(ch[i] == "fifteen") cha[n++] = "25"; 29 else if(ch[i] == "sixteen") cha[n++] = "56"; 30 else if(ch[i] == "seventeen") cha[n++] = "89"; 31 else if(ch[i] == "eighteen") cha[n++] = "24"; 32 else if(ch[i] == "nineteen") cha[n++] = "61"; 33 } 34 for(int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) // 排序 35 { 36 for(int j = 0; j < n-1-i; j++) 37 { 38 if(cha[j] > cha[j+1]) 39 { 40 string b = cha[j]; 41 cha[j] = cha[j+1]; 42 cha[j+1] = b; 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 string ans = ""; 47 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 48 { 49 ans += cha[i]; 50 } 51 bool zero = false; // 判断开头是否有 0 52 for(int i = 0; i < n*2; i++) 53 { 54 if(ans[i] != '0' || zero){ 55 zero = true; 56 cout << ans[i]; 57 } 58 else if(!zero) continue; 59 } 60 if(n == 0) cout << "0 "; // 当句子里没有数字时的特判处理 61 return 0; 62 }
下一题:
题意:
给一个n,然后再给n个正整数,问这n个数怎么组拼成的数最大。
分析:
字典序大的数放前面就可以了。
因此可以用一个sort()函数解决,只需要在sort()里加一个
bool cmp(string a, string b)
{
return a+b > b+a;
}
判断就ok,简单清晰。(参考了洛谷作者King_LRL的题解)
当初我做这题的时候还不会用string与sort函数,结果用char[]与冒泡排序解决了,代码太长还没注释,以至于现在看起来有点头疼。但能AC的代码都是好代码吧。

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 #include<cstring> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int MAX = 21; 6 char num[MAX][10005]; 7 char ans[100000]; 8 bool go = false; 9 int main() 10 { 11 int n; 12 cin >> n; 13 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 14 cin >> num[i]; 15 16 for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) 17 for(int j = 0; j < n - 1 - i; j++) 18 { 19 int j1 = strlen(num[j]); 20 int j2 = strlen(num[j+1]); 21 int x = 0, y = 0; 22 while(x < j1 && y < j2) 23 { 24 if(num[j][x] < num[j+1][y]) 25 { 26 char b[10005]; 27 strcpy(b, num[j]); 28 strcpy(num[j], num[j+1]); 29 strcpy(num[j+1], b); 30 go = true; 31 break; 32 } 33 else if(num[j][x] > num[j+1][y]) { go = true; break; } 34 else if(num[j][x] == num[j+1][y]) x++, y++; 35 } 36 if(!go){ 37 if(j1 < j2){ 38 if(num[j][0] > num[j+1][j1]){ 39 char b[10005]; 40 strcpy(b, num[j]); 41 strcpy(num[j], num[j+1]); 42 strcpy(num[j+1], b); 43 } 44 } else if(j1 > j2){ 45 if(num[j][j2] < num[j+1][0]){ 46 char b[10005]; 47 strcpy(b, num[j]); 48 strcpy(num[j], num[j+1]); 49 strcpy(num[j+1], b); 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 55 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 56 strcat(ans, num[i]); 57 58 cout << ans << endl; 59 60 return 0; 61 }
最后小结:
要想熟练运用字符串,除了要熟悉string以外,STL里的一些容器也要会用。还是得要继续用功啊!
