两张表,学生表,地址表,学生表中的addressId对应地址表中的id。

首先构建两个实体类,Student,Address
package com.maya.model; public class Student { private int id; private String name; private int age; private Address address; public Address getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(Address address) { this.address = address; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Student(int id, String name, int age) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } public Student(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public Student() { super(); } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", address=" + address + "]"; } }
package com.maya.model; public class Address { private int id; private String sheng; private String shi; private String qu; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getSheng() { return sheng; } public void setSheng(String sheng) { this.sheng = sheng; } public String getShi() { return shi; } public void setShi(String shi) { this.shi = shi; } public String getQu() { return qu; } public void setQu(String qu) { this.qu = qu; } @Override public String toString() { return "Address [id=" + id + ", sheng=" + sheng + ", shi=" + shi + ", qu=" + qu + "]"; } }
接下来我们先介绍以下3种不太常用的方式(当然平时做些小项目的话还是很直接很暴力的):
1.
<resultMap type="Student" id="StudentResult"> <id property="id" column="id"/> <result property="name" column="name"/> <result property="age" column="age"/> <result property="address.id" column="addressId"/> <result property="address.sheng" column="sheng"/> <result property="address.shi" column="shi"/> <result property="address.qu" column="qu"/> </resultMap>
当然这是最笨的一种办法,通过成员属性的属性来对应其数据库的字段
2.
<resultMap type="Student" id="StudentResult"> <id property="id" column="id"/> <result property="name" column="name"/> <result property="age" column="age"/> <association property="address" javaType="Address"> <result property="id" column="id"/> <result property="sheng" column="sheng"/> <result property="shi" column="shi"/> <result property="qu" column="qu"/> </association> </resultMap>
通过直接在StudentMapper中的属性中定义association标签来实现
property是属性,javaTye是引用的类型,紧接着将Address的属性也全部配置进来
3.
<resultMap type="Address" id="AddressResult"> <result property="id" column="id"/> <result property="sheng" column="sheng"/> <result property="shi" column="shi"/> <result property="qu" column="qu"/> </resultMap> <resultMap type="Student" id="StudentResult"> <id property="id" column="id"/> <result property="name" column="name"/> <result property="age" column="age"/> <association property="address" resultMap="AddressResult"/> </resultMap>
在studentMapper中定义两个resultMapper,其实这种方式就算不错了,但是如果别的mapper也需要Address呢?很显然这就不是很实用了。
当然这已经很接近我们常用的方法了。
最常用的就是,再定义一个mapper接口和mapper映射,通过association属性来引入,具体代码如下:
0.
首先定义Address的接口与映射文件
package com.maya.mappers; import com.maya.model.Address; public interface AddressMapper { //我们只需要定义这一个方法就ok, //因为当穿过来的Student的外键address时,这里接收的就是其主键值,这样我们就能查到student对应的地址了 public Address getById(int id); }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.maya.mappers.AddressMapper"> <!-- resultMap是要有的,大家都这么写,因为这样重用性高。用其它的方式当然也没错 --> <resultMap type="Address" id="AddressResult"> <id property="id" column="id" /> <result property="sheng" column="sheng" /> <result property="shi" column="shi" /> <result property="qu" column="qu" /> </resultMap> <select id="getById" parameterType="int" resultMap="AddressResult"> select * from address where id=#{id} </select> </mapper>
下面是StudentMapper
<!-- 通常当查询结果是一个集合的话,我们都会在这里定义一个resultMap,用来给下面的方法引用 --> <resultMap type="Student" id="StudentResult"><!-- type就是集合中的类型,id随便你怎么起 --> <id property="id" column="id"></id><!-- property是类的属性名,对应,column是数据库的字段名 --> <result property="name" column="name" /> <result property="age" column="age" /> <association property="address" column="addressId" select="com.maya.mappers.AddressMapper.getById"></association> <!-- property是属性名,column是外键列,select是对应的根据外键id寻找其表中数据的方法 --> </resultMap>
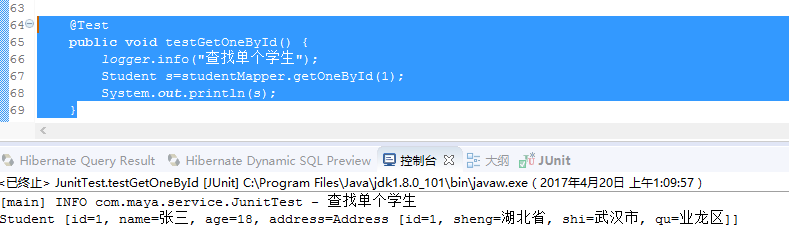
Junit测试结果