1.线程和并发的思维导图:

----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2.并发和并行:
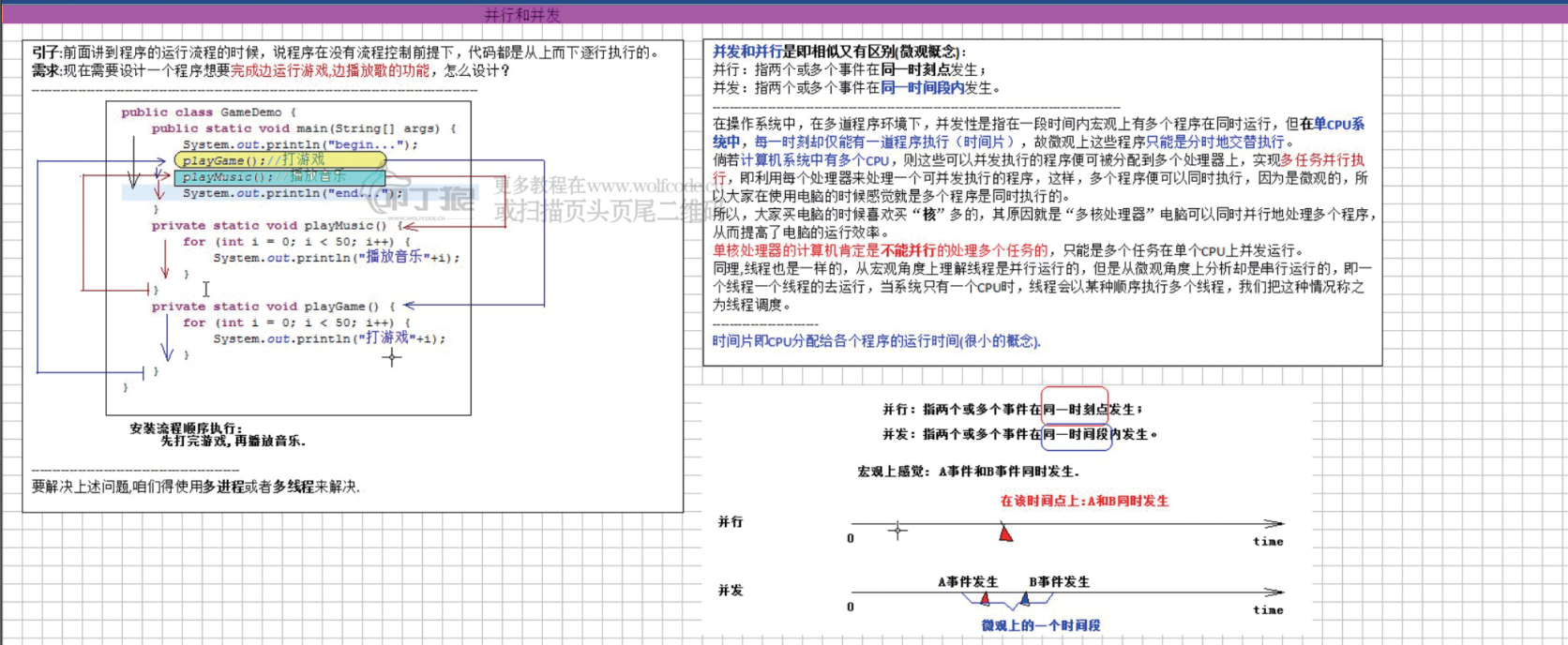
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3.进程和线程:

----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4.多线程的优势:
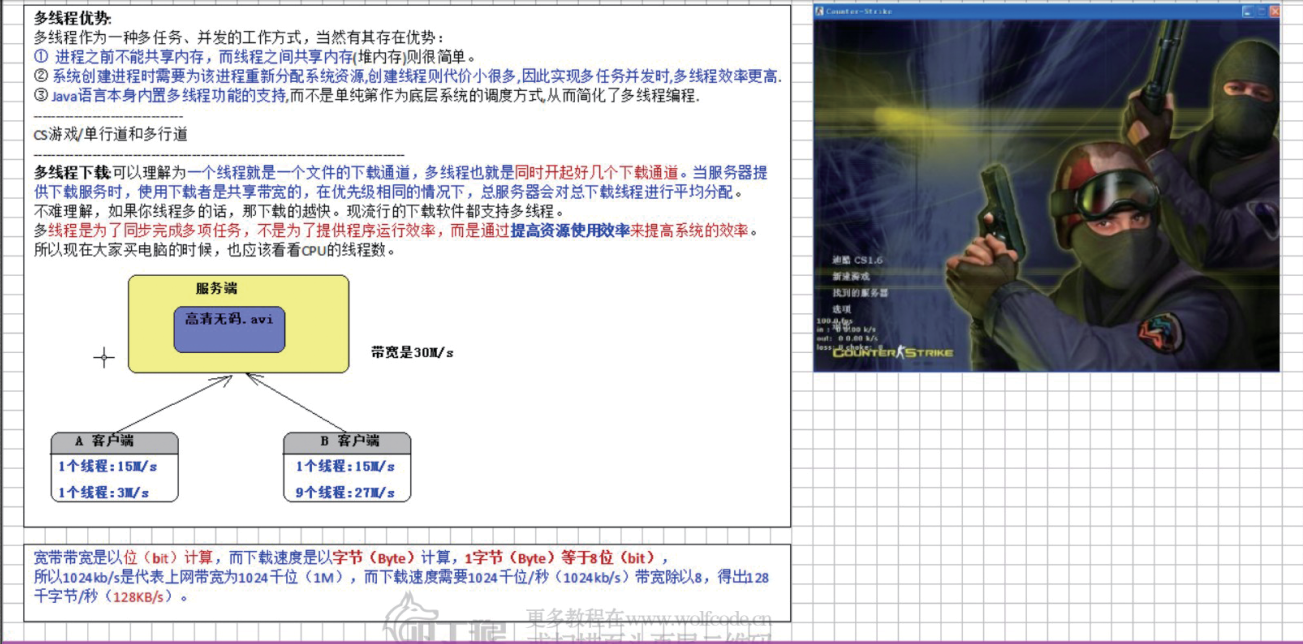
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5.Java操作进程

1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 //Java中如何开启一个进程 如记事本 3 //方式一:使用Runtime类的exec方法 4 Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime(); 5 rt.exec("notepad"); 6 //方式二:processBuilder的start方法 7 ProcessBuilder pb = new ProcessBuilder("notepad"); 8 pb.start(); 9 }
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6.创建和启动线程
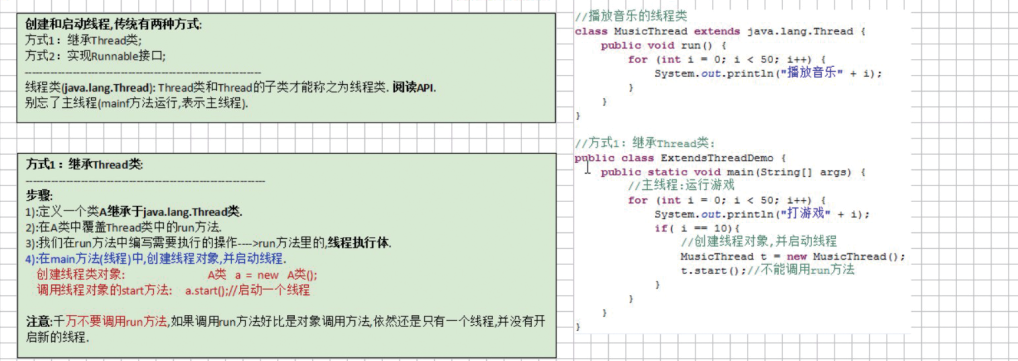
1 class MusicThread extends Thread{//定义的MusicThread类继承自Thread 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 for(int i = 0; i < 50 ; i++) { 5 System.out.println("听音乐..." + i); 6 } 7 } 8 } 9 public class ExtendsThreadDemo { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 //主线程 运行游戏 12 for(int i = 0; i <50; i++) { 13 System.out.println("打游戏..." + i); 14 if(i == 10) { 15 //创建线程对象并且启动 16 MusicThread musicThread = new MusicThread(); 17 musicThread.start();//不能调用run方法 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 }
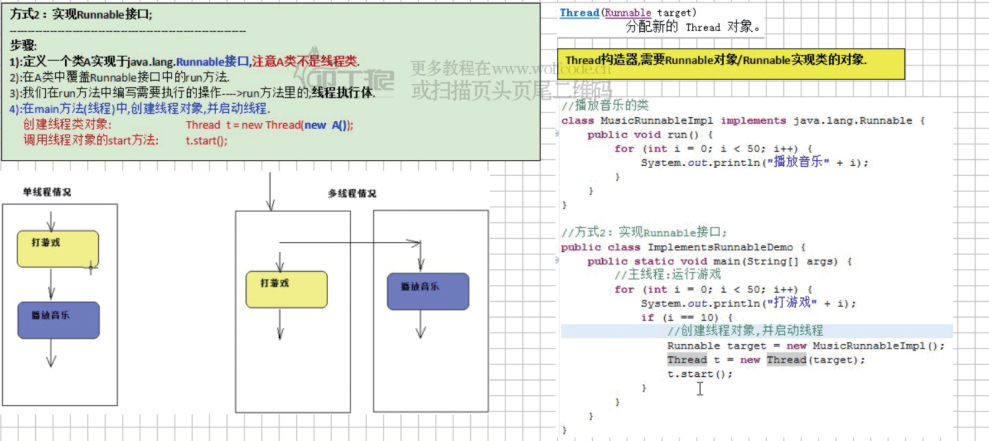
1 class MusicThreadImpl implements Runnable{ 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 for(int i = 0; i < 50 ; i++) { 5 System.out.println("听音乐..." + i); 6 } 7 } 8 } 9 public class ExtendsThreadDemo { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 //主线程 运行游戏 12 for(int i = 0; i <50; i++) { 13 System.out.println("打游戏..." + i); 14 if(i == 10) { 15 //创建线程对象并且启动 16 MusicThreadImpl target = new MusicThreadImpl(); 17 Thread thread = new Thread(target); 18 thread.start(); 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 }

1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 //主线程 运行游戏 3 for(int i = 0; i <50; i++) { 4 System.out.println("打游戏..." + i); 5 if(i == 10) { 6 //创建线程对象并且启动 7 //匿名内部类 方式一: 8 new Thread(new Runnable() { 9 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 for(int i = 0; i < 50 ; i++) { 13 System.out.println("听音乐..." + i); 14 } 15 } 16 }).start(); 17 } 18 } 19 }
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 //主线程 运行游戏 3 for(int i = 0; i <50; i++) { 4 System.out.println("打游戏..." + i); 5 if(i == 10) { 6 //创建线程对象并且启动 7 //匿名内壁类 方式一: 8 new Thread() { 9 public void run() { 10 for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 11 System.out.println("听音乐" + i); 12 } 13 } 14 }.start(); 15 } 16 } 17 }
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7.两种方式对比:引例 吃苹果比赛

1 //方式一 继承Thread类 2 class Person extends Thread{ 3 private int num = 50; 4 public Person(String name) { 5 super(name);//调用父类构造器 6 } 7 public void run(){ 8 for(int i = 0; i < 50; i ++) {
if(num > 0){ 9 System.out.println(getName() + "吃了" + "第" + num-- +"个苹果")};//getName是Thread中的方法 获取线程的名称 10 } 11 } 12 } 13 public class ExtendsThread { 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 //一共50个苹果 3个同学吃 16 Person p1 = new Person("A"); 17 p1.start(); 18 Person p2 = new Person("B"); 19 p2.start(); 20 Person p3 = new Person("C"); 21 p3.start(); 22 } 23 }
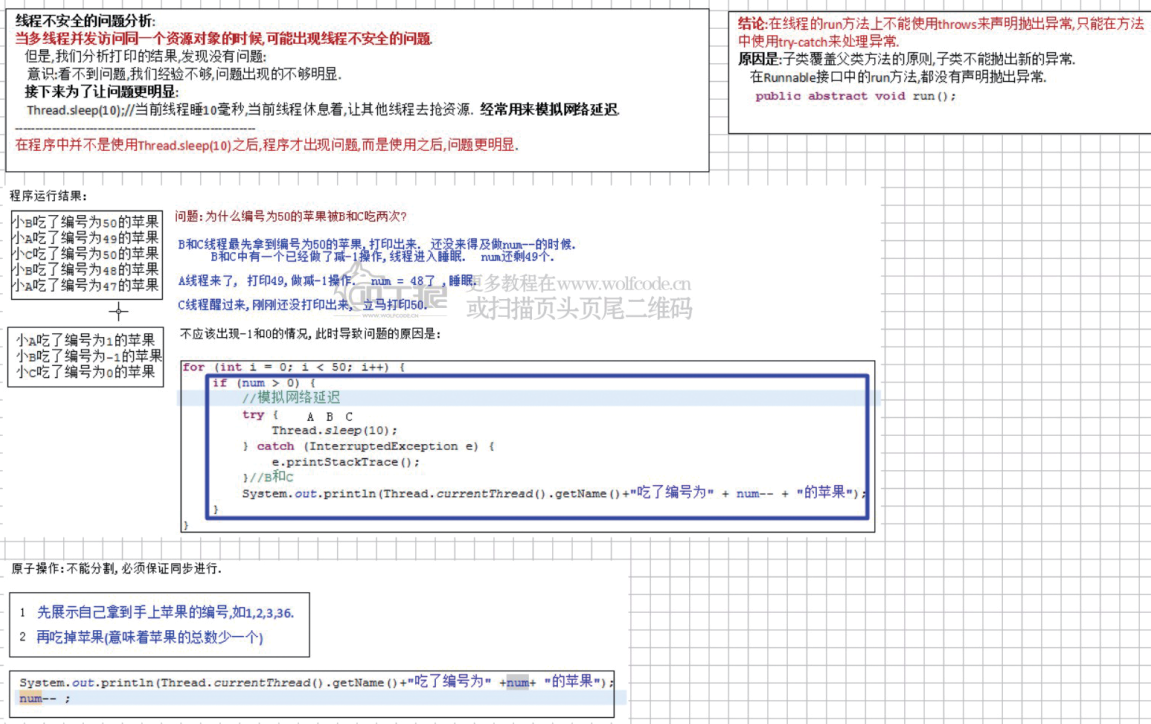
结果:每个同学都吃了50个苹果,上图中有具体原因。

1 //方式二 实现Runnable接口 2 class Person implements Runnable{ 3 private int num = 50; 4 public void run(){ 5 for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 6 if(num > 0) { 7 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "吃了" + "第" + num-- +"个苹果"); 8 } 9 } 10 } 11 } 12 public class ImplementsDemo { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 //一共50个苹果 3个同学吃 15 Person a = new Person(); 16 new Thread(a, "A").start(); 17 new Thread(a, "B").start(); 18 new Thread(a, "C").start(); 19 } 20 }
吃苹果比赛 分析继承方式和实现方式的区别

----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8.线程不安全问题的分析:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
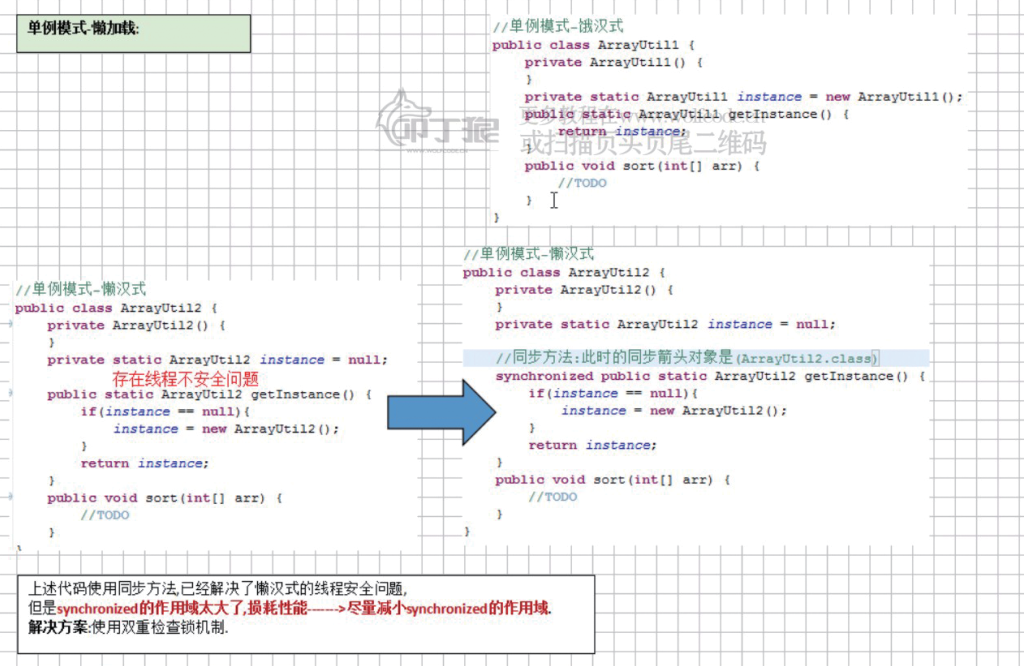
9.解决线程不安全的两种方法:
方法一:synchronized代码块

1 public void run() { 2 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 3 synchronized (this) { 4 if (num > 0) { 5 try { 6 Thread.sleep(10); 7 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 8 e.printStackTrace(); 9 } 10 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "吃了" + num-- + "号苹果"); 11 } 12 } 13 } 14 }
方法二:synchronized方法:

1 public void run() { 2 eat(); 3 } 4 5 private void eat() { 6 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 7 synchronized (this) { 8 if (num > 0) { 9 try { 10 Thread.sleep(10); 11 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } 14 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "吃了" + num-- + "号苹果"); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 19 } 20 }
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
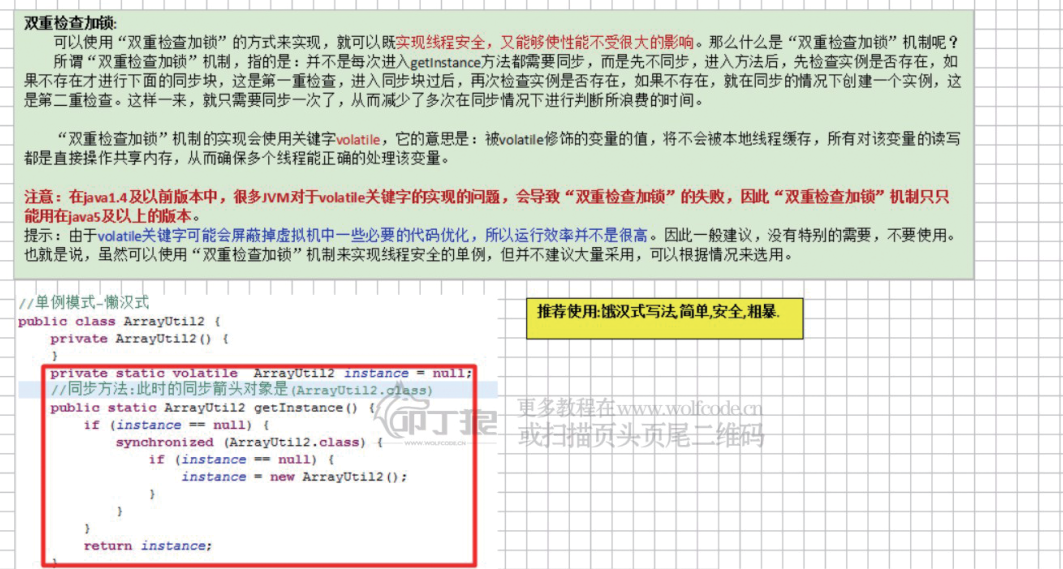
9.synchronized的好与坏:

----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
10。同步锁
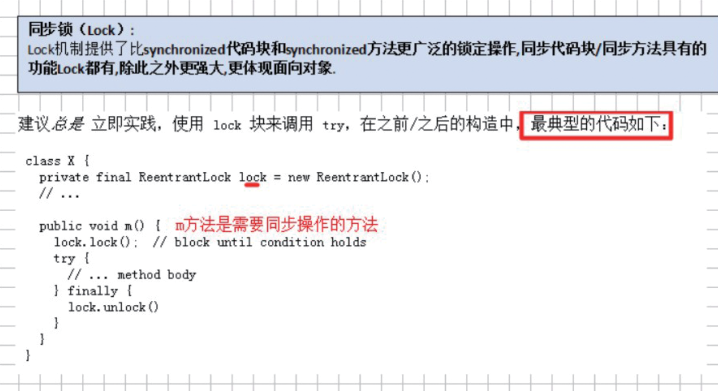
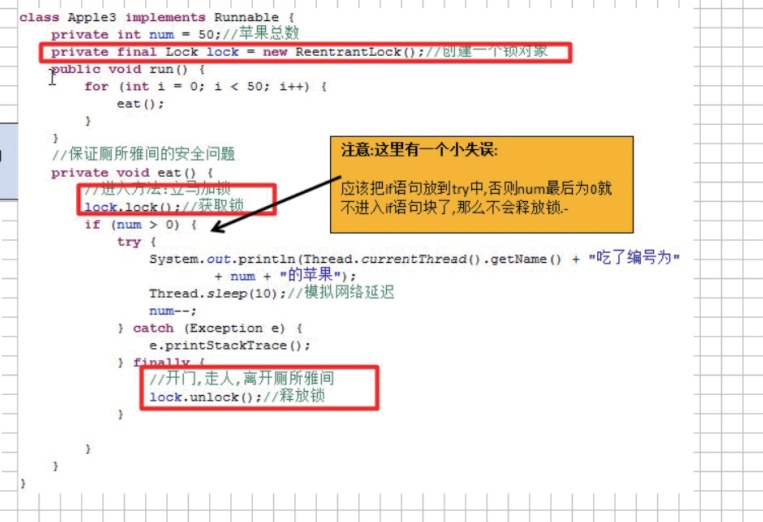

class Apple implements Runnable{ private int num = 5000; private final Lock locks = new ReentrantLock(); @Override public void run() { for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) { eat(); } } private void eat() { locks.lock(); try { if(num > 0) System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " eat " + num + "th " + "apple"); Thread.sleep(10); num --; }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { locks.unlock(); } } } public class LockDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Apple a = new Apple(); new Thread(a, "A").start();; new Thread(a, "B").start();; new Thread(a, "S").start(); } }
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------