1.在IO流中 , 一定要把 读入 , 写出 搞清楚 . 不然学起来很费劲. (站在内存的角度看)
读入 : 向程序中输入数据
写出 : 程序向外输出数据
2.流的分类

3.流的体系结构

4.节点流(文件流)的使用
public class IOTest { //InputStream:继承自InputStream的流都是用于向程序中输入数据的,且数据单位都是字节(8位)。 //OutputSteam:继承自OutputStream的流都是程序用于向外输出数据的,且数据单位都是字节(8位)。 //Reader:继承自Reader的流都是用于向程序中输入数据的,且数据单位都是字符(16位)。 //Writer:继承自Writer的流都是程序用于向外输出数据的,且数据单位都是字符(16位)。 @Test public void test1() throws IOException { //读取hello中的内容 //1.实例化file类的对象 , 表明要操作的文件 File file = new File("D:\workspace\hello.txt"); //2.创建具体的流 FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(file); //3.数据的读入 : read()返回读入的一个字符 , 如果读到最后一个字符 , 返回-1 int read = fileReader.read(); while (read!=-1){ System.out.print((char)read); read = fileReader.read(); } //4.关闭流 : java的回收机制对流是无效的 fileReader.close(); } //read()方法的强化 @Test public void test2(){ FileReader fr = null; try { //1.获取文件 File file = new File("D:\workspace\hello.txt"); //2.获取操作文件的流 fr = new FileReader(file); //3.操作数据 char[] chars = new char[5]; int len; //fr.read(chars) : 返回每次读入到chars数组中字符的个数,读完返回-1 while ((len=fr.read(chars))!=-1){ for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { System.out.print(chars[i]); } } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //4.关闭流 try { fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /* 输出流 : 将内存中的数据输出到硬盘的文件中 1.写入数据时, 如果文件不存在, 自动创建 2.FileWriter(File file, boolean append)构造器append默认为false , 即覆盖原文件内容 */ @Test public void test3()throws Exception{ File file = new File("hello1.txt"); FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(file,true); fileWriter.write("I have a dream! "); fileWriter.write("Do you know?"); fileWriter.close(); } /* 复制文件 */ @Test public void test4(){ FileReader fr =null; FileWriter fw =null; try { //1.创建两个file对象 , 一个读入(已存在) , 一个写出(不存在) File file1 = new File("hello1.txt"); File file2 = new File("hello2.txt"); //2.创建读入流 和 写出流 fr = new FileReader(file1); fw = new FileWriter(file2); //3.读入 和 写出 操作 char[] arr = new char[5]; int len; while ((len = fr.read(arr)) != -1) { //从0 开始 , 写出len个字符 fw.write(arr, 0, len); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //4.关闭流 try { fr.close(); fw.close(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
/* 字节流 : InoutStream OutputStream 字符流 : Reader Writer 1.处理非文本文件(.jpg,.MP3,.mp4,.doc,.avi,.ppt) , 使用字符流 2.处理文本文件(.txt,.java,.c) , 使用字节流 */ //复制图片 @Test public void test(){ FileInputStream fis =null; FileOutputStream fos =null; try { File file1 = new File("图片1.jpg"); File file2 = new File("图片2.jpg"); fis = new FileInputStream(file1); fos = new FileOutputStream(file2); //因为是非文本数据 , 所以需要用byte[] byte[] arr = new byte[5]; int len; //用来记录读取的长度 while ((len = fis.read(arr)) != -1) { fos.write(arr, 0, len); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { fis.close(); fos.close(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
5.处理流
当你用节点流的时候你会发现,它会频繁的访问i/o流的次数,为避免这样而损耗我们的硬盘 这时我们就用处理流。
那到底什么是处理流呢?通俗的说就是包在节点流(文件流)外面的流,类似于包在管道外面的管道。(增强功能)
5.1 缓冲流
/* 处理流 : 就是"包"在已有的流基础之上 缓冲流(处理流的一种): BufferedInputStream BufferedOutputStream BufferedReader BufferedWriter 作用 : 提高读取和写入的速度 , 原因 : 内部提供了一个缓冲区 */ //使用缓冲流复制图片 @Test public void test2(){ BufferedInputStream bis =null; BufferedOutputStream bos =null; try { //1.获取文件 File file1 = new File("图片1.jpg"); File file3 = new File("图片3.jpg"); //2.创建流 //2.1 节点流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file3); //2.2 处理流(缓冲流) bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); //3.操作数据 byte[] buffer = new byte[10]; int len; //用来记录读取的长度 while ((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1) { bos.write(buffer, 0, len); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //4.关闭流 //要求 : 先关外层流, 再关内层流 try { //当外层流关闭时 , 内层流也会自动关闭 bis.close(); bos.close(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
5.2 转换流


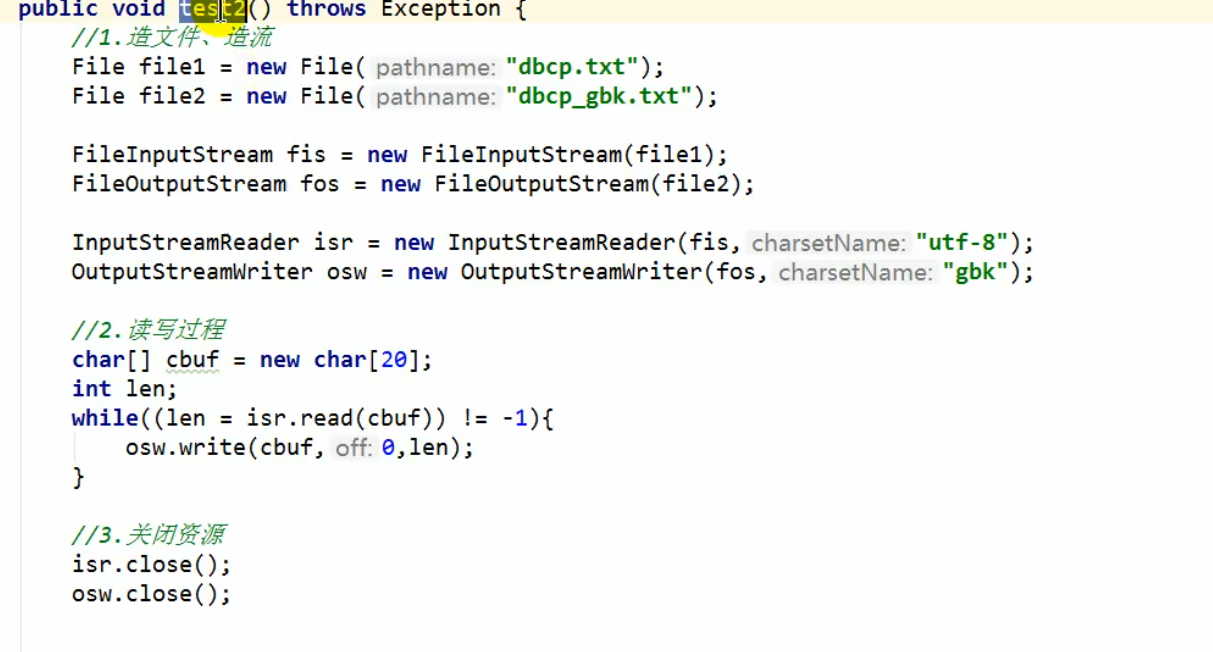
5.3 序列化流 (对象流)

5.3.1 什么是对象的序列化

5.3.2 对象序列化的要求

5.3.3 代码示例
//对象的 序列化 和 反序列化 public class ObjectStream { //序列化 @Test public void test()throws IOException { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("Object.dat")); String str = new String("我爱中国!"); oos.writeObject(str); oos.flush(); oos.close(); } //反序列化 @Test public void test2() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("Object.dat")); Object o = ois.readObject(); String str = (String) o; System.out.println(str); ois.close(); } }
5.4打印流

5.5 数据流

5.6随意操作文件流

