Spring Boot的入口类
1、名为xxxApplication的就是入口类,在main方法中使用SpringApplication.run(SpringBootTestApplication.class, args);启动Spring Boot应用项目。
2、@SpringBootApplication是由@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan的组合注解。其中@EnableAutoConfiguration让Spring Boot 根据类路径中的jar包依赖为当前项目进行自动配置。
Spring Boot定制banner
1、查找顺序:依次在 Classpath 下找 文件 banner.gif , banner.jpg , banner.png 和 banner.txt,都没有找到的话, 用默认的 SpringBootBanner , 就是我们最常见到的那个。
2、测试案例:
新banner.txt
${AnsiColor.BRIGHT_YELLOW}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// //
// ${AnsiColor.BRIGHT_RED}_ooOoo_${AnsiColor.BRIGHT_YELLOW} //
// ${AnsiColor.BRIGHT_RED}o8888888o${AnsiColor.BRIGHT_YELLOW} //
// ${AnsiColor.BRIGHT_RED}88${AnsiColor.BRIGHT_YELLOW}" . "${AnsiColor.BRIGHT_RED}88${AnsiColor.BRIGHT_YELLOW} //
// (| ^_^ |) //
// O = /O //
// ____/`---'\____ //
// .' \| |// `. //
// / \||| : |||// //
// / _||||| -:- |||||- //
// | | \ - /// | | //
// | \_| ''---/'' | | //
// .-\__ `-` ___/-. / //
// ___`. .' /--.-- `. . ___ //
// ."" '< `.___\_<|>_/___.' >'"". //
// | | : `- \`.;` _ /`;.`/ - ` : | | //
// `-. \_ __ /__ _/ .-` / / //
// ========`-.____`-.___\_____/___.-`____.-'======== //
// `=---=' //
// ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ //
// 佛祖保佑 永不宕机 永无BUG //
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
运行结果:
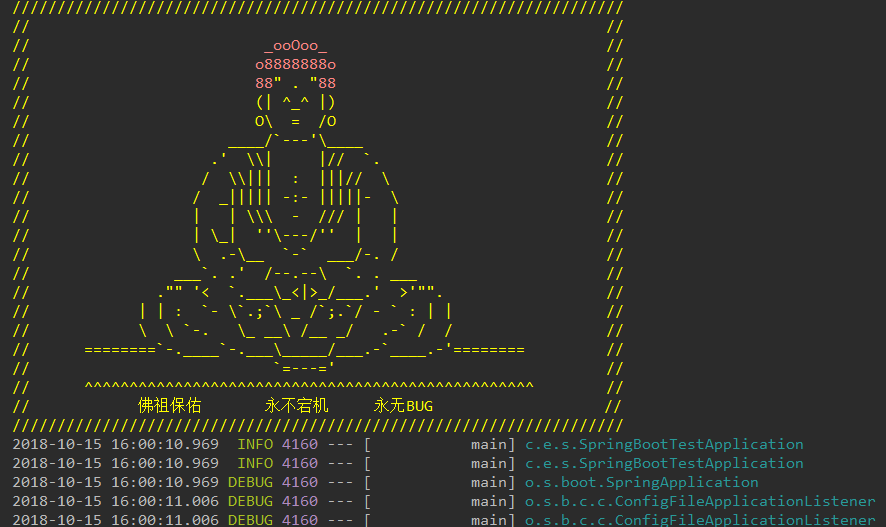
3、关闭banner
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(SpringBootTestApplication.class); springApplication.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF); springApplication.run(args);
Spring Boot配置文件
1、Spring Boot使用一个全局的配置文件application.properties 或application.yml,作用是对一些默认配置的配置值进行修改。
2、profile配置:输Spring 针对不同的环境对不同的配置提供的支持,全局的profile配置使用application-{profile}.properties,通过application.properties中设置spring.profiles.active = prod来指定活动的profile。
测试案例:
spring.profiles.active=daily #修改访问路径 server.servlet.context-path=/springboot my.username=Amy
3、日志配置:默认情况下使用Logback做为日志框架
测试案例:
spring.profiles.active=daily #修改访问路径 server.servlet.context-path=/springboot my.username=Amy #指定日志文件保存地址 logging.file=D:/study/SpringBoot/log.log debug=true
4、常规属性配置:在Spring环境下需要用@PropertySource来指定文件的位置再用@Value来指定注入的值。再Spring Boot 中只需要用@Value的注解
配置文件:
ser.nikename=Saber user.age=21
启动类:
package com.example.spring_boot_test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @SpringBootApplication//开启自动配置 public class SpringBootTestApplication { //通过@Value注入值 @Value("${my.username}") private String userName; public static void main(String[] args) { //关闭banner /*SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(SpringBootTestApplication.class); springApplication.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF); springApplication.run(args);*/ SpringApplication.run(SpringBootTestApplication.class, args); } @RequestMapping("/") String index() { return "hello " + userName + " spring boot !!!"; } }
5、类型安全的配置:如果每次使用@Value注解逐一注入属性会很麻烦,因此可以通过@ConfigurationProperties将properties属性和一个bean关联起来,从而实现类型安全的配置。
配置文件:
ser.nikename=Saber user.age=21
类型安全的Bean:
package com.example.spring_boot_test.entity; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component//要使用这个注解,这样就可以在 component scan时候被发现了,不然会无法自动注入, @PropertySource({"classpath:/my.properties"})//注意路径的书写格式 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user") public class User { String nikename; int age; public String getNikename() { return nikename; } public void setNikename(String nikename) { this.nikename = nikename; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
启动类:
package com.example.spring_boot_test; import com.example.spring_boot_test.entity.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @SpringBootApplication//开启自动配置 public class SpringBootTestApplication { @Autowired private User user; //通过@Value注入值 @Value("${my.username}") private String userName; public static void main(String[] args) { //关闭banner /*SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(SpringBootTestApplication.class); springApplication.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF); springApplication.run(args);*/ SpringApplication.run(SpringBootTestApplication.class, args); } @RequestMapping("/") String index() { System.out.println(user.getNikename() + ":" + user.getAge()); return "hello " + userName + " spring boot !!!"; } }
Spring Boot运行原理
1、@SpringBootApplication是由@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan的组合注解。核心功能由EnableAutoConfiguration提供。
- @Configuration:@SpringBootConfiguration的本质是@Configuration,@Configuration相当于把该类作为spring的xml配置文件中的
<beans>,作用为配置spring容器(应用上下文),任何一个标注了@Configuration的Java类定义都是一个JavaConfig配置类。 - @ComponentScan:@ComponentScan自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件(比如@Component和@Repository等)或者bean定义,最终将这些bean定义加载到IoC容器中。
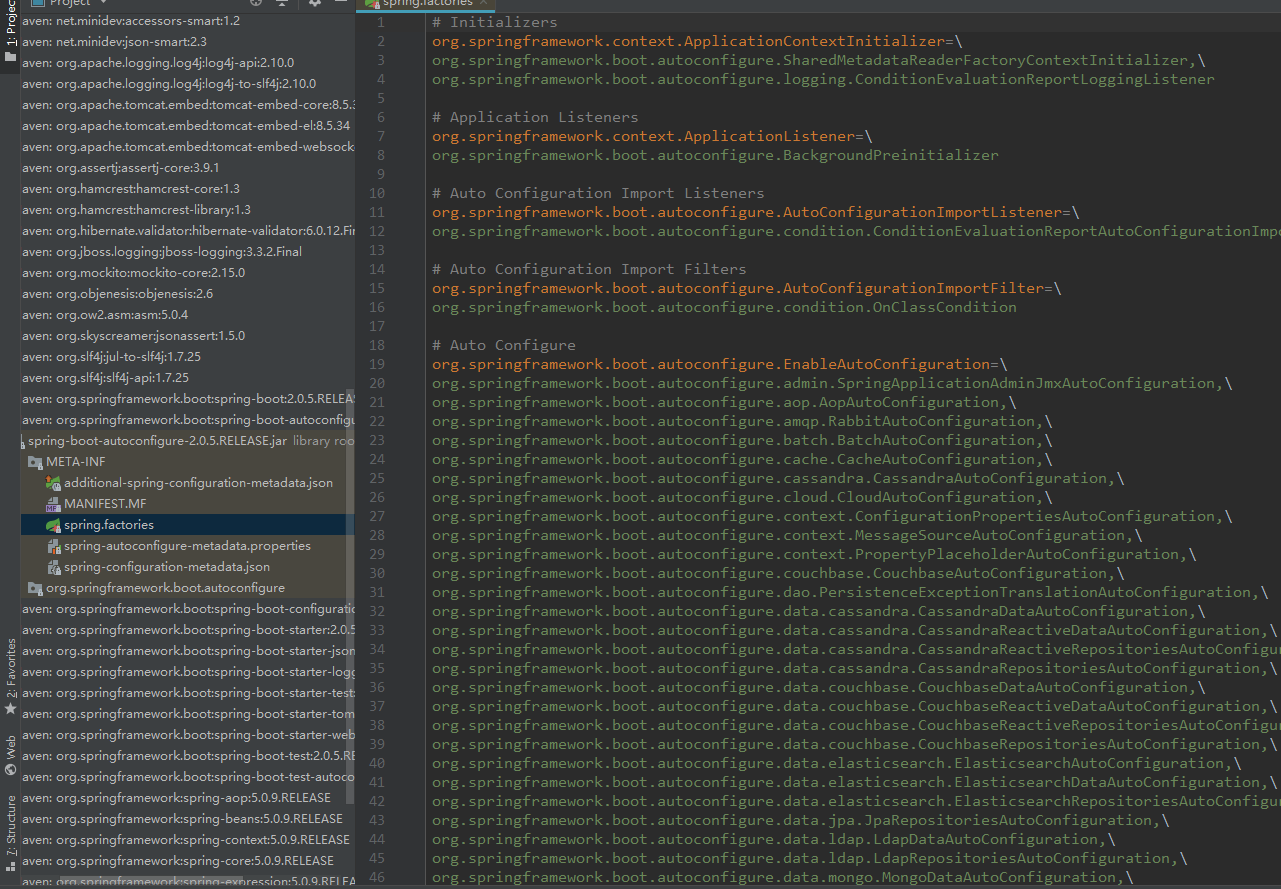
- @EnableAutoConfiguration:@EnableAutoConfiguration的部分源码如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @AutoConfigurationPackage @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration"; Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; String[] excludeName() default {}; }其中@Import注解将所有符合自动配置条件的bean定义加载到IoC容器,AutoConfigurationImportSelector通过getCandidateConfigurations方法来扫描具有MWTA-INF/spring.factories文件的jar包(spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar),spring.factories文件声明了自动配置。然后根据@EnableAutoConfiguration的完整类名org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration作为查找的Key,获取对应的一组@Configuration类,然后通过反射(Java Refletion)实例化为对应的标注了@Configuration的JavaConfig形式的IoC容器配置类,最后汇总为一个并加载到IoC容器。
Spring Boot执行流程
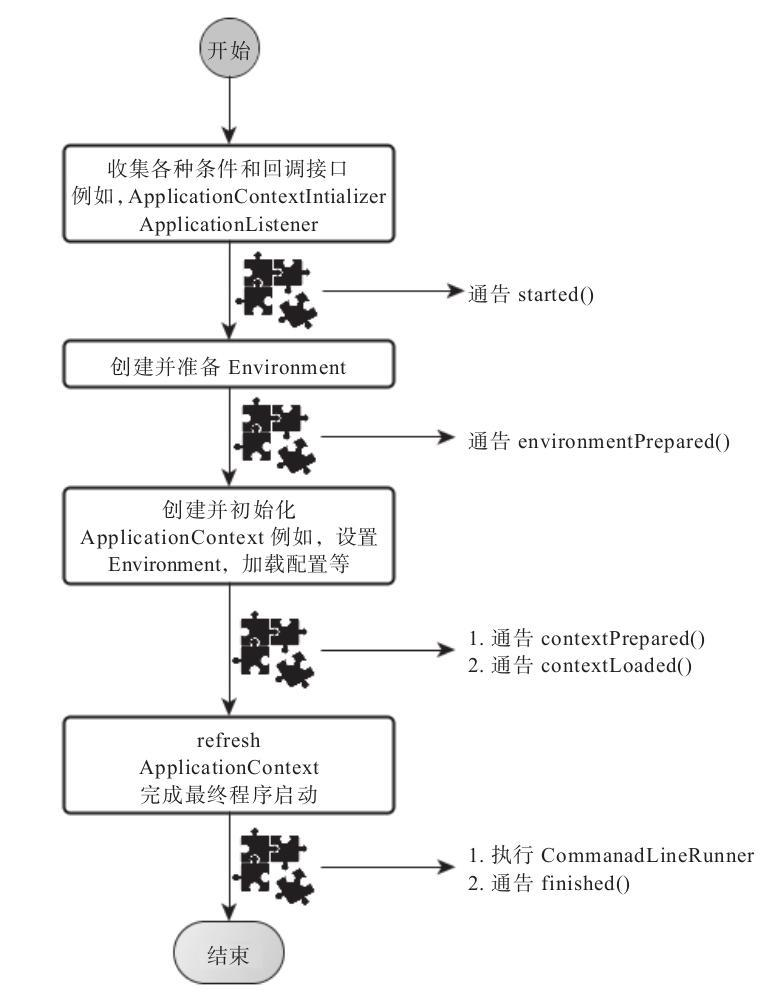
Spring Boot的执行流程主要分为两大部分:创建一个SpringApplication对象实例 ,调用这个创建好的SpringApplication的实例方法。
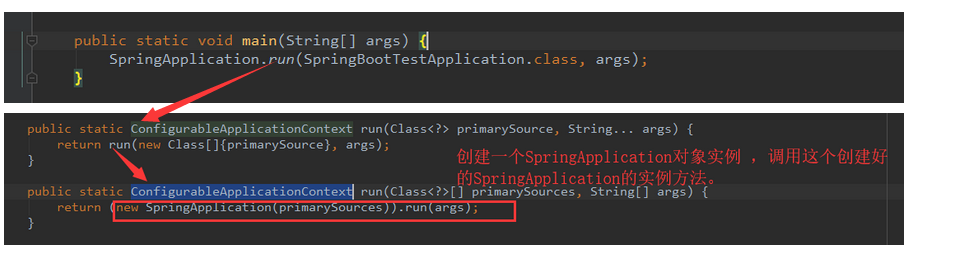
1、创建一个SpringApplication对象实例
public SpringApplication(Class... primarySources) {
//创建一个SpringApplication对象实例
this((ResourceLoader)null, primarySources);
}
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) {
this.sources = new LinkedHashSet();
this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE;
this.logStartupInfo = true;
this.addCommandLineProperties = true;
this.headless = true;
this.registerShutdownHook = true;
this.additionalProfiles = new HashSet();
this.isCustomEnvironment = false;
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//推断应用类型。
this.webApplicationType = this.deduceWebApplicationType();
//使用SpringFactoriesLoader在应用的classpath中查找并加载所有可用的ApplicationContextInitializer。
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//使用SpringFactoriesLoader在应用的classpath中查找并加载所有可用的ApplicationListener。
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//通过抛出异常来获取到异常栈从而得到入口类的名称设置main方法的定义类。
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
2、调用这个创建好的SpringApplication的实例方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { //计时开始 StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList(); this.configureHeadlessProperty(); //获取所有通过SpringFactoriesLoader可以查找到并加载的SpringApplicationRunListener SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting(); Collection exceptionReporters; try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); //创建并配置当前Spring Boot应用将要使用的Environment(包括配置要使用的PropertySource以及Profile)。 //遍历调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的environmentPrepared()的方法,告诉他们:“当前SpringBoot应用使用的Environment准备好了咯!”。 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); //是否打印banner Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment); // 创建上下文对象,根据用户是否明确设置了applicationContextClass类型以及初始化阶段的推断结果,决定该为当前SpringBoot应用创建什么类型的 context = this.createApplicationContext(); //异常报警 exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context); //spring上下文对象的前置处理 this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); //spring上下文对象的刷新 this.refreshContext(context); //spring上下文对象的后置处理 this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); //计算器关闭 stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { (new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } //遍历执行listeners,调用它们的started()方法,告诉这些SpringApplicationRunListener,“嘿,SpringBoot应用要开始执行咯!”。 listeners.started(context); this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable var10) { this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(var10); } try { listeners.running(context); return context; } catch (Throwable var9) { this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null); throw new IllegalStateException(var9); }
Spring Boot中的starter pom
1、Spring Boot为我们提供了简化企业级开发的绝大多数场景的stater pom,只要使用了应用场景所需要的starter pom就会得到Spring Boot为我们提供的自动配置的bean。
2、自定义starter pom 测试案例:
- 新建maven工程

填写完工程名点击finish,工程创建完成
- 修改pom文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-hello</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId> <version>1.4.3.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <version>1.4.3.RELEASE</version> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project> - 属性配置:
package com.example.spring_boot_starter_hello; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; //类型安全的属性配置 @PropertySource({"classpath:/my.properties"})//注意路径的书写格式 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "hello") public class HelloServiceProperties { private static final String MSG="world"; private String msg=MSG; public String getMsg() { return msg; } public void setMsg(String msg) { this.msg = msg; } }是类型安全的属性配置与properties文件中的属性相对应。
- service类
package com.example.spring_boot_starter_hello; public class HelloService { private String msg; public String sayHello(){ return "hello "+msg; } public String getMsg() { return msg; } public void setMsg(String msg) { this.msg = msg; } } - 自动配置类
package com.example.spring_boot_starter_hello; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; //@Configuration标注在类上,相当于把该类作为spring的xml配置文件中的<beans>,作用为:配置spring容器(应用上下文) @Configuration //开启属性输入 @EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloServiceProperties.class) //判断HelloService这个类在类路径中是否存在,且在没有这个bean的情况下会自动配置这个bean @ConditionalOnClass(HelloService.class) //当设置hello=enable的情况下,如果没有设置默认为true,即条件符合 @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "hello",value = "enabled",matchIfMissing = true) public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration { @Autowired private HelloServiceProperties helloServiceProperties; //使用Java配置的方式配置bean @Bean //当容器没有这个bean的时候会新建bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(HelloService.class) public HelloService helloService(){ HelloService helloService = new HelloService(); helloService.setMsg(helloServiceProperties.getMsg()); return helloService; } }
- 注册配置,在src/main/resources下新建META-INF/spring.factories,内容如下:
#注册自动配置类 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration= com.example.spring_boot_starter_hello.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration
- 使用starter 在之前的Spring Boot 中将自定义的starter作为依赖,在pom文件中新增spring-boot-stater-hello的依赖。修改pom文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>spring_boot_test</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <!--spring boot的父级依赖--> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.5.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!--添加web依赖的起步依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!--需要添加依赖ConfigurationProperties才会起作用--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <!--添加spring-boot-stater-hello的依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-hello</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <!--添加springboot的编译插件--> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>通过mvn install安装到本地,或者发布到远程maven私服上。
- 在properties文件中增加属性:hello.msg=hello
- 在Spring Boot中注入HelloService并使用
package com.example.spring_boot_test; import com.example.spring_boot_starter_hello.HelloService; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import javax.annotation.Resource; @RestController @SpringBootApplication//开启自动配置 public class SpringBootTestApplication { @Resource private HelloService helloService;
public static void main(String[] args) { //关闭banner /*SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(SpringBootTestApplication.class); springApplication.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF); springApplication.run(args);*/ SpringApplication.run(SpringBootTestApplication.class, args); } @RequestMapping("hello") String hello() { return helloService.sayHello(); } }
转载请于明显处标明出处