- 传送门 -
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2475
Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3514 Accepted Submission(s): 1040
Problem Description
There are N boxes on the ground, which are labeled by numbers from 1 to N. The boxes are magical, the size of each one can be enlarged or reduced arbitrarily.
Jack can perform the “MOVE x y” operation to the boxes: take out box x; if y = 0, put it on the ground; Otherwise, put it inside box y. All the boxes inside box x remain the same. It is possible that an operation is illegal, that is, if box y is contained (directly or indirectly) by box x, or if y is equal to x.
In the following picture, box 2 and 4 are directly inside box 6, box 3 is directly inside box 4, box 5 is directly inside box 1, box 1 and 6 are on the ground.

The picture below shows the state after Jack performs “MOVE 4 1”:
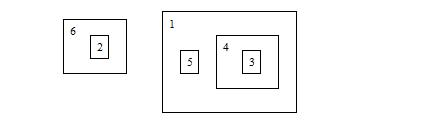
Then he performs “MOVE 3 0”, the state becomes:

During a sequence of MOVE operations, Jack wants to know the root box of a specified box. The root box of box x is defined as the most outside box which contains box x. In the last picture, the root box of box 5 is box 1, and box 3’s root box is itself.
Input
Input contains several test cases.
For each test case, the first line has an integer N (1 <= N <= 50000), representing the number of boxes.
Next line has N integers: a1, a2, a3, ... , aN (0 <= ai <= N), describing the initial state of the boxes. If ai is 0, box i is on the ground, it is not contained by any box; Otherwise, box i is directly inside box ai. It is guaranteed that the input state is always correct (No loop exists).
Next line has an integer M (1 <= M <= 100000), representing the number of MOVE operations and queries.
On the next M lines, each line contains a MOVE operation or a query:
1. MOVE x y, 1 <= x <= N, 0 <= y <= N, which is described above. If an operation is illegal, just ignore it.
2. QUERY x, 1 <= x <= N, output the root box of box x.
Output
For each query, output the result on a single line. Use a blank line to separate each test case.
Sample Input
2
0 1
5
QUERY 1
QUERY 2
MOVE 2 0
MOVE 1 2
QUERY 1
6
0 6 4 6 1 0
4
MOVE 4 1
QUERY 3
MOVE 1 4
QUERY 1
Sample Output
1
1
2
1
1
PS :
1. 做了一天却被 Dalao 嘲讽是水题 手动微笑...我能怎么办, 我也很绝望啊...
2. 这道题将盒子的包含关系转化为点的包含关系很适合拓宽脑洞.
- 代码 -
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int M = 1e5 + 5;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int head[M], pr[M], NEXT[M];
int f[M], c[M][2];
int n, m, g, h;
char st[10];
void read(int &x) {
x = 0; int f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while (ch > '9' || ch < '0') { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { x = x*10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }
x *= f;
}
void Init() {
memset(f, 0, sizeof f);
memset(c, 0, sizeof c);
memset(head, 0, sizeof head);
memset(NEXT, 0, sizeof NEXT);
}
void Add(int in, int out) {
NEXT[in] = head[out];
head[out] = in;
}
void Build(int x) {
f[x] = g;
c[g][1] = x;
g = x;
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = NEXT[i]) {
h = i;
Build(i);
}
f[x + n] = g;
c[g][1] = x + n;
g = x + n; //当一个盒子内部的盒子全部插入完之后, 就可以插入它的另一个节点了
}
void rotate(int x) {
int y = f[x], z = f[y];
int l = c[y][1] == x, r = l ^ 1;
if (z) c[z][c[z][1] == y] = x;
f[x] = z; f[y] = x; f[c[x][r]] = y;
c[y][l] = c[x][r]; c[x][r] = y;
}
void Splay(int x,int k) {
if (x != k)
while (f[x] != k) rotate(x);
}
void Solve(int a) {
Splay(a, 0);
for (; c[a][0]; a = c[a][0]);
printf("%d
",a);
}
void Move(int a, int b) {
if (a == b) return; //第一种非法情况:a == b
Splay(a, 0), Splay(a + n, a);
for(int i = b; i; i = f[i])
if(c[a + n][0] == i)
return ; //第二种非法情况: b 在 a 到 a+n 之间
int x = c[a][0], y = c[a + n][1];
f[x] = f[y] = c[a][0] = c[a + n][1] = 0;
if (x && y) {
for (; c[y][0]; y = c[y][0]);
c[y][0] = x;
f[x] = y; //合并
}
if(!b) return; //得到最外层盒子是 a 的盒子就可以了
int i;
Splay(b, 0);
for (i = c[b][1]; c[i][0]; i = c[i][0]);
Splay(i, b);
f[a] = i;
c[i][0] = a; // 插入
}
int main() {
int tmp = 0, keep = 0;
while (~scanf("%d",&n)) {
if (keep ++) puts("");
Init();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
read(h);
if (h) Add(i, h); //将同级别盒子用链表串起来
else {
pr[tmp] = i;
pr[i] = -1;
tmp = i; //记录最外层的盒子以建树
}
}
for(int i = pr[0]; i != -1; i = pr[i])
g = 0, Build(i);
read(m);
while (m --) {
scanf("%s",st);
if (st[0] == 'Q') read(h), Solve(h);
else read(g), read(h), Move(g, h);
}
}
return 0;
}