一、什么叫单例模式
“单例”从字段意思来讲,故明思议其实就是只有一个实例,那结合面向对象来讲,就是针对一个对象来说,它对外只有一个实例。
单例模式(Signleton)---是一种常用的软件设计模式。在它的核心结构中只包含一个被称为单例的特殊类。通过单例模式可以保证系统中,应用该模式的类一个类只有一个实例。即一个类只有一个对象实例(百度百科)
二、单例模式的目的
保证一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个访问它的全局访问点

说明 :图中GetInstanc()方法即为拿到的唯一入口点,该UML图中只有该方法以public修饰,向外公开,并返回对应Singleton对象
那么我们可以得出结论:
1. 单例类自己保存它的唯一实例----------------------其实就是得到的静态的instance
2. 单例类保证没有其他实例能被创建出来----------只有一个GetInstance()是公开的,Single()是私有构造,只能从GetInstance()创建,在这里保证没有其他实例
3. 单例类可以向外提供一个访问该实例的入口----GetInstance()方法
三、单例模式的应用常景
例如:
1. windows操作系统里的资源管理都是由资源管理器里统一显示
2. 一些小公司的办公室里打印文档都只能通过一台唯一的打印机
3. 远程过程调用对象继承MarshalByRefObject激活模式WellKnownObjectMode.SingleCall确保客户端代理客户只有一个
四、单例模式有那几种类型
1. 一般普通单例(见二中的类图)
2. 安全线程单例
3. 双重锁定的单例
4. 静态初始化单例
5.延迟初始化(这种基本除非常特殊场景外很少实际应用)
五、几种单例的具体实现及分析
1. 普通常见单例
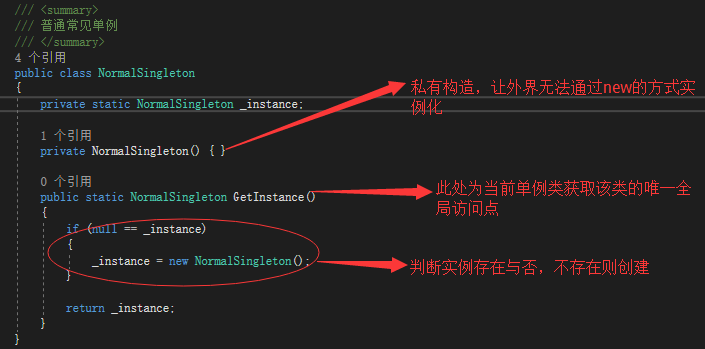

1 /// <summary> 2 /// 普通常见单例 3 /// </summary> 4 public class NormalSingleton 5 { 6 private static NormalSingleton _instance; 7 8 private NormalSingleton() { } 9 10 public static NormalSingleton GetInstance() 11 { 12 if (null == _instance) 13 { 14 _instance = new NormalSingleton(); 15 } 16 17 return _instance; 18 } 19 }

1 static void Main(string[] args) 2 { 3 var normalSingleton = NormalSingleton.GetInstance(); 4 var normalSingleton1 = NormalSingleton.GetInstance(); 5 6 if (normalSingleton.Equals(normalSingleton1)) 7 { 8 Console.WriteLine("normalSingleton与normalSingleton1是同一个对象,HashCode是{0}", normalSingleton.GetHashCode()); 9 } 10 else 11 { 12 Console.WriteLine("normalSingleton与normalSingleton1不是同一个对象"); 13 } 14 15 Console.ReadKey(); 16 }
结果输出:

但之所以我们叫他叫普通常见单例模式,是因为这里只涉及单线程,试想下如果有多个线程同时来请求该单例,同时去调GetInstance()会出现什么情况呢?
我们猜想在这多个线程同时去GetInstance时,因为是没有做线程同步的,这里几乎可以想象到当多个线程去判断一个非线程同步的变量_instance时,自然而然的会生成不同的实例化对象,而这明显不是我们要的,可以看下图中结果

1 class Program 2 { 3 static NormalSingleton singleton = null; 4 5 static void Main(string[] args) 6 { 7 var thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(GetInstance)); 8 var thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(GetInstance)); 9 thread1.Start(); 10 thread2.Start(); 11 12 Console.ReadKey(); 13 } 14 15 static void GetInstance() 16 { 17 singleton = NormalSingleton.GetInstance(); 18 Console.WriteLine("singleton->hashCode is {0}", singleton.GetHashCode()); 19 } 20 }
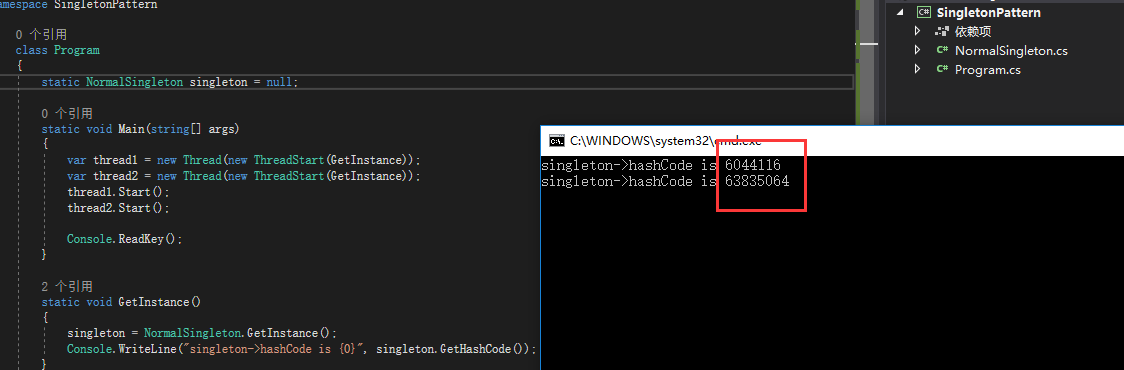
明显此时这2个线程访问的不再是同一个对象了。那么面对这种多线程访问的问题我们该如何处理呢?
其实这就会引入我们的第2种单例--------基于线程安全的单例
2. 线程安全单例
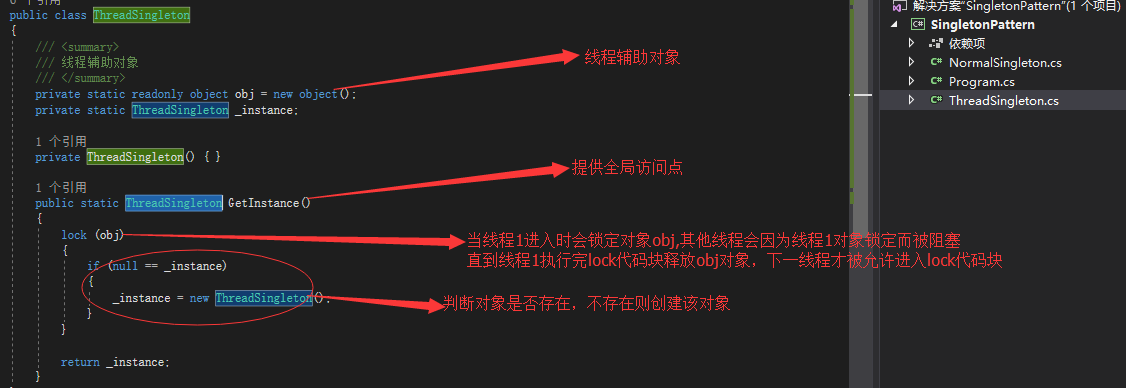
我们尝试引入一个线程辅助对象锁lock(其实本质是实现了Moniter.Entry及Moniter.Exit,这个通过IL代码是可以看到的),这样在一个线程进入临界区lock(obj)代码块后,在该部分代码块未执行完成前,另一个线程是不会进入到该临界区代码块的,直至上一个线程执行完lock代码块后,才被允许进入(本质是前一线程进入lock块后,其他对象是不允许访问该lock的对象而只能等待直至上一线程释放该辅助对象)
OK,我们可以先更改代码,看下效果
首先,更改NormalSingleton至ThreadSingleton

1 public class ThreadSingleton 2 { 3 /// <summary> 4 /// 线程辅助对象 5 /// </summary> 6 private static readonly object obj = new object(); 7 private static ThreadSingleton _instance; 8 9 private ThreadSingleton() { } 10 11 public static ThreadSingleton GetInstance() 12 { 13 lock (obj) 14 { 15 if (null == _instance) 16 { 17 _instance = new ThreadSingleton(); 18 } 19 } 20 21 return _instance; 22 } 23 }
更改原客户端中的NormalSingleton为ThreadSingleton

1 class Program 2 { 3 static ThreadSingleton singleton = null; 4 5 static void Main(string[] args) 6 { 7 var thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(GetInstance)); 8 var thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(GetInstance)); 9 thread1.Start(); 10 thread2.Start(); 11 12 Console.ReadKey(); 13 } 14 15 static void GetInstance() 16 { 17 singleton = ThreadSingleton.GetInstance(); 18 Console.WriteLine("singleton->hashCode is {0}", singleton.GetHashCode()); 19 } 20 }
运行结果:
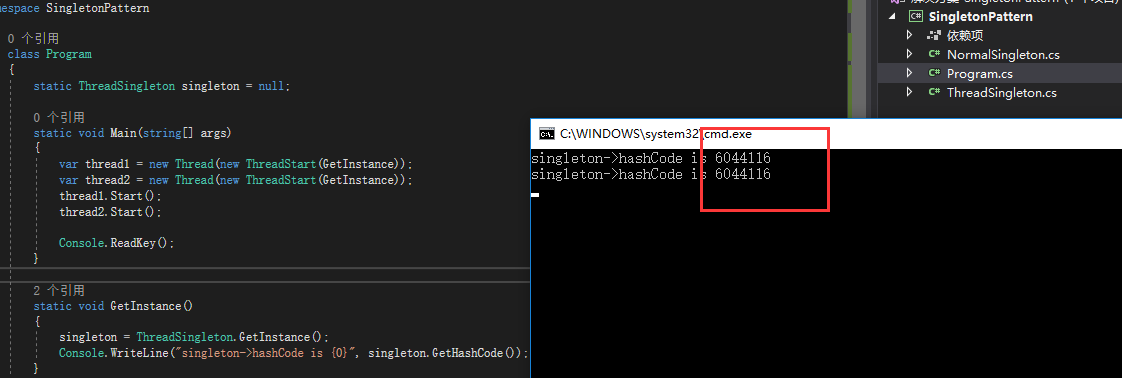
我们看到这时候,2个线程返回的是同一个对象了,那有同学可能疑惑我这2个线程是不是真的一个释放了obj对象另一个线程才访问lock代码块的呢?
OK,我们可以把每个线程的hashcode及开始结束时间打印出来,这样我相信大家就会明了并确信确定是前一线程执行完lock块后后一线程才开始执行的
更改ThreadSingleton如下:

1 public class ThreadSingleton 2 { 3 /// <summary> 4 /// 线程辅助对象 5 /// </summary> 6 private static readonly object obj = new object(); 7 private static ThreadSingleton _instance; 8 9 private ThreadSingleton() { } 10 11 public static ThreadSingleton GetInstance() 12 { 13 lock (obj) 14 { 15 // print current thread hashcode & start time 16 Console.WriteLine("Current thread num is {0}, startTime is {1}", Thread.CurrentThread.GetHashCode(), DateTime.Now); 17 if (null == _instance) 18 { 19 _instance = new ThreadSingleton(); 20 } 21 // print current thread hashcode & end time & singleton instance hashcode 22 Console.WriteLine("Current thread num is {0}, EndTime is {1}, Instance hashcode is {2}" 23 , Thread.CurrentThread.GetHashCode(), DateTime.Now, _instance.GetHashCode()); 24 } 25 26 return _instance; 27 } 28 }
CTRL+ F5后
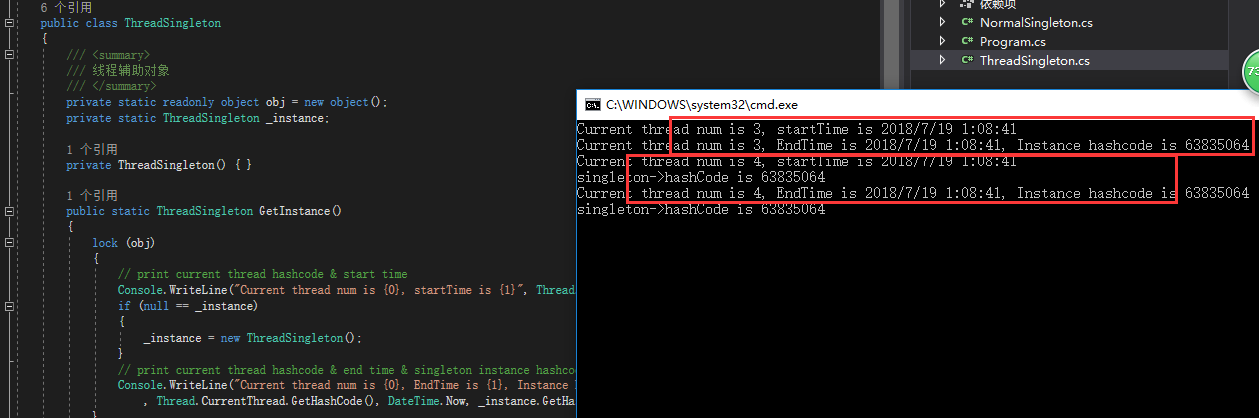
其实第2种模式中,我们发现一个问题,就是我们不管单例类的实例是不是已经有了(_instance是否为null),我们都强行先锁定然后再判断,这样相对为说对对系统资源开消来说可能也是一种浪费,试想如果第2个线程在进来之前发现当前_instance已经被实例化了,我们为毛还要继续去锁定辅助对象obj,这不是浪费吗???
OK,鉴于此,我们是不是考虑在进行lock(obj)前看如果_instance已经实例化了,我们直接返回,是不是会比第2种情况节约很多系统开销? 对,这就是我们接着要讲的第3种单例模式------基于双重锁定的单例
3. 双重锁定单例
第一次线程在对象未初始化时,去判断对象是否已实例化,如果已经实例化,则直接返回,不用每次去加锁操作,减少性能损耗,如果未实例化,则再走2(线程安全的单例)

1 public class DoubleLockSingleton 2 { 3 /// <summary> 4 /// 线程辅助对象 5 /// </summary> 6 private static readonly object obj = new object(); 7 private static DoubleLockSingleton _instance; 8 9 private DoubleLockSingleton() { } 10 11 public static DoubleLockSingleton GetInstance() 12 { 13 // first to judge the instance is inited, if ok then return instance 14 if (null == _instance) 15 { 16 Console.WriteLine("Current instance is not inited ? {0}", null == _instance); 17 // if the instance is not inited then lock the object to avoid other thread into this code regein when curren thread accesses the code 18 lock (obj) 19 { 20 // print current thread hashcode & start time 21 Console.WriteLine("Current thread num is {0}, startTime is {1}", Thread.CurrentThread.GetHashCode(), DateTime.Now); 22 if (null == _instance) 23 { 24 _instance = new DoubleLockSingleton(); 25 } 26 // print current thread hashcode & end time & singleton instance hashcode 27 Console.WriteLine("Current thread num is {0}, EndTime is {1}, Instance hashcode is {2}" 28 , Thread.CurrentThread.GetHashCode(), DateTime.Now, _instance.GetHashCode()); 29 } 30 } 31 32 return _instance; 33 } 34 }

修改客户端如下:

1 class Program 2 { 3 static DoubleLockSingleton singleton = null; 4 5 static void Main(string[] args) 6 { 7 var thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(GetInstance)); 8 var thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(GetInstance)); 9 thread1.Start(); 10 thread2.Start(); 11 Thread.Sleep(1000); 12 var thread3 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(GetInstance)); 13 thread3.Start(); 14 15 Console.ReadKey(); 16 } 17 18 static void GetInstance() 19 { 20 singleton = DoubleLockSingleton.GetInstance(); 21 Console.WriteLine("singleton->hashCode is {0}", singleton.GetHashCode()); 22 } 23 }
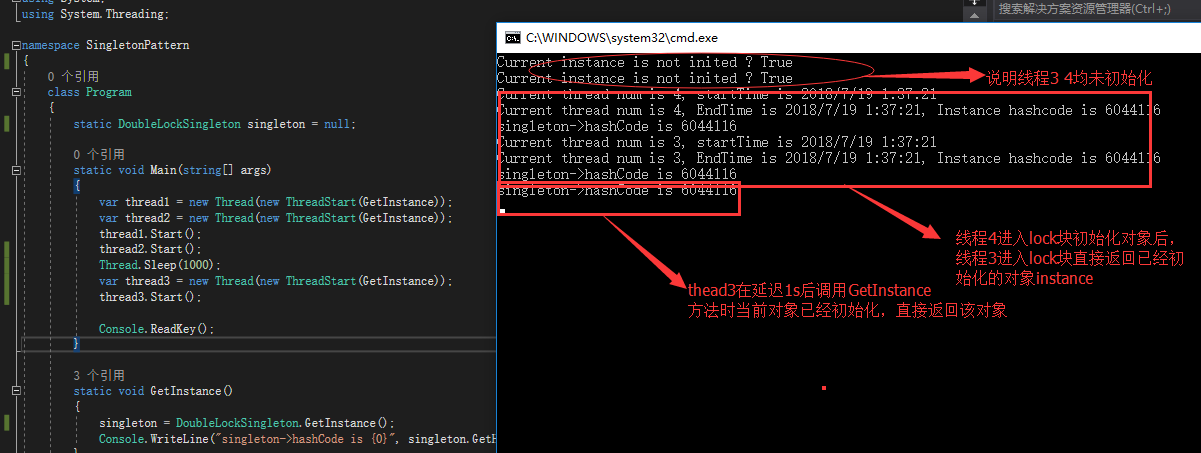
其实在我们实际应用中,C#本身也提供了一套“静态初始化”方法,这种方法不需要编写线程安全代码,来我们看看静态初始化单例
4. 静态初始化单例
公共运行库提供静态初始化单例,一种密封类,防止派生类的产生,变量采用readonly修饰,只能在静态初始化期间(此处显示的示例)或在类构造函数中分配变量

1 public sealed class SealdSingleton 2 { 3 private static readonly SealdSingleton _instance = new SealdSingleton(); 4 private SealdSingleton() { } 5 6 public static SealdSingleton GetInstance() 7 { 8 return _instance; 9 } 10 }

修改客户端代码,还是用SealdSingleton替换原来singleton,Ctrl + F5效果如下:

5. 延迟初始化单例
延迟初始化采用内部类的方式,在内部类中初始化该对象

1 public class NestedSingleton 2 { 3 NestedSingleton() { } 4 5 public static NestedSingleton Instance 6 { 7 get 8 { 9 return NestedClass.instance; 10 } 11 } 12 13 class NestedClass 14 { 15 NestedClass() { } 16 17 internal static readonly NestedSingleton instance = new NestedSingleton(); 18 } 19 }

同时客户端修改:用NestedSingleton替换single,然后Ctrl + F5
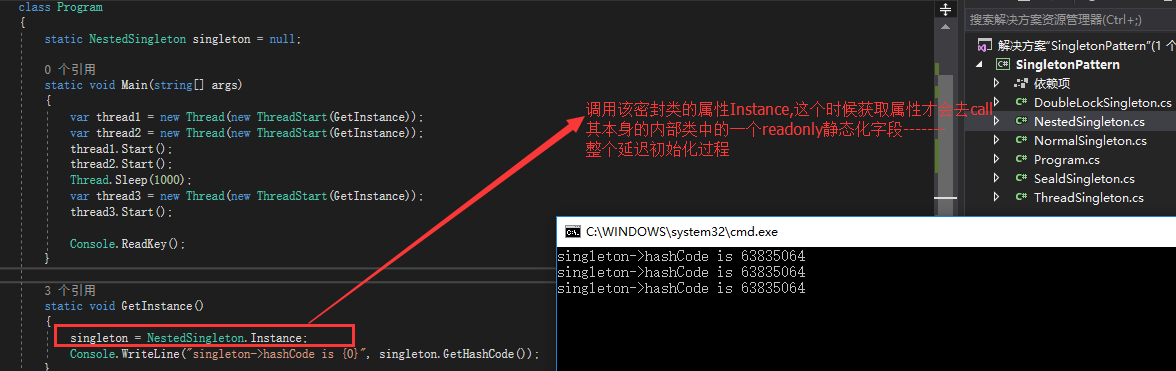
但因为此种实际应用中几乎很少使用,故不作推荐
至此,整个单例模式讲解完毕,相关代码稍后会提交至github及csdn中,有兴趣可以下载调试研究
git地址:https://gitee.com/jimmyTown_admin_admin/SingletonPattern
