输入一棵二叉树前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建该二叉树。
class Solution { public: vector<int> pre,in;//简化传参; map<int,int> mp;//hash改进,减少每次都要查找 TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) { int n = preorder.size(); if ( n == 0) return NULL; for(int i = 0; i <n; i++) mp[inorder[i]] = i;//hash pre = preorder; in = inorder; return build(0,n-1,0,n-1); } TreeNode* build(int l1,int r1,int l2,int r2){ if(l1 > r1) return NULL; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(pre[l1]);//注意新建 int r = mp[pre[l1]];//hash int len = r - l2; root->left = build(l1+1,l1+len,l2,r-1); root->right = build(l1+len+1,r1,r+1,r2); return root; } };
给定一棵二叉树的其中一个节点,请找出中序遍历序列的下一个节点。
class Solution { public: TreeNode* inorderSuccessor(TreeNode* p) { //如果有右子树 if(p->right){ p = p->right; //找到右子树的最左节点 while(p->left) p = p->left; return p; } //没有右子树,则找到最近左子树的父节点; while(p->father && p != p->father->left) p = p->father; return p->father; } };
43. 不分行从上往下打印二叉树(层序遍历)
class Solution { public: vector<int> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> res; if(!root) return res; queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(root); while(q.size()){ int len = q.size(); while(len--){ auto t = q.front(); q.pop(); res.push_back(t->val); if(t->left) q.push(t->left); if(t->right) q.push(t->right); } } return res; } };
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。
如果是则返回true,否则返回false。
假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
二叉搜索树的中序遍历就是排好序的,可以根据中序遍历和后序遍历建立二叉树,再验证;
也可以不需要用中序遍历,直接根据后序遍历最后一个数是根节点来做:
class Solution { public: vector<int> seq; bool verifySequenceOfBST(vector<int> sequence) { int n = sequence.size(); seq = sequence; return dfs(0,n-1); } bool dfs(int l , int r){ if(l >= r) return true; int k = l; //k指向右子树的第一个节点 while(k < r && seq[k] < seq[r]) k++; //判断右子树是否都小于根节点 for(int i = k; i < r;i++) if(seq[i] < seq[r]) return false; //递归左子树和右子树 return dfs(l,k-1) && dfs(k,r-1); } };
输入一棵二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。
从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> res; int sum; void dfs(TreeNode* p,vector<int> t,int cnt){ cnt += p->val;t.push_back(p->val); if(cnt > sum) return; if(!p->left && !p->right){ if(cnt == sum) res.push_back(t); return; } if(p->left) dfs(p->left,t,cnt); if(p->right) dfs(p->right,t,cnt); } vector<vector<int>> findPath(TreeNode* root, int _sum) { if(!root) return res; sum = _sum; vector<int> temp; dfs(root,temp,0); return res; } };
过倒是能过,不过还是有很多地方可以优化的地方:
- temp数组多次传递,导致空间浪费;
- 可以传递sum,然后让sum去减;
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> temp; void dfs(TreeNode* p,int sum){ if(!p) return; sum -= p->val;temp.push_back(p->val); if( sum < 0) {temp.pop_back();return;}//注意 if(!p->left && !p->right && sum==0) res.push_back(temp); dfs(p->left,sum); dfs(p->right,sum); temp.pop_back();//空间优化 } vector<vector<int>> findPath(TreeNode* root, int sum) { if(!root) return res; dfs(root,sum); return res; } };
还有就是dfs的回溯时要记得弹出最后一个元素;
dfs不一定要在最后处理,在过程中间判断也行;
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。
要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。
注意:
- 需要返回双向链表最左侧的节点。
例如,输入下图中左边的二叉搜索树,则输出右边的排序双向链表。
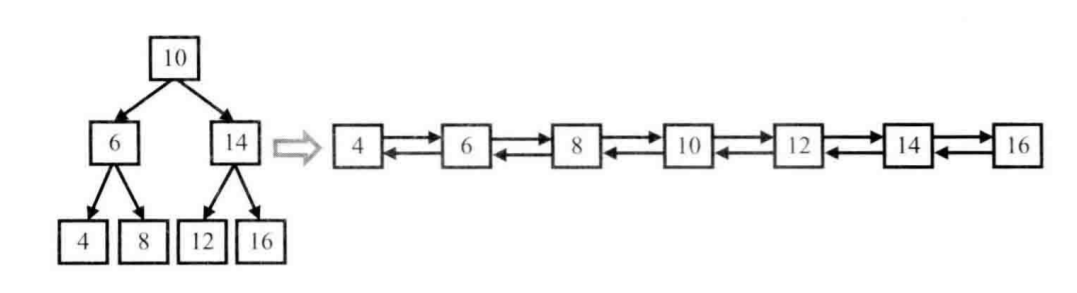
就在中序递归遍历的基础上改了一点点,用一个pre指针保存中序遍历的前一个结点。
因为是中序遍历,遍历顺序就是双线链表的建立顺序;
每一个结点访问时它的左子树肯定被访问过了,所以放心大胆的改它的left指针,不怕树断掉;
同理,pre指向的结点保存的数肯定小于当前结点,所以其左右子树肯定都访问过了,所以其right指针也可以直接改。
最后需要一直向左找到双向链表的头结点。
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* convert(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return NULL; dfs(root); while(root->left) root = root->left; return root; } TreeNode* pre; void dfs(TreeNode* cur){ if(!cur) return; dfs(cur->left); cur->left = pre; if(pre) pre->right = cur; pre = cur; dfs(cur->right); } };