A Candies
观察这个式子左边,这玩意就等于 (x(2^k-1))。于是我们枚举所有的 (2^k-1),看看是否存在 (x)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int T, n;
int a[] = { 0, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, 1023, 2047, 4095, 8191, 16383, 32767, 65535, 131071, 262143, 524287, 1048575, 2097151, 4194303, 8388607, 16777215, 33554431, 67108863, 134217727, 268435455, 536870911, 1073741823 };
int main()
{
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i < 30; i++)
if(n % a[i] == 0)
{
printf("%d
", n / a[i]);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
B Balanced Array
先说说不合法的情况——(n/2) 是奇数:因为奇数个奇数是奇数,奇数个偶数是偶数,所以两边不可能相等。
偶数部分按照类似 (2,4,6,8...) 这样随便构造,奇数部分的前面 (=) 偶数部分对应数 (-1),最后一个再把和变成一样的。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int T, n, sum1, sum2, a[1000000];
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
if((n / 2) % 2 != 0) { printf("NO
"); continue; }
printf("YES
");
a[0] = sum1 = sum2 = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n / 2; i++) a[i] = a[i - 1] + 2, sum1 += a[i];
for(int i = n / 2 + 1; i < n; i++) a[i] = a[i - n / 2] - 1, sum2 += a[i];
a[n] = sum1 - sum2;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("
");
}
return 0;
}
C Alternating Subsequence
如果把连续的正数算作一组,连续的负数算作一组,题面就是要求在每一组中选出一个数,使和最大。只要在每一组里面取出一个最大数加到答案里就行。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
long long T, n, ans = 0, max_, a[1000000];
int main()
{
scanf("%lld", &T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%lld", &n);
max_ = ans = a[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%lld", &a[i]);
if(a[i] < 0 && a[i - 1] > 0 || a[i] > 0 && a[i - 1] < 0 || i == 1)
{
ans += max_;
max_ = a[i];
}
else max_ = max(max_, a[i]);
}
ans += max_;
printf("%lld
", ans);
}
return 0;
}
D Constant Palindrome Sum
先枚举 (x)。如果把 (a[i]) 和 (a[n-i+1]) 算作一组,每一组都有 (3) 种情况:不需要改/改一个数/改两个数。
(1.) 预处理 (cnt[i]) 表示和本来就等于 (i) 的有几组,那么就有 (cnt[x]) 组根本不需要改。
(2.) 大部分只需要改一个。若两个数分别为 (x_0,x_1),只要把 (x_0) 改为 (x-x_1) 或把 (x_1) 改为 (x-x_0) 即可。
(3.) 若 (x_0 >= x) && (x_1 >= x) 或 (x-x_0 > k) && (x - x_1 > k),这种需要两个数都改。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2333333;
int T, n, k, ans = 0x3f3f3f3f, a[N], cnt[N], b[N], sum1[N], sum2[N], c[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n / 2; i++)
{
cnt[a[i] + a[n - i + 1]]++;
b[max(a[i], a[n - i + 1])]++;
c[min(a[i], a[n - i + 1])]++;
}
sum1[0] = sum2[2 * k + 1] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * k; i++) sum1[i] = sum1[i - 1] + b[i];
for(int i = 2 * k; i > 0; i--) sum2[i] = sum2[i + 1] + c[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * k; i++)
{
if(i > k) ans = min(ans, n / 2 - cnt[i] + sum1[i - k - 1]);
else ans = min(ans, n / 2 - cnt[i] + sum2[i]);
}
printf("%d
", ans);
for(int i = 1; i <= n / 2; i++)
{
cnt[a[i] + a[n - i + 1]] = 0;
b[max(a[i], a[n - i + 1])] = 0;
c[min(a[i], a[n - i + 1])] = 0;
}
ans = 0x3f3f3f3f;
}
return 0;
}
E Weights Distributing
一道可爱的图论题~
首先肯定不需要真的先去构造边权再跑最短路,而是应该设计一种走法,按照一定方式加入边权,满足花费最少。
这个“一定方式”很简单:从小到大把边权安排在 走过的路上,至于那些没走过的,我们不关心。
有两种情况:
(1.) 没有重复走,直接 (bfs) 最短路
(2.) 重复走了(如下图):
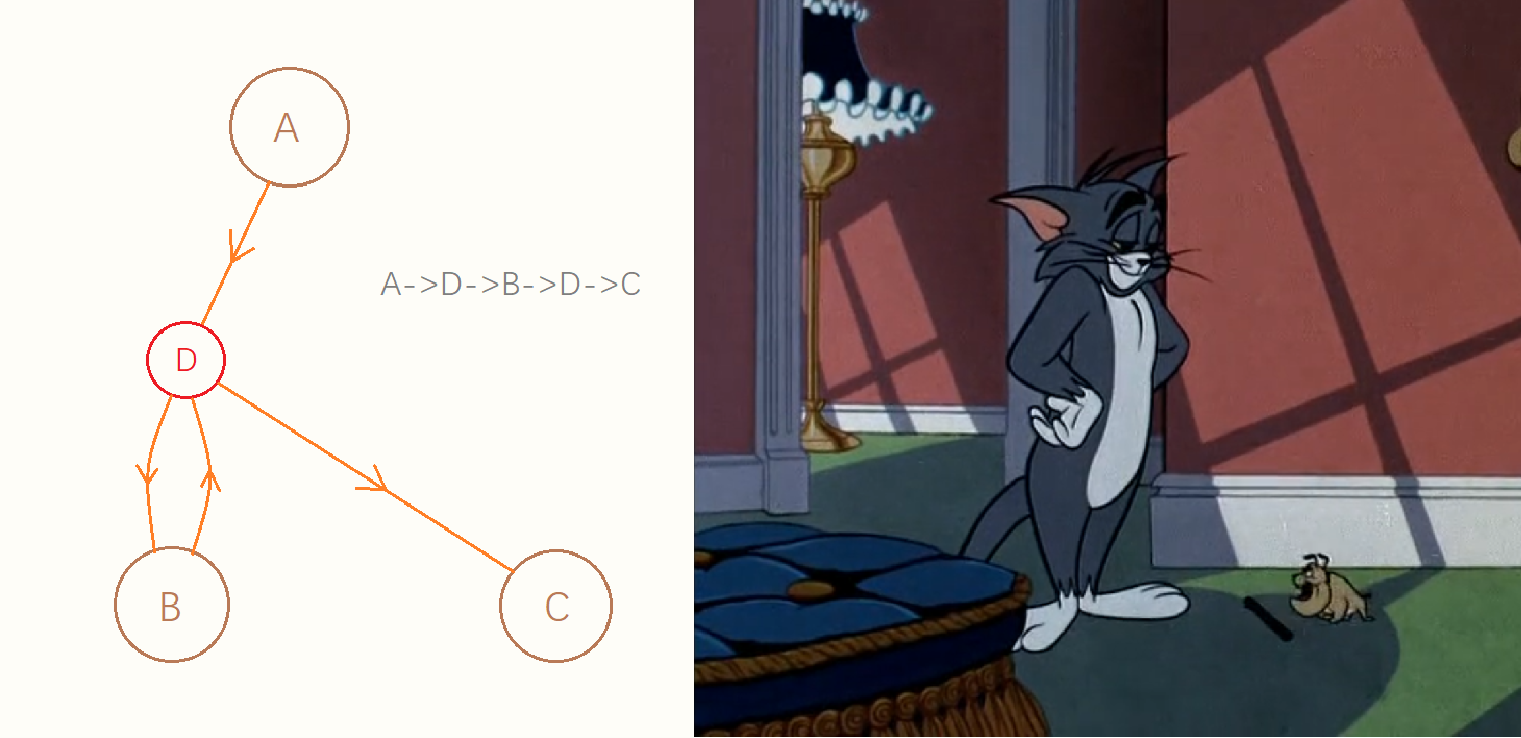
枚举这个点 D,然后把如上图的 (4) 部分路径算出来,全部相加即可。当 D=A 或 B 时,与第一种情况相同,所以不需要单独写第一种情况。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 666666;
struct edge { int nxt, to; } e[N];
int T, n, m, a, b, c, cnt = 0;
int vis[N], dis[3][N], head[N], p[N];
LL sum[N], ans = 999999999999999;
void add(int x, int y)
{
e[++cnt] = (edge) { head[x], y };
head[x] = cnt;
e[++cnt] = (edge) { head[y], x };
head[y] = cnt;
}
void bfs(int k)
{
queue <int> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) vis[i] = 0, dis[k][i] = 0;
if(k == 0) vis[a] = 1, q.push(a);
if(k == 1) vis[b] = 1, q.push(b);
if(k == 2) vis[c] = 1, q.push(c);
while(!q.empty())
{
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nxt)
{
int v = e[i].to;
if(vis[v]) continue;
dis[k][v] = dis[k][u] + 1;
vis[v] = 1, q.push(v);
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &a, &b, &c);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) scanf("%d", &p[i]);
sort(p + 1, p + m + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + p[i];
for(int i = 1, u, v; i <= m; i++)
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v), add(u, v);
bfs(0), bfs(1), bfs(2);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int re = dis[1][i], len = dis[0][i] + re + dis[2][i];
if(len > m) continue;
ans = min(ans, sum[re] + sum[len]);
}
printf("%lld
", ans);
// Clear
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) head[i] = vis[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) e[i].nxt = e[i].to = 0;
cnt = 0, ans = 9999999999999999;
}
return 0;
}
F Restore the Permutation by Sorted Segments
这道题不会做(捂脸),在网上找了一篇题解
由于不会用 (set),而数据范围那么小,直接在 (dfs) 里面暴力乱搞,顺便判断合不合法就好。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 333;
int T, n, vis[N], k[N], a[N][N], use[N], b[N];
bool check(int x, int num)
{
int tot, id, y;
vis[x] = 1, use[num] = x;
if(num == n) return true;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
tot = 0;
for(int j = 1; j <= k[i]; j++)
if(!vis[a[i][j]]) tot++, y = a[i][j];
if(tot == 1) { id = i; break; }
}
if(tot == 1)
{
int fl = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= k[id]; i++) b[a[id][i]] = 1;
for(int i = num; i >= num - k[id] + 2; i--)
if(!b[use[i]]) fl = false;
for(int i = 1; i <= k[id]; i++) b[a[id][i]] = 0;
if(fl == false) return false;
else return check(y, num + 1);
}
else return false;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &k[i]);
for(int j = 1; j <= k[i]; j++)
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) vis[j] = 0;
if(check(i, 1))
{
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
printf("%d ", use[j]);
printf("
");
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}